Search results with tag "Law of thermodynamics"
CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF …
astrowww.phys.uvic.ca1 CHAPTER 7 THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS 7.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics, and Internal Energy The First Law of thermodynamics is: The increase of the internal energy of a system is equal to the sum of the heat added to the system plus the work done on the system. In symbols: dU = dQ + dW.7.1.1 You may regard this, according to taste, …
Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery - Free
160592857366.free.fr2. Basic Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics: Definitions of Efficiency 23 Introduction 23 The equation of continuity 23 The first law of thermodynamics internal energy 24 The momentum equation Newton’s second law of motion 25 The second law of thermodynamics entropy 29 Definitions of efficiency 30 Small stage or polytropic efficiency 35
Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics
www.mhtl.uwaterloo.caFirst law of thermodynamics: one of the most fundamental laws of nature is the conservation of energy principle. It simply states that during an interaction, energy can change from one form to another but the total amount of energy remains constant. Second law of thermodynamics: energy has quality as well as quantity, and actual processes occur ...
Second Law of Thermodynamics - Simon Fraser University
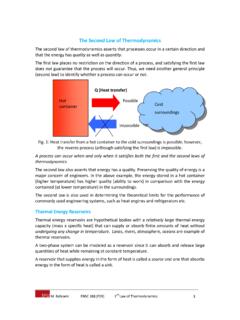
www.sfu.caThe Second Law of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity. The first law places no restriction on the direction of a process, and satisfying the first law
ENTROPY AND THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
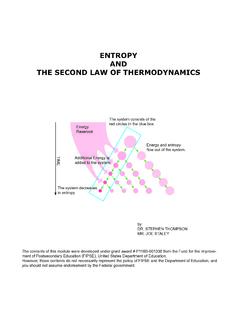
www.smallscalechemistry.colostate.eduSecond Law of Thermodynamics and can be stated as follows: For combined system and surroundings, en-tropy never decreases. Actually, it always increases. This is really what makes things happen. The fi rst law of thermodynamics, that energy is conserved, just ells us what can happen; it is the second law that makes things go.
Physical Chemistry, 4th Edition
ndl.ethernet.edu.etThe second law of thermodynamics deals with the natural direction of processes and the question of whether a given chemical reaction can occur by itself. The second law was formulated initially in terms of the efficiencies of heat engines, but it also leads to the definition of entropy, which is important
Chapter 5 The Second Law of Thermodynamics - CPP
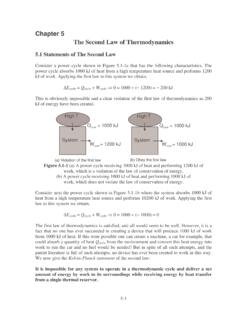
www.cpp.edulaw to this system we obtain, DE cycle = Q cycle + W cycle 0 = 1000 + (- 1000) = 0 The first law of thermodynamics is satisfied, and all would seem to be well. However, it is a fact that no one has ever succeeded in creating a device that will produce 1000 kJ of work from 1000 kJ of heat.
Chemistry 223: Introductory Physical Chemistry I
ronispc.chem.mcgill.caLecture11. Temperature: thezeroth law of thermodynamics 11 6 Lectur e1 2. Mechanics,Work, and Heat 22 7 Lectur e1 3. Reversible and irrev e rsible changes 22 7 Lectur e1 4. TheFirst Law of Thermodynamics: Energy 22, 3 7 Lecture15. Enthalpy,Hess’sLaw 23, 4 7 Lecture16. HeatCapacities, Kirchoff ’ sLaw 247 Lecture17.
3 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
www.geo.utexas.eduThermodynamics is the study of energy in systems, and the distribution of energy among components. In chemical systems, it is the study of chemical potential, reaction potential, reaction direction, and reaction extent 3.2.1 First Law of Thermodynamics: dU=dq + dw where U is the internal energy, q is the heat transferred to a system from the
Chapter 4 EFFICIENCY OF ENERGY CONVERSION
personal.ems.psu.edudefinition would be trivial, as shown in Figures 3-3 and 4-1. The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that energy is conserved in all its transformations. So the ratio of energy output to energy input is always unity, or 100%. The meaning of the word ‘useful’ depends on the purpose of the device. For example,
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
www.sfu.cast Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems 2 Fig. 1: Sign convention: positive if to the system, negative if from the system. Modes of Heat Transfer Heat can be transferred in three different modes conduction, convection, and radiation.
