Transcription of Certified Healthcare Safety Professional (CHSP ...
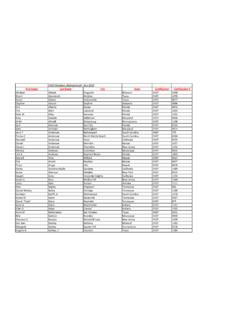
1 Certified Healthcare Safety Professional ( chsp ) examination blueprint / outline (Effective October 1, 2017) Exam Domains 150 Items 1. Safety Management A. Leadership & Management (14 Items/9%) B. Safety Management (27 Items/18%) C. Organizational Dynamics (10 Items/7%) 51 Items (34%) 2. Hazard Control A. Hazard Control Practice (9 Items/6%) B. Accident/Hazard Prevention (19 Items/13%) C. Healthcare Hazards & Risks (16 Items/10%) 44 Items (29%) 3. Compliance & Standards A. Accreditation & Voluntary Standards (25 Items/17%) B. Governmental Compliance (30 Items/20%) 55 Items (37%) IBFCSM uses KR-20 statistics to determine reliability. Domain 1 Safety Management (51 Items/34%) This domain is subdivided into three content areas as reflected in subdomains 1A, 1B, & 1C. This domain requires exam candidates to demonstrate competency by using recall, recognition, comprehension, and application of knowledge to correctly answer items related to Healthcare Safety , leadership, and management to promote Safety as an operational priority in Healthcare organizations.
2 IBFCSM ensures distribution of all exam types of items throughout the examination . Knowledge and job practice skills include the following: a. Design, implement, and maintain comprehensive management systems by defining requirements, developing policies, and procedures to protect patients, staff, visitors, property, and environment. b. Implement policies, procedures, and directives in systematic manner to protect patients, staff, visitors, property, and the environment. c. Determine the effectiveness of Safety related functions and relevant systems by measuring and evaluating performance indicators to ensure continuous improvement to protect patients, staff, visitors, and contractors. d. Apply sound management and leadership practices to efficiently use resources to improve Safety . e. Use appropriate methods to ensure stake-holders understand their roles in formulation and implementation of Safety .
3 F. Present technical information effectively to management, contractors, vendors, and the public about compliance requirements. g. Accept responsibility to promote Safety by providing technical counsel and advice on issues related to accreditation and consensus standards to protect people, property, and environment. Domain 1A Leadership & Management (14 Items/9%) 1. Communication 2. Decision-making 3. Facility Safety priorities 4. Human factors 5. Leadership principles 6. Management functions 7. Management involvement 8. Management tools 9. Occupational health 10. Organizational dynamics 11. Safety behaviors 12. Safety costs 13. Safety responsibilities 14. Supervising Safety Domain 1B Safety Management (27 Items/18%) 1. Accident/hazard reporting 2. Disaster preparedness 3. Education/training 4. Emergency drills 5. Emergency management 6. Employee health 7. Management concepts 8. Patient Safety 9. Performance improvement 10.
4 Risk management 11. Quality improvement 12. Risk management 13. Safety assessment 14. Safety authority 15. Safety communication 16. Safety effectiveness 17. Organizational improvement 18. Safety process improvement 19. Safety improvement methods 20. Safety leadership 21. Safety management 22. Safety policies 23. Safety priorities 24. Safety responsibilities 25. Security management 26. System Safety 27. Training/orientation Domain 1C Organizational Dynamics (10 Items or 7%) 1. Communication effectiveness 2. High reliability concepts 3. Organizational priorities 4. Medical errors 5. Operational culture 6. Organizational performance 7. Patient Safety challenges 8. Safety improvement 9. Safety involvement 10. System Safety methods Domain 2 Hazard Control (44 Items/29%) This domain is subdivided into three content areas as reflected in subdomains 2A, 2B, and 2C. Each subdomain requires exam candidates to demonstrate competency by using recall and recognition, comprehension, and application of knowledge to correctly answer items related to Healthcare hazards.
5 Exam items can focus on the identification, analysis, and control of hazards to prevent accidents, reduce risks, and maintain a safe environment for staff, patients, and visitors. Items are distributed throughout the examination . Knowledge and job practice skills include the following: a. Evaluate facilities, products, systems, equipment, workstations, and processes by applying qualitative techniques to identify the hazards and assess their risks. b. Recommend controls through design and engineering to eliminate hazards and reduce the risks posed by Safety hazards. c. Evaluate controls by analyzing feasibility, effectiveness, reliability, and costs to achieve best solutions. d. Implement strategies by using the results of hazard identification and risk analyses to eliminate and/or reduce harmful exposure to people, property, and the environment. e. Obtain compliance certifications, listings, approvals or authorizations by identifying applicable regulations, and standards to ensure facility Safety .
