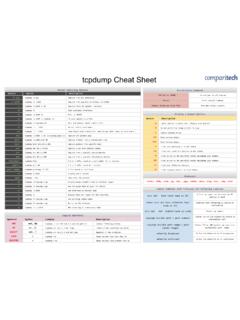
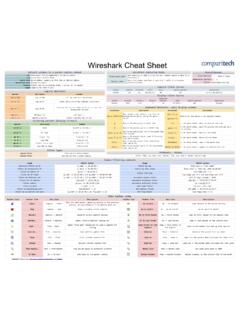
Transcription of Common TCP Protocols CISSP Cheat Sheet Series OSI ...
1 CISSP Cheat Sheet SeriesOSI Reference Model7 layers, Allow changes between layers, Standard hardware/software , OSI MnemonicsAll People Seem To Need Data ProcessingPlease Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza AwayLayerDataSecurityApplicationDataC, I, AU, NPresentationDataC, AU, EncryptionSessionDataNTransportSegmentC, AU, INetworkPacketsC, AU, IData linkFramesCPhysicalBitsCC=Confidentialit y, AU=Authentication, I=Integrity, N=Non repudiationLayer (No)FunctionsProtocolsHardware / FormatsPhysical (1)Electrical signalBits to voltageCables, HUB, USB, DSL Repeaters, ATMData Link Layer (2)Frames setupError detection and controlCheck integrity of packetsDestination address, Frames use in MAC to IP address - PPTP - L2TP - - ARP - RARP - SNAP - CHAP - LCP - MLP - Frame Relay - HDLC - ISL - MAC - Ethernet - Token Ring - FDDIL ayer 2 Switch - bridgesNetwork layerRouting, Layer 3 switching, segmentation, logical addressing.
2 ATM. - BGP - OSPF - RIP - IP - BOOTP - DHCP - ICMPL ayer 3 Switch - RouterTransportSegment - Connection orientedTCP - UDP datagrams. Reliable end to end data transfer -Segmentation - sequencing - and error checkingRouters - VPN concentrators - GatewaySession LayerData, simplex, half duplex, full dupl Eg. peer - UDP - NSF - SQL - RADIUS - and RPC - PPTP - PPPG atewaysPresentation layerData compression/decompression and encryption/decryptionTCP - UDP messagesGateways JPEG - TIFF - MID - HTMLA pplication layerDataTCP - UDP - FTP - TELNET - TFTP - SMTP - HTTP CDP - SMB - SNMP - NNTP - SSL - ModelLayersActionExample ProtocolsNetwork access Data transfer done at this layerToken ring Frame Relay FDDI Ethernet small data chunks called datagrams to be transferred via network access layerIP RARP ARP IGMP ICMPT ransportFlow control and integrityTCP UDPA pplicationConvert data into readable formatTelnet SSH DNS HTTP FTP
3 SNMP DHCPTCP 3-way HandshakeSYN - SYN/ACK - ACKC ommon TCP ProtocolsPortProtocol20,21 FTP22 SSH23 TELNET25 SMTP53 DNS110 POP380 HTTP143 IMAP389 LDAP443 HTTPS636 Secure LDAP445 ACTIVE DIRECTORY1433 Microsoft SQL3389 RDP137-139 NETBIOSA ttacks in OSI layersLayerAttackApplicationPhishing - Worms - TrojansPresentationPhishing - Worms - TrojansSessionSession hijackTransportSYN flood - fraggleNetworksmurfing flooding - ICMP spoofing - DOSData linkCollision - DOS /DDOS - EavesdroppingPhysicalSignal Jamming - WiretappingLAN TopologiesTopologyProsConsBUS Simple to setup No redundancy Single point of failure Difficult to troubleshootRING Fault tolerance No middle pointStart Fault tolerance Single point of failureMesh Fault
4 Tolerance Redundant Expensive to setupHardware DevicesHUBL ayer 1 device forward frames via all portsModemdigital to analog conversionRoutersInterconnect networksBridgeInterconnect networks in EthernetGatewaysInbound/outbound data entry points for networksSwitchFrame forward in local balancersShare network traffic load by distributing traffic between two devicesProxiesHide internal public IP address from external public internet /Connection caching and and VPN concentratorsUse to create VPN or aggregate VPN connections provide using different internet linksProtocol analyzersCapture or monitor network traffic in real-time ad offlineUnified threat managementNew generation vulnerability scanning applicationVLANsCreate collision domains.
