Factor Repeated Measure Anova
Found 12 free book(s)One Factor Repeated Measure ANOVA (Multivariate …
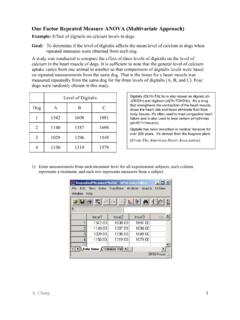
gchang.people.ysu.eduA. Chang 1 One Factor Repeated Measure ANOVA (Multivariate Approach) Example: Effect of digitalis on calcium levels in dogs Goal: To determine if the level of digitalis affects the mean level of calcium in dogs when repeated measures were obtained from each dog. A study was conducted to compare the effect of three levels of digitalis on the level of
Statistics: Analysing repeated measures data
statstutordevelopment.lboro.ac.uk1. Use a mixed measures ANOVA (the variable defining the groups would be the between subjects factor). Note that in SPSS this is done in the same way as repeated measures ANOVA, except you specify a between subjects factor as well as defining your within subjects variable. 2.
Repeated Measures ANOVA and Mixed Model ANOVA
www.cogsci.bme.huRepeated Measure ANOVA Assumptions: Sphericity? y b 1 4 4 9 1 1 8 0 t t W. e df . s r t d n a s. n. t ... Two-way mixed ANOVA with one within-subjects factor and one between-groups factor. Partner-proximity (sleep with spouse vs. sleep alone) is the within-subjects factor…
REPEATED MEASURES (ANOVA)
oak.ucc.nau.eduTo conduct a repeated-measures ANOVA in SPSS, we do not specify the repeated-measures factor and the dependent variable in the SPSS data file. Instead, the SPSS data file contains several quantitative variables. The number of quantitative variables is equal to the number of levels of the within-subjects factor.
Mixed Model Repeated Measures (MMRM)
www.lexjansen.comeffect is a measure of deviation from the hypothesis of equality of mean responses among the measurement times for all groups combined. Repeated measures ANOVA also provides a test of this hypothesis. In simplest case of repeated measure ANOVA, which is presented here, the group and the evaluation time are cross-classified main effects.
ANOVA – Analysis of Variance
homepages.inf.ed.ac.uko Within-subject (or repeated measures) Mixed designs – a bit of both o • Main effect o Effect of a factor averaged across all other factors • Interactions o Effect of a particular combination of factors – i.e. 1 factor at a specific level of another factor. ANOVA as Regression
Three-way ANOVA
www.ou.eduThree-way ANOVA • ABC is not significant • AB is not significant • AC is not significant • BC is not significant • A is significant • B is significant • C is not significant You can follow up and interpret the A and B main effects. Repeated Measures Designs • Simple repeated Measures Design: Uses the same subjects in all conditions.
Mixed Models for Repeated - University of Vermont
www.uvm.edugroups factor as well as a within-subjects (repeated measures) factor. For now my purpose is to show the relationship between mixed models and the analysis of variance. The relationship is far from perfect, but it gives us a known place to start. More importantly, it allows us to see what we gain and what we lose by going to mixed models.
Repeated Measures ANOVA - Stony Brook
www.ams.sunysb.eduAs with any ANOVA, repeated measures ANOVA tests the equality of means. However, repeated measures ANOVA is used when all members of a random sample are measured under a number of different conditions or at different time points. As the sample is exposed to each condition, the measurement of the dependent variable is repeated.
repeated-measures within-participants
www.open.ac.ukOne-Way Repeated-Measures ANOVA Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a common and robust statistical test that you can use to compare the mean scores collected from different conditions or groups in an experiment. There are many different types of ANOVA, but this tutorial will introduce you to One-Way Repeated-Measures ANOVA.
Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
www.discoveringstatistics.comsimilar to that for one -way ANOVA, except that there is a space to specify covariates. Select Libido and drag this variable to the box labelled Dependent Variable or click on . Select Dose and drag it to the box labelled Fixed Factor(s) and then select Partner_Libido and drag it to the box labelled Covariate(s).
Anova Experimental Design Analysis - IIT Kanpur
home.iitk.ac.inFactor: A factor is a variable defining a categorization. A factor can be fixed or random in nature. A factor is termed as a fixed factor if all the levels of interest are included in the experiment. A factor is termed as a random factor if all the levels of interest are not included in the experiment and those
Similar queries
Factor Repeated Measure ANOVA Multivariate, Factor Repeated Measure ANOVA Multivariate Approach, Repeated, ANOVA, Factor, Repeated Measures ANOVA and Mixed Model ANOVA, Repeated measure ANOVA, Measure, University of Vermont, Repeated measures ANOVA, Repeated-measures, Repeated-Measures ANOVA, Analysis of Covariance ANCOVA, Anova Experimental