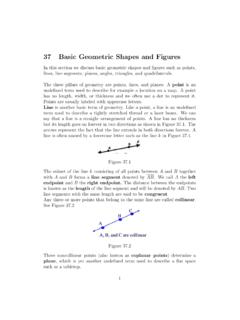
Transcription of A Basic Course in the Theory of Interest and Derivatives ...
1 A Basic Course in the Theory of Interest andDerivatives Markets:A Preparation for the Actuarial Exam FM/2 Marcel B. FinanArkansas Tech Universityc All Rights ReservedPreliminary DraftLast updatedMarch 24, 20172In memory of my parentsAugust1, 2008 January 7, 2009 PrefaceThis manuscript is designed for an introductory Course in the Theory of in-terest and annuity. This manuscript is suitablefor a junior level Course in themathematics of calculator, such as TI BA II Plus, either the solar or battery version, willbe useful in solving many of the problems in this book. A recommendedresource link for the use of this calculator can be found recommended approach for using this book is to read each section, workon the embedded examples, and then try the problems.
2 Answer keys areprovided so that you check your numerical answers against the correct taken from previous exams will be indicated by the symbol .This manuscript can be used for personal use or class use, but not for com-mercial purposes. If you find any errors, I would appreciate hearing fromyou: project has been supported by a research grant from Arkansas B. FinanRussellville, ArkansasMarch 200934 PREFACEC ontentsPreface3 The Basics of Interest Theory91 The Meaning of Interest .. 102 Accumulation and Amount Functions .. 153 Effective Interest Rate (EIR).
3 254 Linear Accumulation Functions: Simple Interest .. 325 Date Conventions Under Simple Interest .. 406 Exponential Accumulation Functions: Compound Interest .. 467 Present Value and Discount Functions .. 568 Interest in Advance: Effective Rate of Discount .. 639 Nominal Rates of Interest and Discount .. 7510 Force of Interest : Continuous Compounding .. 8811 Time Varying Interest Rates .. 10412 Equations of Value and Time Diagrams .. 11113 Solving for the Unknown Interest Rate .. 11814 Solving for Unknown Time .. 127 The Basics of Annuity Theory15515 Present and Accumulated Values of an Annuity-Immediate.
4 15616 Annuity in Advance: Annuity Due .. 17017 Annuity Values on Any Date: Deferred Annuity .. 18118 Annuities with Infinite Payments: Perpetuities .. 19119 Solving for the Unknown Number of Payments of an Annuity .. 19920 Solving for the Unknown Rate of Interest of an Annuity .. 20921 Varying Interest of an Annuity .. 21922 Annuities Payable at a Different Frequency than Interest is Con-vertible .. 22456 CONTENTS23 Analysis of Annuities Payable Less Frequently than Interest isConvertible .. 23024 Analysis of Annuities Payable More Frequently than Interest isConvertible .. 23925 Continuous Annuities.
5 24926 Varying Annuity-Immediate .. 25527 Varying Annuity-Due .. 27228 Varying Annuities with Payments at a Different Frequency thanInterest is Convertible .. 28129 Continuous Varying Annuities .. 294 Rate of Return of an Investment30130 Discounted Cash Flow Technique .. 30231 Uniqueness of IRR .. 31332 Interest Reinvested at a Different Rate .. 32033 Interest Measurement of a Fund: Dollar-Weighted Interest Rate 33134 Interest Measurement of a Fund: Time-Weighted Rate of Interest 34135 Allocating Investment Income: Portfolio and Investment YearMethods .. 35136 Yield Rates in Capital Budgeting.
6 360 Loan Repayment Methods36537 Finding the Loan Balance Using Prospective and RetrospectiveMethods.. 36638 Amortization Schedules .. 37439 Sinking Fund Method .. 38740 Loans Payable at a Different Frequency than Interest is Convertible40141 Amortization with Varying Series of Payments .. 407 Bonds and Related Topics41742 Types of Bonds .. 41843 The Various Pricing Formulas of a Bond .. 42444 Amortization of Premium or Discount .. 43745 Valuation of Bonds Between Coupons Payment Dates .. 44746 Approximation Methods of Bonds Yield Rates .. 45647 Callable Bonds and Serial Bonds.
7 464 CONTENTS7 Stocks and Money Market Instruments47348 Preferred and Common Stocks .. 47549 Buying Stocks .. 48050 Short Sales .. 48651 Money Market Instruments .. 493 Measures of Interest Rate Sensitivity50152 The Effect of Inflation on Interest Rates .. 50253 The Term Structure of Interest Rates and Yield Curves .. 50754 Macaulay and Modified Durations .. 51755 Redington Immunization and Convexity .. 52856 Full Immunization and Dedication .. 536An Introduction to the Mathematics of Financial Derivatives 54557 Financial Derivatives and Related Issues .. 54658 Derivatives Markets and Risk Sharing.
8 55259 Forward and Futures Contracts: Payoff and Profit Diagrams .. 55660 Call Options: Payoff and Profit Diagrams .. 56861 Put Options: Payoff and Profit Diagrams .. 57862 Stock Options .. 58963 Options Strategies: Floors and Caps .. 59764 Covered Writings: Covered Calls and Covered Puts .. 60565 Synthetic Forward and Put-Call Parity .. 61166 Spread Strategies .. 61867 Collars .. 62768 Volatility Speculation: Straddles, Strangles, and Butterfly Spreads63469 Equity Linked CDs .. 64570 Prepaid Forward Contracts On Stock .. 65271 Forward Contracts on Stock .. 65972 Futures Contracts.
9 67373 Understanding the Economy of Swaps: A Simple CommoditySwap .. 68174 Interest Rate Swaps .. 69375 Risk Management .. 703 Answer Key711 BIBLIOGRAPHY7458 CONTENTSThe Basics of Interest TheoryA component that is common to all financial transactions is the investmentof money at Interest . When a bank lends money to you, it charges rent forthe money. When you lend money to a bank (also known as making a depositin a savings account), the bank pays rent to you for the money. In eithercase, the rent is called Interest .In Sections 1 through 14, we present the Basic Theory concerning the studyof Interest .
10 Our goal here is to give a mathematical background for this area,and to develop the Basic formulas which will be needed in the rest of BASICS OF Interest THEORY1 The Meaning of InterestTo analyze financial transactions, a clear understanding of the concept ofinterest is required. Interest can be defined in a variety of contexts, such asthe ones found in dictionaries and encyclopedias. In the most common con-text,interestis an amount charged to a borrower for the use of the lender smoney over a period of time. For example, if you have borrowed $100 andyou promised to pay back $105 after one year then the lender in this caseis making a profit of $5, which is the fee for borrowing his money.