An Introduction To Respiration
Found 6 free book(s)Blow Up a Balloon with Cellular Respiration
saacs.chem.ufl.eduBlow Up a Balloon with Cellular Respiration Introduction: Yeasts are unicellular microorganisms of the fungi kingdom. They are facultative anaerobe, which means that they can respire or ferment depending upon environmental conditions. In the presence of oxygen, respiration takes place (aerobic respiration). Without
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration, TE - Scarsdale Public Schools
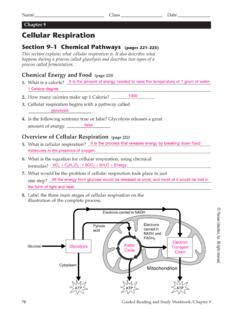
www.scarsdaleschools.k12.ny.usrespiration, called the Krebs cycle. It also explains how high-energy electrons are used during the third stage, called electron transport. Introduction (page 226) 1. At the end of glycolysis, how much of the chemical energy in glucose is still unused? About 90 percent 2. Because the final stages of cellular respiration require oxygen,
An Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
www.palmbeachstate.eduSection 1: An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1.1 Briefly describe the difference between anatomy and physiology. 1.2 Describe how to use the text and art together to master learning. 1.3 Explain how to approach complex concepts with multiple parts. 1.4 Describe the anatomical position and how you
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODY
nursingnsn.weebly.comCHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODY At the end of this chapter, student will be able to: a) Define the terms anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology. Use an example to explain how they are related. b) Name the levels of organization of the body from simplest to most complex, and explain each.
INTRODUCTION TO STRESS MANAGEMENT
www.uakron.eduIntroduction Stress is a fact of life, wherever you are and whatever you are doing. You cannot avoid stress, but you can learn to manage it so it doesn’t manage you. Changes in our lives—such as going to college, getting married, changing jobs, or illness—are frequent sources of stress. Keep in mind that changes that cause stress
The Nervous System
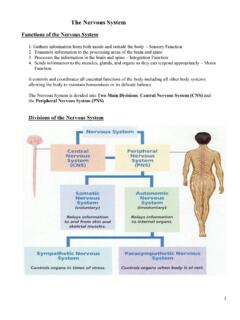
www.soinc.org3 Reflex Arc Components of a Reflex Arc A. Receptor - reacts to a stimulus B. Afferent pathway (sensory neuron) - conducts impulses to the CNS C. Interneuron - consists of one or more synapses in the CNS (most are in the spine) D. Efferent pathway (motor neuron) conducts impulses from CNS to effector. E. Effector - muscle fibers (as in the Hamstring muscle) or …