5 Routers separate broadcast domainsIDS/IPSI ntrusion detection and AddressesPublic IPv4 address space Class A: Class B: Class C: IPv4 address space Class A: Class B: Class C: Masks Class A: Class B: Class C: bit octetsIPv6128 bit hexadecimalNetwork TypesLocal Area Network (LAN)Geographic Distance and are is limited to one building. Usually connect using copper wire or fiber opticsCampus Area Network (CAN)Multiple buildings connected over fiber or wirelessMetropolitan Area Network (MAN)Metropolitan network span within citiesWide Area network (WAN)Interconnect LANs over large geographic area such as between countries or private internal networkExtranetconnects external authorized persons access to intranetInternetPublic networkNetworking Methods & StandardsSoftware defined networking (SDN)
6 Decoupling the network control and the forwarding -Agility, Central management, Programmatic configuration, Vendor Protocols for media transferTransfer voice, data, video, images, over single Channel over Ethernet (FCoE)Running fiber over Ethernet Label Switching (MPLS)Transfer data based on the short path labels instead of the network IP addresses. No need of route table Small Computer Interface (ISCI)Standard for connecting data storage sites such as storage area networks or storage arrays. Location ProtocolsEncryption and different Protocols at different levels. Disadvantages are hiding coveted channels and weak over Internet Protocol (VoIP)Allows voice signals to be transferred over the public Internet transfer mode (ATM)Packet switching technology with higher bandwidth.
7 Uses 53-byte fixed size cells. On demand bandwidth allocation. Use fiber optics. Popular among ISPsX25 PTP connection between Data terminal equipment (DTE) and data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE)Frame RelayUse with ISDN interfaces. Faster and use multiple PVCs, provides CIR. Higher performance. Need to have DTE/DCE at each connection point. Perform error Data Link Control (SDLC)IBM proprietary protocol use with permanent dedicated leased Data Link Control (HDLC)Use DTE/DCE communications. Extended protocol for name system (DNS)Map domain names /host names to IP Address and vice RangesPoint to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)Authentication methods: PAP=Clear text, unencrypted CHAP=unencrypted, encrypted MS-CHAP=encrypted, encryptedChallenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)Encrypt username/password and re-authenticate periodically.
8 Use in 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Use with IPsec for Header (AH)Provide authentication and integrity, no Security Payload (ESP) Encrypted IP packets and preserve Associations (SA)Shared security attributes between two network ModePayload is ModeIP payload and IP header are Key Exchange (IKE)Exchange the encryption keys in AH or Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)Password is encrypted but user authentication with v3 Encrypts the Ports49152 - 65535 Remote Access ServicesTelnetUsername /Password authentication. No login (rlogin)No password (Secure Shell)Secure telnetTerminal Access Controller Access-Control System (TACACS)User credentials are stored in a server known as a TACACS server.
9 User authentication requests are handled by this +More advanced version of TACACS. Use two factor Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS)Client/server protocol use to enable AAA services for remote access private network (VPN)Secure and encrypted communication channel between two networks or between a user and a network. Use NAT for IP address conversion. Secured with strong encryptions such as L2TP or encryption optionsPoint-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) PPP for authentication No support for EAP Dial in Connection setup uses plaintext Data link layer Single connection per sessionLayer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Same as PPTP except more secure Commonly uses IPsec to secure L2TP packetsInternet Protocol Security (IPsec)
10 Network layer Multiple connection per session Encryption and authentication Confidentiality and integrityCommunication Hardware DevicesConcentratorDivides connected devices into one input signal for transmission over one output via Combines multiple signals into one signal for Retransmit signal received from one port to all Amplifies signal / WAN MediaTwisted PairPair of twisted copper wires. Used in ETHERNET. Cat5/5e/6. Cat5 speed up to 100 Mbps over 100 meters. Cat5e/6 speed Twisted Pair (UTP)Less immune to Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)Similar to UTP but includes a protective CableThick conduit instead of two copper wires.