Transcription of Blood Test Results: CMP Explained
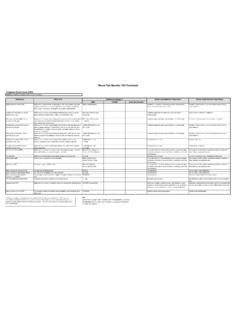
1 Blood Test results : CMP ExplainedComprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP)Definition: Measures kidney and liver function, electrolyte levelsSubstanceWhat It IsReference Ranges *What a Low Number May MeanWhat a High Number May MeanUSAUK/EUAustralia/CanadaGlucose (fasting or non-fasting)Sugar in the blood70-99 mg/dL (fasting)70-125 mg/dL (non-fasting)Hypoglycemia, liver disease, adrenal insufficiency, excess insulinHyperglycemia, certain types of diabetes, prediabetes, pancreatitis, hyperthyroidismSodium (Na)An electrolyte which keeps your body in balance136-144 mEq/LUse of diuretics, diarrhea, adrenal insufficiencyKidney dysfunction, dehydration, Cushing's syndromePotassium (K)An electrolyte and mEq/LUse of diuretics or corticosteroids (such as prednisone or cortisoneAcute or chronic kidney failure, Addison's disease, diabetes, dehydrationChloride (Cl))
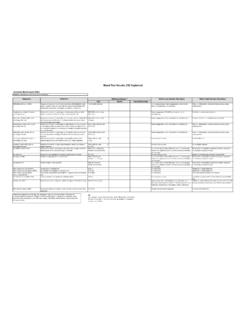
2 An electrolyte 96-106 mmol/LEmphysema, chronic lung diseaseDehydration, Cushing's syndrome, kidney diseaseCarbon dioxide (bicarbonate) (CO2)Gaseous waste product from metabolism20-29 mmol/LKidney disease, certain toxic exposures, severe infectionLung diseases, including COPDBUN ( Blood urea nitrogen) A waste product formed in the liver and carried to the kidneys, filtered out of Blood , and excreted through urine7-20 mg/dLMalnutritionLiver or kidney disease, heart failureCreatinineA chemical waste produced by muscle mg/dLLow muscle mass, malnutritionChronic or temporary decrease in kidney functionBUN/creatinine ratio10:1 to 20:1 MalnutritionBlood in bowels, kidney obstruction, dehydrationCalcium (Ca)A mineral stored in the hard part of mg/dLCalcium, magnesium, or Vitamin D deficiency; malnutrition; pancreatitis; neurological disordersKidney disease, hyperparathyroidism, cancer, excess vitamin D intakeMagnesium (Mg)An mEq/LDiabetes, high Blood calcium levels, kidney disease, pancreatitis, hypoparathyroidismDehydration, Addison's disease, hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism, kidney failureProtein (total)Chains of amino acids essential for the growth and repair of g/dLMalnutrition, liver disease, kidney diseaseLiver disease, kidney disease, dehydration, multiple myeloma, WMAlbuminProtein that keeps fluid from leaking out of Blood vessels and that nourishes tissues and transports nutrients through the g/dLMalnutrition, liver disease, kidney diseaseDehydration GlobulinAlpha, beta, and gamma proteins.
3 Some are produced by the liver and others by the immune g/dLMalnutrition, liver disease, kidney diseaseMultiple myeloma, WM, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other autoimmune diseasesAlbumin/globulin myeloma, WM, autoimmune diseases, liver disease, kidney diseaseCertain genetic conditions, some leukemias, liver dysfunction, hypogammaglobulinemiaBilirubin (direct or total)A pigment in the bile, a digestive fluid produced by the mg/dL (direct) mg/dL (total) Generally not a concernLiver disease, bile duct disorder, red cell destructionAlkaline phosphatase (ALP)Enzyme found in the liver and bones44-147 IU/LMalnutritionPaget's disease or certain cancers that spread to bone, bile duct obstruction, liver cancerAlanine amino-transferase (ALT)Enzyme found mostly in the liver8-37 IU/LGenerally not a concernCertain toxins such as excess acetaminophen or alcohol, hepatitisAspartate amino-transferase (AST)Enzyme found in liver, muscle, and other tissues10-34 IU/LGenerally not a concernExcess acetaminophen, hepatitis muscle injuryGlomerular filtration rate (GFR)Checks how well the kidneys are working by estimating how much Blood passes through the glomeruli (filters) of the kidneys each minute90-120 mL/ m2 Chronic kidney disease or kidney failure.
4 GFR decreases progressively with ageGenerally not a concernKEYmg: milligram g: gram mmol: millimole mEq: milliequivalent dL: deciliterIU: international unit L: liter mcL: microliter pg: picogram fL: femtoliterm: meter mL: milliliter* Reference ranges can vary by age, sex, methods of testing, and other factors. There are no nationally established reference ranges for CMP and CBC values; instead, each laboratory tests a population and establishes its own reference ranges. Therefore, the reference ranges quoted are only approximate.