Transcription of CMU walls comply with energy codes for …
1 CMU walls comply with energy codes for commercial buildings in many climates WITHOUT the addition of continuous insulation Here are compliance options for above grade, non residential, single wythe CMU walls . Prescriptive Compliance Software Whole Building Analysis Using IECC* Table (1)1 COMcheck2 and ENVSTD3 energy 104, energy +5. While the first option indicated in the table for mass and DOE-26. Compliance software, developed specifically to walls specifies continuous insulation for Climate demonstrate code compliance, is relatively Zones 3, 4 , 5, 6, 7, and 8, footnotes to the table Buildings can comply to the IECC. straightforward to learn and use. Two of the most provide for the following options which might be using whole-building analysis commonly used programs are ENVSTD and preferred.
2 Software (IECC section 806), such COMcheck. ENVSTD is applicable only to as energy -10, energy Plus or DOE- ASHRAE Standard COMcheck is applicable Climate Zones 1 and 2: No insulation is required for 2. These programs were developed to many energy standards, and it is the more mass walls . to analyze annual total energy use, widely used. Built into both programs are thermal rather than simply to demonstrate property constants for various wall, roof and floor Climate Zones 3 and 4: compliance to energy codes , as systems including masonry. Within COMcheck, Fill ungrouted cells with insulation such as compliance software typically various wall design options are offered according vermiculite, perlite, or foamed in place, with does. The user must demonstrate to which energy code is selected by the user.
3 For Conductivity < BTU-in/hr- ft2 0F that the energy costs of their example, a user demonstrating compliance with (R/inch > ). Note that insulation is not required building will be less than or equal one of the ASHRAE versions will see different in Climate Zone 3B nor is it required below the to those of a standard building. drop-down lists of masonry walls than will a user Warm-Humid Line in Climate Zone 3A. See Climate This is a more rigorous analysis demonstrating compliance with one of the many Zone Map. than for COMcheck: the user must IECC versions available. A concern with this include not only building envelope approach is that user-defined masonry walls may Climate Zones 5-8: characteristics, but also not be getting the full thermal mass benefits that 1.
4 Choose the prescriptive R option for assemblies information on mechanical and default masonry walls receive. NCMA is with continuous insulation,** lighting. Climate variables are investigating this further. OR 2. show that wall assembly complies with embedded within the program. Of For integrally-insulated (masonry cell insulation). ASHRAE Maximum U Value, the programs listed above, energy in single wythe walls , the U-factors embedded in OR 3.> use Compliance Software, 10 is probably the easiest to learn, the programs assume conventional CMU with both OR 4.> use Whole Building Analysis. followed by energy Plus. vertical and horizontal partial grout. Hence, the U- *2006 IECC International energy Conservation code factor displayed is conservative in many cases.
5 For ** R= Zone 5; R= Zone 6; R= Zone 7; R= Zone 8. a wall with better thermal properties than the For additional information call default values provided in the programs, a user (703) 713 1900. ASHRAE 20047 Table -1 thru -8 NCMA 2007. can define a unique wall system, although the user Zone 1 & 2 3 & 4 5 6 7 8 must then provide additional information to justify UMAX the data entered. Marine (C). Marine (C). Warm- BelWarm-Humid ow White Line Below White Line All of Alaska is in Zone 7 except All ofthe following Alaska is in Boroughs whichthe Zone 7 except are in Zone 8: following Boroughs, which are in ZoneBethel 8: Northwest Arctic Dellingham Bethel Northwest Arctic Fairbanks N. Star Zone 1 Includes Dellingham Nome Southeast Fairbanks Hawaii, Guam, Fairbanks N.
6 Star North Slope Wade Hampton Puerto Rico, Nome Southeast Fairbanks North Slope Wade Hampton and the Virgin Islands References: 1) 2006 International energy Conservation code International code Conference, Inc. 5) EnergyPlus Version , Department of energy 2) COMcheck Software Version Department of energy 6) DOE-2 Version E, Department of energy 3) ENVSTD Version energy Software Department of energy 7) ASHRAE Standard energy Standard for Buildings Except 4) energy -10 Version , Copyright Midwest Research Institute Low-Rise Residential 2004. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers, Inc. Provided by: Concrete Block Insulating Systems, Inc. NCMA TEK. (CBIS). National Concrete Masonry Association an information series from the national authority on concrete masonry technology INTERNATIONAL energy CONSERVATION TEK 6-12C.
7 energy & IAQ (2007). code AND CONCRETE MASONRY. Keywords: ASHRAE, commercial buildings, energy codes , energy software, heat capacity, insulation, Interna- tional energy Conservation code , R-value, thermal mass requirements based on the building's percentage glazing. Each table includes minimum requirements for windows and glass INTRODUCTION doors, skylights, slab or below-grade walls , roofs, above-grade walls , and floors over outdoor air or unconditioned space. Each The International energy Conservation code (IECC) (refs. of these elements must independently meet the stated require- 1, 2) serves as a written model for states, counties, cities or ment in order for the building to comply using prescriptive other jurisdictions to develop local codes for energy efficient compliance.
8 In other words, if the building's roof insulation building design. does not meet the code minimum, the building does not comply , For commercial buildings, the IECC provides three even if other elements exceed the minimum requirements. alternatives for demonstrating building compliance, using: The charging paragraph for above grade walls , code section prescriptive criteria; a whole-building performance analysis; , states: Concrete masonry units (CMU) at least 8 inches or demonstrating compliance with ASHRAE/IESNA Standard (203 mm) nominal in thickness with essentially equal amounts , energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residen- of mass on either side of the insulation layer are considered tial Buildings (ref. 3). Although not specifically referenced in as having integral insulation; however, the thermal resistance the code , the COMcheck software program (ref.)
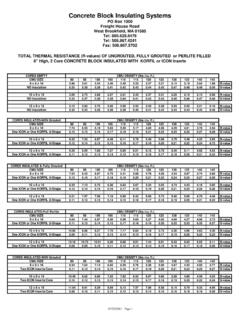
9 4) developed of that insulation shall not be considered when determining by the U. S. Department of energy is a commonly accepted compliance. The intent of this statement is to make the user compliance tool. aware that the R-value of masonry cell insulation has already The prescriptive criteria present an independent require- been accounted for in determining the prescriptive require- ment for each building envelope component. ments listed in the tables, and should not be counted towards The whole-building performance compliance option is meeting the code -mandated insulation R-value. based on an analysis which simulates a full year of building As an example, consider Table 1a which shows the above operation, accounting for virtually all aspects of building en- grade wall prescriptive requirements for commercial buildings in ergy use.
10 Detailed energy analysis software, such as DOE-2 Chicago, Illinois. The requirements for CMU > 8 in. (203 mm). (ref. 5), is typically used when employing this option. This with integral insulation and no framing are: R-value cavity =. compliance path offers the maximum design flexibility, but NA and R-value continuous = R-5. This means that to comply , requires a fairly rigorous and detailed analysis. a masonry wall, > 8 in. (203 mm) nominal thickness, must have The third compliance option simply refers the reader to continuous R-5 minimum insulation in addition to the integral ASHRAE Standard Standard includes software that insulation to comply , , the R-value of the integral insulation allows the user to trade off the performance of one building does not count toward meeting the R-5 requirement.