Search results with tag "First law of thermodynamics"
Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics
www.mhtl.uwaterloo.caFirst law of thermodynamics: one of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an interaction, energy can change from one form to another but the total amount of energy remains constant. Second law of thermodynamics: energy has quality as well as quantity, and actual processes occur ...
The Ideal Gas Law Lecture 2: Atmospheric Thermodynamics
www.ess.uci.eduThe first law of thermodynamics ESS55 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu Heat and Energy Energy is the capacity to do work. Heat is one form of energy. Heat is one form of internal energy which is associated with the random, disordered motion of molecules and atoms. Internal kinetic/potential energy are different from the macroscopic kinetic/potential energy. water
UNIT 61: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
www.freestudy.co.uk2. THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS When you have completed section two, you should be able to explain and use the following terms. The First Law of Thermodynamics. Closed systems. The Non-Flow Energy Equation. Open systems. The Steady Flow Energy Equation. 2.1 THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
Chapter 2: Internal Energy (U), Work (w), Heat (q ...
scienide2.uwaterloo.caChapter 2: Internal Energy (U), Work (w), Heat (q), Enthalpy (H) Internal Energy (excludes motion and rotation of vessel) o Look at isolated part of universe U U U system Environment Total = isolated First law of thermodynamics: - Total U for isolated system is constant - Energy can be exchanged between various components
Thermodynamics - NJCTL
content.njctl.org(A) First Law of Thermodynamics (B) Second Law of Thermodynamics (C) Mechanical equivalent of heat (D) Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics (E) Thermal expansion of solids 2. An aluminum plate has a circular hole. If the temperature of the plate increases, what happens to the size of the hole? (A) Increases (B) Decreases (C) Stays the same
THERMODYNAMICS
www.ncert.nic.in12.3 Zeroth law of Thermodynamics 12.4 Heat, internal energy and work 12.5 First law of thermodynamics 12.6 Specific heat capacity 12.7 Thermodynamic state variables and equation of state 12.8 Thermodynamic processes 12. 9 Heat engines 12.10 Refrigerators and heat pumps 12.11 Second law of thermodynamics 12.12 Reversible and irreversible ...
THERMODYNAMICS & ICE CREAM
www.driftwoodlib.orgThe first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the principle of conservation of energy. It states that energy can be transformed (changed from one form to another), but cannot be created or destroyed.[25] The first law is usually formulated by saying that the change in the internal energy of a closed thermodynamic
Thermodynamics Fundamentals for Energy Conversion …
esc.fsu.eduThis law is the basis of temperature measurement. First Law of Thermodynamics: The change in internal energy of a closed system is equals to the heat added to the system (or absorbed from the environment) minus the work done by the system (or on the environment). This law is a consequence of conservation of energy.
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
www.sfu.caThe first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy gained by the system must be exactly equal to the amount of energy lost by the surroundings. A closed system can exchange energy with its surroundings through heat and work transfer.
First Law of Thermodynamics for an Open System
www.isisvarese.edu.it1 FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS FOR AN OPEN SYSTEM Thermodynamic systems can be open, if they exchange mass with external environment, or closed if they don't exchange mass. They usually exchange energy as mechanical energy (work) and/or thermal energy (heat), if the system doesn't exchange mass and energy it is called isolated.
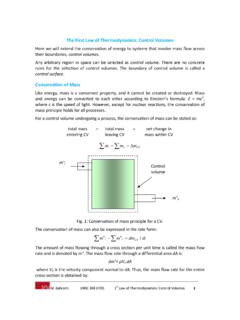
First Law of Thermodynamics Control Volumes
www.sfu.cast Law of Thermodynamics: Control Volumes 2 m V dA (kg/s) A n Assuming one‐dimensional flow, a uniform (averaged or bulk) velocity can be defined: m°= ρ V A (kg/s) where V (m/s) is the fluid velocity normal to the cross sectional area. The volume of the