Transcription of Concept Paper On - MPOnline
1 0 Concept Paper On BIRTH AND DEATH REGISTRATION PRIA 42, Tughlakabad Institutional Area New Delhi 110 062 Ph: 011-2995 6908, 2996 0931/32/33 E-Mail: Web: 1 Preface Ensuring Birth and Death registration and thereby obtaining certificates are vital for the citizen as well as the Government for a sensible operation of local self-governance. The urban local bodies are entrusted to ensure the registration of birth and death in urban areas. The 12th schedule of 74th Constitutional Amendment Act (CAA) has also assigned the urban local bodies to ensure proper registration and distribution of birth and death certificate.
2 In India, more than 30 percent of birth and death occurred are going unregistered every year. The poor registration system is prevailed in the states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Assam and Manipur. In India, majority of the people after registering the occurrence of birth and death has not collected the certificate from the municipality. It has also been revealed that the poor registration of birth and death is prevailed among the slum dwellers and marginalized groups due to their lack of awareness on the process of registration and the importance birth and death certificate.
3 PRIA s perspective on strengthening urban governance takes in to account in the new the political milieu opened by the 74th CAA. In the year 2000, PRIA along with its partners started intervention on strengthening urban governance in some municipal areas of five states in India. By the end of the year 2003, the urban intervention was spread over 48 towns across 12 states in India. The experience of the pilot phase intervention highlighted the need to undertake systematic and intensive intervention in respect of urban governance.
4 As a follow up of it, in a number of urban focal points where PRIA along with its partners have been intervening identified strengthening registration of birth and death for intensive intervention. This document is hence prepared to give an overview on the existing system of birth and death registration in India. We hope that the content of this document would provide insight for effective intervention in promoting registration of birth and death in urban areas. The document also covers the key issues and strategies to be observed while intervening on promoting birth and death registration.
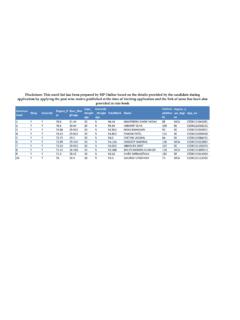
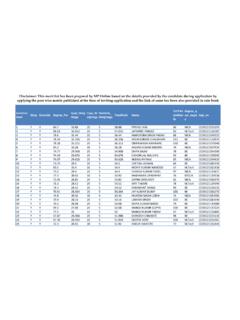
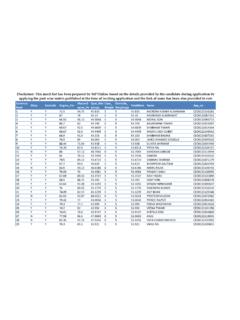
5 I would like to extend my gratitude to Dr. Rajesh Tandon, Jaitli, Anand and Ms. Shalini Grover of PRIA who supported in providing their ideas and inputs in shaping the document. Anil B PRIA, New Delhi 2 Contents Sl. No Particular Page I Introduction 3 Indian Context 5 Table on birth registration 6 II. a. b. Table on death registration 7 III Civil Registration System in India 8 IV. RBD Act - 1969 and the salient features 9 V Importance of Birth registration 10 VI Importance of Death Registration 12 VII Hierarchical Structure of Birth and Death Registration System in India 13 VIII Role of functionaries in Birth and Death Registration 14 IX State level functionaries in Civil Registration System 16 X How to access the facilities for Birth and Death Registration in Urban Local Bodies?
6 22 a. Reporting 22 b. Date of registration 23 c. Form for registration 24 d. Issuing of Birth and Death certificate 24 e. Entry of name in birth certificate 25 f. Registration of birth occurring outside India. 25 XI National rule on Birth and Death registration 25 XII Issues pertaining to Birth and Death Registration 25 XIII Strategies for improving Birth and Death Registration 27 XIV Conclusion 28 XV Annexure (1) National rule on birth and death registration (2) Forms for registration 3I. Introduction Birth registration opens the door for a newborn child to enter into a permanent identity and death registration relives one from all such records.
7 A birth certificate is considered a ticket to citizenship, without which an individual does not officially exist and therefore lacks legal access to the privileges and protection of a nation1. On the other hand, a death certificate is a mandatory proof for relieving a person from the entire social, legal and financial obligation. A birth certificate as a government document supports an individual to enjoy the rights and protection of the nation. While a death certificate supports his family members on enjoying the property rights and schemes like policy benefits and other entitled privileges.
8 In a nutshell, a birth certificate is a supportive document for the survival of an individual and a death certificate is a document to serve his family members. The registration of birth not only provides acknowledgment but also gives legal status to one s existence. It opens the door for accessing other fundamental rights including education, health care and protection. Apart from the proof of identity and entitlement for different services, birth registration to a larger extent helps the government to determine some important basic concerns like doses of immunization vaccine to be supplied, educational and other childcare facilities to be provided in the country.
9 The registration of death is also important for the government to analyse the life expectancy, population of the country and other information related to the services to be provided. A poor registration system can lead to the poor calculation of birth and death rate. Indeed an effective birth and death registration system is elementary to the sensible operation of polity in the new era of local self-governance. Article 7 of the Convention on Rights of the Child (CRC) states Every child shall be registered immediately after birth and shall have the right from birth to name and the right to acquire nationality.
10 191 countries across the world, except Somalia and United States ratified this CRC and are therefore obliged to ensure the effective implementation of the registration system. In most of the countries Civil Registration System (CRS) is taken as the basic tool for the registration of birth and death. In the civil registration system, the local-governance institutions are entitled to ensure the registration of birth and death at the grass root level. However many developing countries like Afghanistan, Cambodia, Ethiopia, Namibia and Oman do not have a mandatory birth and death registration system.