Soil Soil Ph
Found 8 free book(s)Testing Your Soil Why and How to Take a Soil-Test Sample
www.nrcs.usda.govA soil analysis can help farmers and gardeners answer these questions. A basic soil analysis provides informa-tion on two important soil characteristics: • Soil pH is a measurement on a scale from acid (low pH) to alkaline (high pH). Most soils are on the acid side of the pH spectrum. Good soils for crop produc-
Inherent Factors Affecting Soil pH - USDA
www.nrcs.usda.govPage 1 Guides for Educators Soil pH is a measure of soil acidity or alkalinity. It is an important indicator of soil health. It affects crop yields, crop suitability, plant nutrient availability, and soil micro-organism activity which influence key soil processes.
Basic Soil Properties - Purdue Agriculture
ag.purdue.eduAgronomy 105 Soil & Water: Basic Soil Properties 2 Three Categories of Soil Properties •Physical: texture (proportions of sand, silt and clay), structure, bulk density, moisture, infiltration, porosity •Chemical: nutrient content, salinity, pH, organic matter, mineral content (parent material)
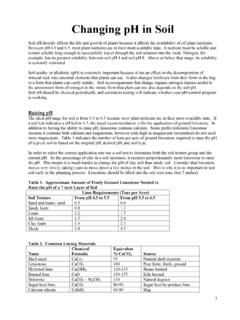
Changing pH in Soil - University of California, Davis
vric.ucdavis.eduthe ammonium form of nitrogen to the nitrate form that plant can use also depends on the soil pH. Soil pH should be checked periodically and consistent testing will indicate whether your pH-control program is working. Raising pH The ideal pH range for soil is from 6.0 to 6.5 because most plant nutrients are in their most available state. If a ...
SOILS, SOIL CHARACTERISTICS AND SOIL MANAGEMENT
www.agronomy.k-state.eduThe soil has three major horizons (Fig. 2). 2 “A” horizon is the top layer of the soil in which organic matter has accumulated from plant and animal residues and from which clay and chemical elements have been leached into lower layers. The “A” horizon, then, is the leached layer of soil. “B” horizon is the middle layer of soil into ...
Soil Bulk Density as related to Soil Texture, Organic ...
www.ijsrp.orgA pH and Electrical Conductivity of soil samples were measured by Soil Testing Kit Model 161E. A 20 gms of collected soil was weighed out into a 150 ml plastic jar and 100 ml distill water was added to it. Lid of jar was packed tightly and stirred continuously for …
Soil Analysis - Clemson University
www.clemson.edutest. Soluble salts, pH P K Ca Mg and nitrates will be determined on a saturated water extract. _____ SBD – Bulk Density of soilless mixes _____$10.00 . LAB USE ONLY . L A B U S E O N L Y. LAB USE ONLY LAB USE ONLY . Soil Analysis . Agricultural Service Laboratory . 171 Old Cherry Road / Clemson, SC 29634 . Phone: 864-656-2068 Fax: 864-656-2069
Soil Lab - UWSP
www.uwsp.edu4. pH is a measure of how acidic or basic things are. We assign a number scale from 0 to 14 to things to tell us how acidic or basic they are. A pH of 7 is neutral, less than 7 is acidic like vinegar with a pH of 3.5, and more than 7 is basic like ammonia with a pH of 10. (When soil pH is basic, it is usually called “alkaline.”) a.