Transcription of 360 .• 460 • 510 SERIES TRACTORS - TractorPoint.com
1 SERVICE MANUAL 360 . 460 510 series tractors LONG MFG. INC. Box 1139, 111 Fairview St., Tarboro, 27886 Tel. (919) 823-4151, Telex #510-929-o695 Form 756006 Rev. 8183 . \''' A SAFETY PRECAUTIONS A AVOID ACCIDENTS Most accidents, whether they occur in industry, on the farm. at home or on the highway, are caused by the failure of some indi-vidual to follow simple and fundamental safety rules or precau-tions. For this reason MOST ACCIDENTS CAN BE PREVENTED by recognizing the real cause and doing something about it be-fore the accident occurs. Regardless of the care used in the design and construct1on of any type of equipment there are many conditions that cannot be completely safeguarded against without interfering w1th reasonable accessibility and efficient operation. A careful operator is the best insurance against an accident.
2 The complete observance of one simple rule would prevent many thousand serious injuries each year. That rule is: NEVER ATTEMPT TO CLEAN, OIL OR ADJUST A MACHINE WHILE IT IS IN MOTION. NATIONAL SAFETY COUNCIL A WARNING A On machines having hydraulically, mechanically, and/or cable controlled equipment (such as fork lifts. combmes. shovels, loaders, dozers, scrapers, etc.) be certain the equipment is lowered to the ground before servicing, adjusting and/or repairing. If it is necessary to have the hydraulically, mechanically, and/or cable controlled equipment partially or fully raised to gain access to certain items, be sure the equipment is suitably supported by means oth8r than the hydraulic lift cylinders, cable and/or mechanical devices used for controlling the equipment. A WARNING A ALWAYS USE proper tools and procedures as recommended in Service and Operator's Manual.
3 ALWAYS READ all Caution and Note paragraphs in Service and Operator's Manual before proceedmg with service or repair work . A. I. A. II. A. Ill. MASTER INDEX A. ENGINE Specifications Removal Installation crankcase Cylinder Head 011 Sump Valves & Timing Mechanism Crank Gear Assembly A. VI. A. VIII. Fuel System Lubrication Cooling Fits & Tolerances Torque Specifications B. POWER TRAIN Description Clutch Transmissions Bevel Gear & Differential Brakes Independent Hand Brake B. VII. B. VIII. Final Drive & Rear Wheels Power Take Off Front Axle and Steering Front Drive Axle (Side Drive) Front Drive Axle (Center Drive) Fits & Tolerances Torque Specifications C. HYDRAULICS Hydraulic Lift & Linkage Power Steering Fits & Tolerances Torque Specifications D. ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ~.
4 A. II. A. II. Flta a r A. ENGINE INDEX Specifications Removal Installation Description .. 3 Specifications .. 4 Fault-Finding .. 5 Removing Engine from Tractor .. 6 Disassembly and Reassembly .. 8 Installation .. 8 crankcase Cylinder Head Oil Sump crankcase and Cylinder Liners .. 11 Checking and Cleaning the crankcase .. 11 Cylinder Liner Re-boring and Replacement .. 11 Cylinder Head .. 12 Oil Sump .. 14 Valves and Timing Mechanism General .. 15 Timing Data .. 15 Camshaft .. 15 Valves, Guides and Springs .. 17 Valve Gap Adjustment .. 19 Tappets, Push-Rods and Rocker Arms .. 19 Timing Gear Assembly .. 20 Tachourmeter .. 21 Crank Gear Assembly General .. 22 Crankshaft .. 22 Crankshaft Bearings .. 25 Pistons and Rings .. 25 Connecting Rods .. 27 Engine Flywheel .. 28 Fuel System Air Supply.
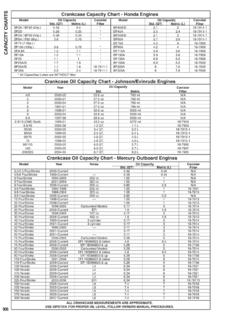
5 29 Fuel Supply .. 29 Fuel Tank .. 30 Fuel Priming Pump .. 30 Fuel Filters .. 30 INJECTION PUMP .. 33 General Description .. 33 Injection Pump Removal .. 33 Pump Installation and Timing .. 35 Injectors .. 35 Starting Aid .. 36 A. V. Lubrication General .. 38 Oil Pump .. 39 Oil Filter .. 39 Low Oil Pressure Warning Light .. 39 Lube and Capacity Chart .. 41 Cooling General .. 42 Water Pump .. 43 Radiator .. 44 Thermostat .. 45 Fan .. 46 Water Temperature Gauge .. 46 Fits and Tolerances Torque Speciflca tions Fits and Tolerances 360/460 .. 47 Fits and Tolerances 510 .. 50 Torque Specifications .. 53 Engine 2 SPECIFICATIONS REMOVAL INSTALLATION DESCRIPTION The engine installed in the wheel tractor models 360, 460 and 510, is a high speed diesel unit with four strokes and three cylinders-inline. The engine crankcase is a cast iron unibloc with dry type replaceable cylinder liners, and with the housings for the crankshaft main bearings and valve tappets.