Biochemical Thermodynamics - Jones & Bartlett …
samples.jbpub.comBasic Quantities and Concepts 3 First Law: Energy Conservation The fi rst law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved. The forms of energy can be interconverted, but the sum of the energies must remain constant.
UNIT 61: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
www.freestudy.co.uk2. THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS When you have completed section two, you should be able to explain and use the following terms. The First Law of Thermodynamics. Closed systems. The Non-Flow Energy Equation. Open systems. The Steady Flow Energy Equation. 2.1 THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
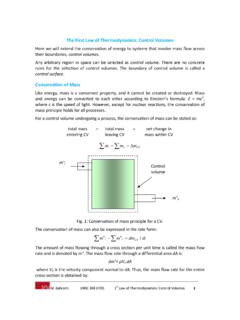
First Law of Thermodynamics Control Volumes
www.sfu.cast Law of Thermodynamics: Control Volumes 2 m V dA (kg/s) A n Assuming one‐dimensional flow, a uniform (averaged or bulk) velocity can be defined: m°= ρ V A (kg/s) where V (m/s) is the fluid velocity normal to the cross sectional area. The volume of the
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems - SFU.ca
www.sfu.caM. Bahrami ENSC 388 (F09) 1 st Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems 6 Fig. 4: the area under P‐V diagram represents the boundary work.
First Law, Heat Capacity, Latent Heat and Enthalpy
faculty.uca.eduFirst Law, Heat Capacity, Latent Heat and Enthalpy Stephen R. Addison January 29, 2003 Introduction In thissection, weintroduce the first law of thermodynamics andexamine sign conventions. Heat and Work Heat is the spontaneous flow of energy from one object to another caused by a difference in temperature. Work is defined as any other ...
[Turn over - TNPSC
www.tnpsc.gov.in101. Match the following : Tech~ology Scientific Principles (a) Aeroplane 1. Newton's Law (b) Air Balloon 2. Bernoulli's Principle (c) Rocket 3. Law of thermodynamics
Thermodynamics - NJCTL
content.njctl.org(A) First Law of Thermodynamics (B) Second Law of Thermodynamics (C) Mechanical equivalent of heat (D) Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics (E) Thermal expansion of solids 2. An aluminum plate has a circular hole. If the temperature of the plate increases, what happens to the size of the hole? (A) Increases (B) Decreases (C) Stays the same
THERMODYNAMICS, HEAT TRANSFER, AND FLUID FLOW …
sites.ntc.doe.gov1.25 STATE the Second Law of Thermodynamics. 1.26 Using the Second Law of Thermodynamics, DETERMINE the maximum possible efficiency of a system. 1.27 Given a thermodynamic system, CONDUCT an analysis using the Second Law of Thermodynamics. 1.28 Given a thermodynamic system, DESCRIBE the method used to determine: a. The …
THERMODYNAMICS - NCERT
www.ncert.nic.informs the basis of the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, which states that ‘two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system separately are in thermal equilibrium with each other’. R.H. Fowler formulated this law in 1931 long after the first and second Laws of thermodynamics were stated and so numbered . The Zeroth Law clearly suggests ...
Thermodynamics Fundamentals for Energy Conversion …
esc.fsu.eduThis law is the basis of temperature measurement. First Law of Thermodynamics: The change in internal energy of a closed system is equals to the heat added to the system (or absorbed from the environment) minus the work done by the system (or on the environment). This law is a consequence of conservation of energy.
Similar queries
Thermodynamics, Law of Thermodynamics, Of thermodynamics, First Law, THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS, Second Law of Thermodynamics, The second law, Heat engines, Physical Chemistry, And Heat, Systems, Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems, Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems, Biochemical Thermodynamics, 3 First Law, UNIT 61: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS, First Law of Thermodynamics, First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems, Boundary, First, Closed