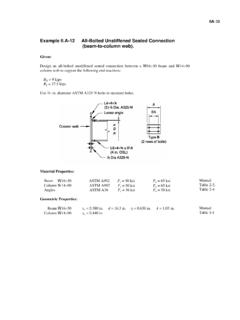
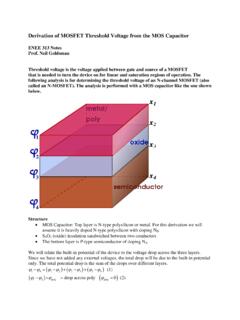
Transcription of DERIVATION OF MOSFET I VS. V C GS V - UMD
1 DERIVATION OF +VGSD erive the current expressions in the MOSFET :Linear Region:ID= CoxWL[(VGS VTH)VDS V2DS2]Saturation Region:ID= CoxW2L(VGS VTH) RegionFigure Contours in Linear Region. A uniform nar-row channel :VG VS=VG VC+VC VSVG VS=VGSVG VC=VGCVC VS=V(x)VGS=VGC+V(x) orVGS V(x) =VGC12 DERIVATION OF +VGST otal charge density at x on capacitor(COX) isQT(x):QT(x) =VGCCOX= (VGS V(x))COXQT(x) =Q(x)mobile+Q(x)depletionQ(x)mobile=mobi le electron charge in channel at xQ(x)mobile= [VGS V(x) VTH]COXUse mobile charge to get current:Jn=q nE+qDndndx=q nE(no diffusion current in the channel)qn(x) =Q(x)mobile=Qm(x)Jn=Qm(x) E, butE= dVdxJn= Qm(x) dVdx, substitute forQm(x)Jn= Cox(VGS V(x) VTH)dVdx, separate variables and neglect (-) sign.
2 Consideronly the Cox[(VGS VTH) V(x)]dVDue to continuity,Jn=constant(no hole current or no generation, recombina-tion). Integrating from source to drain or from x=0 to x=L, where L=gate length:Jn L0dx= Cox V(L)V(0)[(VGS VTH) V(x)]dVV(L) = VDS , V(0)=0Jn L0dx= Cox VDS0[(VGS VTH) V(x)]dVJnL= Cox[(VGS VTH)V V22]VDS0Jn= CoxL[(VGS VTH)VDS V2DS2] DERIVATION OF +VGS3ID=JnW(W=Device Width)Jnfor channel is Amp/cm sinceQm=Charge/cm2 IDfor Linear Region:ID= CoxWL[(VGS VTH)VDS V2DS2] RegionWhenVDS (VGS VTH) channel pinches off. This means that the channelcurrent near the drain spreads out and the channel near drain can be approximatedas the depletion region. After this occurs, atVDS= (VGS VTH), if you makeVDSlarger, the currentIDdoes not change (to zero approximation).
3 This is becauseany additionalVDSyou add will get dropped across the depletion region and won tchange the forVDS (VGS VTH) we findIDby settingVDS= (VGS VTH) substitutinginto the linear CoxWL[(VGS VTH)(VGS VTH) (VGS VT H)22]IDfor Saturation Region:ID= CoxW2L(VGS VTH)24 DERIVATION OF +VGSn=10^17n=10^15sourcedrainFigure Contours in Linear Region. A uniform nar-row channel ^17n=10^15sourcedrainFigure Contours in Saturation Region. Channelnarrow near source and spreads out and widens near drain, said to be pinched off.