6 Helical-teeth timing gears, camshaft located in the crankcase and overhead valves; intake valves are shielded to increase turbulence of the aspirated air. The power train is driven by the crankshaft which revolves in four thin-shell main 14709 FIG. Three-Quarter Right Front View of Engine 1. First fuel filter; 2. Fuel Injection pump; 3. Air Intake manifold; 4. Starting aid reservoir; 5. Injec-tor; 6. Second fuel filter; 7. Thermostat location; 9. Hydraulic system oil pump; 10. Fuel lift pump; 11. Electric starting motor bearings and includes: Light alloy pistons with toroidal combustion chamber built in top, three piston rings (two oil scrapers and one compres-sion ring), forged steel connecting rods and liners lubrication and a second one through the small end for piston cooling. Aspirated air is filtered through an oil bath air cleaner.
7 Fuel is injected directly into the high turbulence combustion chamber built in piston top. Double diaphragm fuel lift pump, double filters connected in SERIES and water trap on the first filter. 14710 ' FIG. Three-Quarter Left Rear View of Engine With Clutch 12. Exhaust manifold; 13. Engine lifting eye; 14. Engine oil filter; 15. Engine and clutch unit; 16. 011 pressure sending unit connection; 17. Breather pipe; 18. 011 dipstick; 19. Alternator Engine 3 Injection pump of the plunger type with all speed governor and automatic timing device: type Rotary,wlth fly-weight mechanical governor. Separate four hole nozzles (360/460) or three hole nozzles (510) clamped to the cylinder head. Forced feed lubrication from camshaft driven gear-type pump with built in relief valve. Full flow filter screwed to the crankcase and pro-vided with an Internal relief valve which bypasses the oil flow when filter is clogged.
8 CIRCULATING WATER AND RADIATOR COOL lNG SYSTEM A centrifugal pump, belt-driven by the crankshaft-mounted drive pulley, forces the coolant flow which enters the radiator when the temperature reaches up to thermostat setting. The cold air drawn by the fan which is secured to the water pump hub, cools the coolant inside the radiator. Direct electric starting with solenoid engage-ment, 12 volt motor and starting aid for low temperatures. SPECIFICATIONS -ENGINE 360 460 510 Type .. Diesel .. Diesel .. Diesel Strokes .. 4 .. 4 .. 4 Number of Cylinders .. 3 .. 3 .. 3 Bore and Stroke .. x in .. x in .. x in. (95 x 110 mm) (95 x 110 mm) (102 x 110 mm) Displacement .. 143 cu. in .. 143 cu. in .. cu. in. (2340 cu. em.) (2340 cu. em.) (2696 cu. em.) Static Timing .. 13 8 TDC .. 13 8 TCD .. 13 8 TCD Number of Main Bearings.
9 4 .. 4 .. 4 Injection Sequence .. 1-2-3 .. 1-2 3 .. 1-2-3 Compression Ratio .. 17:1 .. 17:1 .. 17:1 Sense of Rotation (As seated in the driver's seat) .. Counterclockwise: .. Counterclockwise .. Counterclockwise Rated Speed .. 2255 RPM .. 2400 RPM .. 2400 RPM High Idling .. 2355 RPM .. 2550 RPM .. 2550 RPM Low Idling .. 600 RPM .. 600 RPM .. 600 RPM RPM to Engine RPM 164-168 .. 600-650 .. 600 650 .. 675-725 540 ' .. 1970 .. 1970 .. 2160 600 .. 2189 .. 2189 .. 2400 659 .. 2400 .. 2400 .. 2600 Starter Pinion to Flywheel Crown Gear Ratio .. 9:110 .. 9:110 .. 9:110 Engine/Alternator Speed Ratio .. 1:1827 ..' .. 1:1827 .. 1:1827 Lubrication Pressure (Max.) .. 294-392 kPa .. 294-392 kPa .. 294-392 kPa ( PSI) ( PSI) ( PSI) Minimum Pressure .. kPa (5 PSI) .. kPa (5 PSI) .. kPa (5 PSI) Engine/Oil Pump Speed Ratio.
10 1 .. 1 .. 1 Engine/Water Pump Speed Ratio .. 1 .. 1 .. 1 Hourmeter Calibration (1 Hr.) .. 96,000 Engine Revs.. 96,000 Engine Revs .. 96,000 Engine Revs Engine Weight (Without Air Cleaner and Lubricating Oil) .. 660 lbs. (299 kg) .. 660 lbs. (299 kg) .. 660 lbs. (299 kg) HORSEPOWER Manufacturer's Maximum Observed Horsepower at Rated Engine Speed .. 35 ( kw) .. (31 .3 kw) .. ( kw) Engine-4 ----------------FINDING THE PROBLEM IN CASE OF POOR ENGINE PERFORMANCE If test specifications cannot be met: 1. Check, by excluding one cylinder at a time, that the compression pressure drop is cons tant in order to ascertain the functional effi ciency and uniformity of nozzles or try once again using a set of calibrated test nozzles. 2. Look for the causes of poor engine perfor mance. Use a compression tester applying it in succession to each cylinder, to which the present test data and procedure refer.