Unit 5 Vectors
Found 9 free book(s)1. Vectors, contravariant and covariant
www.seas.upenn.edubasis vectors. As shown on Figure 1, the dual basis vectors are perpendicular to all basis vectors with a di erent index, and the scalar product of the dual basis vector with the basis vector of the same index is unity. The basis set for dual vectors enables any dual vector P~ to be written: P~ = P 1~e 1 + P 2e~ 2 = P ~e
1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal ...
www.mathematics.pitt.edu1. (a) (5 points) Find the unit tangent and unit normal vectors T and N to the curve r(t) = h3cost;4t;3sinti at the point P= 3 p 2;3ˇ; 3 p 2 . (b) (5 points) Find curvature of …
Chapter 1 Units and Vectors: Tools for Physics
www2.tntech.eduRelations among the unit vectors for vector products are: i×j = k j×k = i k×i = j (1.10) 1.2. WORKED EXAMPLES 5 A B C A B C (a) (b) f Figure 1.3: (a) Finding the direction of A × B. Fingers of the right hand sweep from A to B in the shortest and least painful way. The extended thumb points in the direction of C. (b) Vectors A, B and C.
Vectors - Clemson University
people.cs.clemson.eduTwo nonparallel vectors always define a plane, and the angle is the angle between the vectors measured in that plane. Note that if both a and b are unit vectors, then kakkbk= 1, and ab = cos . So, in general if you want to find the cosine of the angle between two vectors a and b, first compute the unit vectors aˆ and bˆ in the directions of a ...
Vectors in Linear Algebra - University of Texas at Austin
www.cs.utexas.eduThese vectors are also referred to as the standard basis vectors. Other terms used for these vectors are natural basis and canonical basis. Indeed, “unit basis vector” appears to be less commonly used. But we will use it anyway! Homework 1.2.2.1 Which of the following is not a unit basis vector? (a) 0 B B B B B @ 0 0 1 0 1 C C C C C A (b) 0 ...
Vectors and Vector Spaces
www.math.tamu.eduVectors and Vector Spaces 1.1 Vector Spaces Underlying every vector space (to be defined shortly) is a scalar field F. ... (viii) ex = x where e is the multiplicative unit in F. 7. 8 CHAPTER 1. VECTORS AND VECTOR SPACES The “closed” property mentioned above means that for all α,β∈F and x,y ∈V
1 Vectors in 2D and 3D - Stanford University
mc.stanford.eduThe e ect of multiplying a vector ~uwith scalars 2.5, 1 and 0.3 is given in Figure 2 in di erent colors. Note that the di erent vectors all lie on top of each other as scalar multiplication of a vector cannot change the direction of the vector, except for reversing it. But scalar multiplication does change the magnitude of ~u! x y ~u (0,0) u~ 2 ...
IntroductiontoAppliedLinearAlgebra Vectors,Matrices ...
web.stanford.eduPreface ThisJuliaLanguageCompanionaccompaniesourbookIntroductiontoApplied LinearAlgebra:Vectors,Matrices,andLeastSquares(referredtohereasVMLS ...
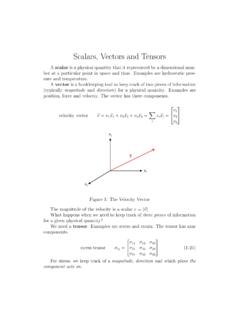
Scalars, Vectors and Tensors
zeus.plmsc.psu.eduScalars, Vectors and Tensors A scalar is a physical quantity that it represented by a dimensional num-ber at a particular point in space and time. Examples are hydrostatic pres-sure and temperature. A vector is a bookkeeping tool to keep track of two pieces of information (typically magnitude and direction) for a physical quantity. Examples are