First Law Of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
Found 12 free book(s)UNIT 61: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
www.freestudy.co.uk2. THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS When you have completed section two, you should be able to explain and use the following terms. The First Law of Thermodynamics. Closed systems. The Non-Flow Energy Equation. Open systems. The Steady Flow Energy Equation. 2.1 THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
www.sfu.caThe first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy gained by the system must be exactly equal to the amount of energy lost by the surroundings. A closed system can exchange energy with its surroundings through heat and work transfer.
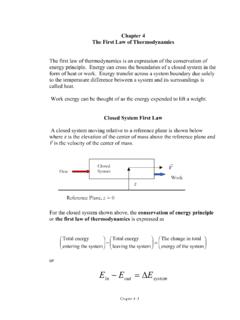
Chapter 4 The First Law of Thermodynamics
resources.saylor.orgThe First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat or work. Energy transfer across a system boundary due solely to the temperature difference between a system and its surroundings is called heat.
First Law of Thermodynamics for an Open System
www.isisvarese.edu.it1 FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS FOR AN OPEN SYSTEM Thermodynamic systems can be open, if they exchange mass with external environment, or closed if they don't exchange mass. They usually exchange energy as mechanical energy (work) and/or thermal energy (heat), if the system doesn't exchange mass and energy it is called isolated.
THERMODYNAMICS
ncert.nic.in2. Closed System In a closed system, there is no exchange of matter, but exchange of energy is possible between system and the surroundings [Fig. 6.2 (b)]. The presence of reactants in a closed vessel made of conducting material e.g., copper or steel is an example of a closed system. Fig. 6.2 Open, closed and isolated systems.
Second Law of Thermodynamics - Simon Fraser University
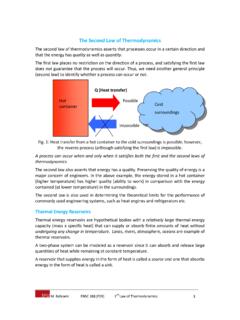
www.sfu.caThe Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity. The first law places no restriction on the direction of a process, and satisfying the first law
Thermodynamics: First Law, Calorimetry, Enthalpy Calorimetry
www.chem.tamu.eduThermodynamics: First Law, Calorimetry, Enthalpy Monday, January 23 CHEM 102H T. Hughbanks Calorimetry Reactions are usually done at either constant V (in a closed container) or constant P (open to the atmosphere). In either case, we can measure q by measuring a change in T (assuming we know heat capacities). Calorimetry: constant volume
THERMODYNAMICS
www.ncert.nic.informs the basis of the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, which states that ‘two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system separately are in thermal equilibrium with each other’. R.H. Fowler formulated this law in 1931 long after the first and second Laws of thermodynamics were stated and so numbered . The Zeroth Law clearly suggests ...
THERMODYNAMICS & ICE CREAM
www.driftwoodlib.orgThe first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the principle of conservation of energy. It states that energy can be transformed (changed from one form to another), but cannot be created or destroyed.[25] The first law is usually formulated by saying that the change in the internal energy of a closed thermodynamic
Thermodynamics Fundamentals for Energy Conversion …
esc.fsu.eduThis law is the basis of temperature measurement. First Law of Thermodynamics: The change in internal energy of a closed system is equals to the heat added to the system (or absorbed from the environment) minus the work done by the system (or on the environment). This law is a consequence of conservation of energy.
HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER - UPM
webserver.dmt.upm.es• A temperature increase in a closed system is not necessarily due to a heat input; it can be due to a work input (e.g. ∆E=mc∆T=W for Q=0 in (1)), either with dissipation (e.g. internal stirring), or without (isentropic compression). • The First Law (1) shows that, for a steady state without work exchange,the heat loss by a system
Heat transfer and thermal modelling
webserver.dmt.upm.esThe First Law applied to a regular interface (a non-dissipating one) implies that the heat loss by a system must pass integrally to another system, and the Second Law means that the hotter system gives off heat while the colder one takes it. In Thermodynamics, one refers sometimes to ‘heat in an isothermal
Similar queries
UNIT 61: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS, First Law of Thermodynamics, First Law of Thermodynamics. Closed systems, Systems, First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems, Closed, The First Law of Thermodynamics, The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics, Thermodynamics, Law of Thermodynamics, First Law, First, Of thermodynamics