Transcription of AME 20231 Homework Solutions1 Spring 2012
1 AME 20231 Homework Solutions1 Spring 2012 Last updated: May 7, 2012 , 23:48 ContentsHomework 1 ..2 Quiz 1 ..4 Homework 2 ..5 Quiz 2 ..8 Homework 3 ..9 Quiz 3 ..13 Homework 4 ..14 Quiz 4 ..18 Quiz 5 ..19 Homework 5 ..20 Quiz 6 ..24 Homework 6 ..25 Quiz 7 ..32 Homework 7 ..33 Quiz 8 ..40 Homework 8 ..41 Quiz 10 ..49 Homework 9 ..50 Quiz 11 ..56 Homework 10 ..57 Homework 11 ..64 Quiz 12 ..70 Homework 12 ..711 Solutions adapted from Borgnakke, Sonntag (2008) Solutions Manual, Fundamentals of Thermodynamics, 7th Edition,and previousAME 20231 Homework 11. hydraulic lift in an auto-repair shop has a cylinder diameter of m. To what pressure shouldthe hydraulic fluid be pumped to lift 40 kg of piston/arms and 700 kg of a car?
2 Given:d= m,marms= 40 kg,mcar= 700 kgAssumptions:Patm= 101 kPaFind:PGravity force acting on the mass, assuming they-direction is on the axis of the piston: Fy=ma F=(marms+mcar)( m/s2) = balance this force with the pressure force:F= N = (P Patm)(A) P=Patm+F/AA= d24= ( m)24= m2P= 101 kPa + m2= 204 kPa = piston/cylinder with cross sectional area of m2has a piston mass of 200 kg resting on thestops, as shown in Fig. With an outside atmospheric pressure of 100 kPa, what should the waterpressure be to lift the piston?Given:m= 200 kg,Ac= m2,Patm= 100 kPaAssumptions:Find:PThe force acting down on the piston comes from gravitation and the outside atmospheric pressure actingover the top surface. Force balance: F=0 PAc=mg+PatmAcNow solve forP:P=Patm+mgAc= 100 103Pa +(200 kg)( m/s2) m2= 100 kPa + kPa = kPa = Q.
3 StudentAME 2023120 january 2012 This is a sample file in the text formatter LATEX. I require you to use it for the following reasons: It produces the best output of text, figures, and equations of any program I ve seen. It is machine-independent. It runs on Linux, Macintosh (see TeXShop), and Windows (see MiKTeX)machines. You can e-mail ASCII versions of most relevant files. It is the tool of choice for many research scientists and engineers. Many journals accept LATEX sub-missions, and many books are written in basic instructions are given below. Put your text in here. You can be a little sloppy about spacing. Itadjusts the text to look can make the text a line for a new paragraph. You can use italics ( Thermodynamics is everywhere) letters are a snap.
4 Equations within text are easy A well known Maxwell thermodynamicrelation is T p s= v s p. You can also set aside equations like so:du=Tds pdv,first law(1)ds law(2)Eq. (2) is the second law. References2are available. If you have an postscript file, say ,in the same local directory, you can insert the file as a figure. Figure 1, below, plots an isotherm for airmodeled as an ideal (kPa)v (m3/kg)P v = R TR = kJ/kg/KT = 300 KFigure 1:Sample figure plottingT= 300 Kisotherm for air when modeled as an ideal LATEXYou can create a LATEX file with any text editor (vi, emacs, gedit, etc.). To get a document, you needto run the LATEX application on the text file. The text file must have the suffix .tex On a Linux clustermachine, this is done via the commandpdflatex generates three , , The most important This filecan be viewed by any application that , such as Adobe Acrobat must have a closing statement as , L.
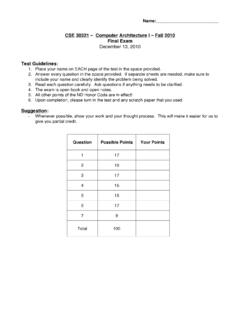
5 , 1986,LATEX: User s Guide & Reference Manual, Addison-Wesley: Reading, 11. Steam turbines, refrigerators, steam power plants, fuel cells, False,coal, natural gas, nuclear, True or false (An air separation plant separates air into its various components, which inaddition to oxygen and nitrogen include argon and other gases.)4 Homework 22. U-tube manometer filled with water, density 1000 kg/m3, shows a height differenceof 25 cm. What is the gauge pressure? If the right branch is tilted to make an angle of 30with the horizontal, as shown in Fig. , what should the length of the column in thetilted tube be relative to the U-tube?Given: = 1000 kg/m3,h= m, = 25 Assumptions:g= m/s2 Find:P,lP=F/A=mg/A=V g/A=h g= ( m)(1000 kg/m3)( m/s2)= Pa= kPa =Ph=(l)(sin 25 )l=h/sin 25 = 59 cm =l56 50050100 1000100200300400500600700 CelsiusTemperatureProblem FahrenheitRankineKelvin Celsius7 Quiz 21.
