Motion Energy
Found 8 free book(s)DIFFERENT FORMS OF ENERGY - Teachers College, Columbia ...
www.tc.columbia.eduENERGY (or heat energy) is the energy of moving molecules. The energy that comes from a fire is thermal energy. MECHANICAL ENERGY is the energy stored in objects by tension. When the tension is released, motion occurs. A spring that is pressed down has mechanical energy. RADIANT ENERGY (or light energy) is related to the movement of light. The
STEMonstrations - Kinetic and Potential Energy - NASA
www.nasa.govPotential energy (PE) is a stored form of energy that can produce motion, i.e. the “potential for motion.” Think of PE as stored energy that can become kinetic energy. You can calculate potential energy using an object’s mass and its height. PE is measured in Joules (J). PE = mgh where m = mass (kg), g = acceleration due to gravity
Chapter 7 – Kinetic energy, potential energy, work - Physics
physics.ucf.eduI. Kinetic energy Energy associated with the state of motion of an object. (7.1) 2 K 1 mv2 Units: 1 Joule = 1J = 1 kgm2/s2 = N m II. Work Energy transferred “to” or “from” an object by means of a force acting on the object. To +W From -W - Constant force: F x ma x d v v v v axd ax 2 2 2 0 2 2 0 2 Work done by the force = Energy
Derivation of Equations of Motion for Inverted Pendulum ...
www.cas.mcmaster.caKinetic Energy De nition The energy which an object possesses due to its motion It is de ned as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy E k of a point object is de ned by its mass m and velocity v: E k …
Lecture L16 - Central Force Motion - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.edumeans that when r increases, the kinetic energy is transformed to potential energy such that, at infinity, the residual velocity is equal to zero. Hyperbolic Trajectory (e > 1) For a hyperbolic orbit, e > 1 and the semimajor axis a is negative. The energy is constant and given by 2 2 E = − 2 µ a = v 2 − µ r = v 2 ∞ (11)
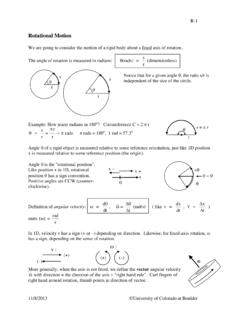
Rotational Motion - Physics
physicscourses.colorado.eduConservation of energy problem with rolling motion: A sphere, a hoop, and a cylinder, each with mass M and radius R, all start from rest at the top of an inclined plane and roll down to the bottom. Which object reaches the bottom first? Apply Conservation of Energy to determine v final. Largest v final will be the winner.
Chapter 11 Density of States, Fermi Energy and Energy Bands
homepages.wmich.edu11-3 ! p k (11.6) Knowing the momentum p = mv, the possible energy states of a free electron is obtained m k m p E mv 2 2 2 1 2 2 ! (11.7) which is called the dispersion relation (energy or frequency-wavevector relation). Effective Mass In reality, an electron in a crystal experiences complex forces from the ionized atoms.
Radiation Interactions with Matter ... - MIT OpenCourseWare
ocw.mit.edu• The linear rate of energy loss is a maximum as the particle energy approaches 0. Rate of energy loss along an alpha particle track. • The peak in energy loss at low energies is exemplified in the Figure, above, which plots -dE/dx of an alpha particle as a …