6 F. Communicate hazards, risks, and controls to employees, management, and the public. Domain 2A Hazard Control Practice (9 Items/6%) 1. Biohazards 2. Chemical hazards 3. Departmental hazards 4. Equipment risks 5. Evaluating risks 6. Facility wide hazards 7. Healthcare hazards 8. Mitigating hazards 9. Personal protective equipment Domain 2B Accident/Hazard Prevention (19 Items/13%) 1. Accident prevention 2. Accident causal factors 3. Accident investigations 4. Antimicrobial solutions 5. Clinical risks 6. Employee protection 7. Evaluating hazards 8. Facility wide risks 9. Hazard protection 10. Hazardous material controls 11. Hazardous material risks 12. Infection control 13. Job Safety 14. Medical equipment risks 15. Personal protective equipment responsibilities 16. Personal protective equipment assessment 17. Personal protective equipment education 18. Reporting hazards & injuries 19. Support department Safety Domain 2C Healthcare Hazards & Risks (16 Items/10%) 1.
7 Clinical area Safety 2. Implementing controls 3. Safety priorities 4. Support departmental risks 5. Environmental hazards 6. Facility assessments 7. Clinical department exposures 8. Hazard identification 9. Facility wide Safety issues 10. Gases and vapors 11. Hazard assessment processes 12. Hazardous substances 13. Human factor risks 14. Infection control response 15. Infection prevention education 16. Support department Safety Domain 3 Compliance & Accreditation (55 Items/37%) This domain is subdivided into two content areas as reflected in subdomains 3A and 3B. Exam candidates must demonstrate competency by using recall and recognition, comprehension, and application of knowledge to correctly answer items related to ethical Professional Healthcare Safety practice including adherence to compliance, accreditation, and voluntary consensus standards. Develop effective education and training by establishing objectives to impart knowledge and facilitate understanding of compliance, accreditation, and voluntary standards.
8 Exam items appear throughout the exam. Job knowledge and practice skills include the following: a. Evaluate compliance through performance assessments and various forms of feedback in to assure that training is effective. b. Maintain a recordkeeping and data capture system to acquire, analyze, and distribute accurate data and meet compliance requirements. c. Hold paramount protection of people, property, and environment by working with management and government agencies. d. Adhere to Professional conduct by limiting practice to areas of competence. e. Improve competency through continuing education and proficient use of technologies. f. Refer to appropriate standards to guide compliance and accreditation actions: Accreditation standards (JC, DNV, HFAP, CMS) Code of Federal Regulations (CFR 10, 21, 29, 40, 42, 44, 49) Federal Agencies (CDC, DHS, DHHS, DHS, DOT, EPA, FDA, FEMA, NRC, & OSHA) Voluntary Organizations (ANSI, ASTM, ASHRAE, ASME, CGA, FGI, NFPA, NIOSH, UL) Domain 3A Accreditation & Voluntary Standards (25 Items/17%) 1.
9 Accreditation 2. Clinical Safety 3. EOC Safety 4. Compressed gases 5. Consensus standards 6. Emergency drills 7. Environmental management 8. Environmental risks 9. Ergonomic issues 10. Facility Safety standards 11. Facility Safety topics 12. Facility warnings 13. Fire codes 14. Life Safety issues 15. Fire Safety risks 16. Bio-hazardous materials 17. Fire Safety management 18. Life Safety standards 19. Flammable/combustible risks 20. Hazardous occupational exposures 21. Lab Safety risks 22. Hazardous materials disposal 23. Natural disasters 24. Patient Safety standards 25. Patient Safety goals Domain 3B Governmental Standards (30 Items/20%) 1. Antimicrobial/disinfectant regulations 2. Biohazards 3. Clinical Safety 4. Compliance inspections 5. Emergency preparedness 6. Employee injuries 7. EPA standards 8. Ergonomics and human factors 9. Facility compliance 10. Federal agency compliance requirements 11. Federal agency compliance reporting 12. Federal agency compliance resources 13.
10 Federal agency compliance standards 14. Hazardous exposures 15. Hazardous materials monitoring 16. Hazardous materials training 17. Healthcare facility compliance 18. Biohazards compliance 19. Infection control 20. Ionizing & non-ionizing radiation 21. Medical equipment requirements 22. Medical waste standards 23. Occupational risks 24. Occupational health 25. Occupational Safety standards 26. OSHA compliance standards 27. OSHA training requirements 28. OSHA hazard exposure limits 29. OSHA Safety compliance 30. OSHA reporting & recordkeeping