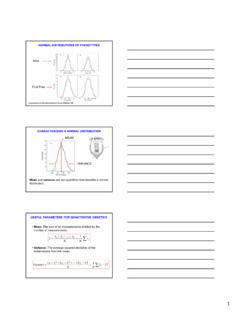
6 Water has a density of 997 kg/m3. Rationally estimate the pressure difference between thedifference between the surface and the bottom of a typical Olympic swimming pool locatedon Earth. Make any necessary will vary. Assuming no atmospheric pressure difference between the surface andbottom of the pool and a depth of 3 m, the pressure difference Pis P= gh= (997 kg/m3)( m/s2)(3 m)= 29 kPa = was acceptable to leave the heighthin the solution as a variable. Atmospheric pressureacts on the surfaceandthe bottom of the pool so it should not factor into the pressuredifference of the 31. spherical helium balloon of 11 m in diameter is at ambientTandP, 15 C and100 kPa. How much helium does it contain? It can lift a total mass that equals the massof displaced atmospheric air.
7 How much mass of the balloon fabric and cage can then belifted?Given:d= 11 m,T= 15 C,P= 100, kPaAssumptions:Find:mHe,mlif tWe need to find the masses and the balloon volume:V= 6d3= 6(11 m)3= V=Vv=(100 kPa)( )( K)(288 K)= kg =mHemair=(100 kPa)( )( K)(288 K)= 843 kgmlif t=mair mHe= kg =mlif t9103. cylinder has a thick piston initially held by a pin as shown in Fig. cylinder contains carbon dioxide at 200 kPa and ambient temperature of 290 K. Themetal piston has a density of 8000 kg/m3and the atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa. The pinis now removed, allowing the piston to move and after a while the gas returns to ambienttemperature. Is the piston against the stops?Given: p= 8000 kg/m3,P1= 200 kPa,Patm= 101 kPa,T= 290 KAssumptions:Find:P2Do a force balance on piston determines equilibrium float pressure.
8 Piston:mp=(Ap)(l)( )Pext=Patm+mpgAp= 101 kPa +(Ap)( m)(8000 kg/m3)( m/s2)(Ap)(1000)= kPaThe pin is released, and sinceP1>Pext, the piston moves , so if the piston stops,thenV2=V1 H2/H1=V1 150/100. Using an ideal gas model withT2=T0givesP2=(P1)(V1/V2) = (200)(100/150) = 133 kPa>Pext P2= 133 kPaTherefore, the piston is at the stops for the ideal gas for the tabulated solution:To findP2, we must do some extrapolation because Table does not list 200 kPa. Wefirst interpolate to find the specific volume atT1= 290 K = C at 400 kPa and 800kPa, and then extrapolate using those points to find the specific volume at 200 kPa, the area of the piston isAp= (100 mm)24= m2, the mass ofcarbon dioxide in the cylinder ismCO2=V1v1=(Ap)(100 mm) m3/kg=( m2)( m) m3/kg= m3/kg= kgSince the cylinder is closed, the mass of the carbon dioxide does not change, but the volumedoes, so we will assume the piston is at the stops andV2= m3, sov2=V2mCO2= m3/kg.
9 Now we have two state variables (T2andv2), so let s go back to and find a third state variable,P2. Interpolating between 400 kPa and 800 kPa givesP2= 291 kPa, which means our original assumption that the piston is against the stopswas incorrect. A similar iterative approach could be used to findP2in the tables. Thepiston is not against the stops. This problem was difficult, so it was only worth two received two points for a reasonable attempt with some calculations, one point for justwriting something, and no points for not attempting it. +2 indicates you were awarded twopoints for part (b), and they were not bonus 36 ft3rigid tank has air at 225 psia and ambient 600 R connected by a valveto a piston cylinder.
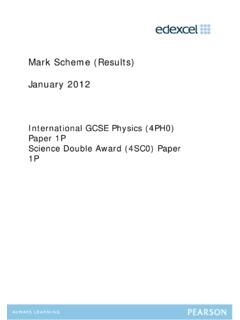
10 The piston of area 1 ft2requires 40 psia below it to float, Fig. valve is opened and the piston moves slowly 7 ft up and the valve is closed. During theprocess air temperature remains at 600 R. What is the final pressure in the tank?11 Given:VA= 36 ft3,PA= psia,T= 600 R, isothermal processAssumptions:Find:PA2mA=PAVART=(22 5)(36)(144)( )(600)= lbmNow find the change in mass during the process:mB2 mB1= VAvB= VBPBRT=(1)(7)(40)(144)( )(600)= lbmMA2=mA (mB2 mB1) = = lbmPA2=mA2 RTVA=( )( )(600)(36)(144)= 217 psia =PA2200250300350400050010001500200025003 000350040004500 Problem (Kelvin)Pressure (kPa) Wagner s EquationAppendix values12 Quiz 31. A fixed mass of water exists in a fixed volume at the saturated liquid state withv= is added to the water isochorically.