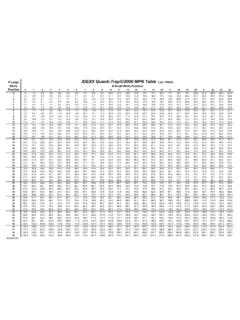
Transcription of Diagnosing, Staging, and Treating Chronic Kidney Disease ...
1 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is diagnosed based on evaluation of all available clinical and diagnostic information in a stable patient. Following diagnosis of CKD, the IRIS Board recommends using serum creatinine or SDMA (ideally both) to stage CKD with substaging based on assessment of arterial blood pressure and , Staging, and Treating Chronic Kidney Disease in Dogs and CatsJun 13 Jun 12 Jun 11 CreatinineCreatinine increasing within the reference interval where no prerenal cause is apparentreference intervalJulyAugSeptJuneSDMASDMA increasing within the reference interval where no prerenal cause is apparentreference intervalOne or more of these diagnostic findings.
2 To diagnose Stage 1 and early Stage 2 CKDP ersistent increased SDMA* >14 g/dLBoth of these diagnostic findings:1234 Persistent renal proteinuria UPC > in dogs; UPC > in catsUrine protein to creatinine (UPC) ratio Sept 15 Oct 15 Nov creatinine and SDMA concentrationsResults of both tests should be interpreted in light of patient s hydration specific gravity< specific gravity< Feline Canine Kidney imagingTo diagnose more advanced CKD (late Stage 2 4)OR12 Clinical signs and physical examination findings worsen with increasing severity of Kidney Disease Step 1.
3 Diagnose CKDC linical presentationConsider age, sex, breed predispositions, and relevant historical information, including medication history, toxin/toxicant exposure, and diet. Can be subclinical in early stage CKD. Signs may include polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss, decreased appetite, lethargy, dehydration, vomiting, and bad examination findingsCan be normal in early stage CKD. Findings may include palpable Kidney abnormalities, evidence of weight loss, dehydration, pale mucous membranes, uremic ulcers, evidence of hypertension, , retinal for more detailed staging, therapeutic, and management guidelines.
4 Note that some cats can produce hypersthenuric urine in the face of renal 2: Stage CKD*SDMA = IDEXX SDMA TestSee for more detailed staging, therapeutic, and management 1No azotemia(Normal creatinine)Stage 2 Mild azotemia(Normal or mildly elevated creatinine)Stage 3 Moderate azotemiaStage 4 Severe azotemiaCreatinine in mg/dLLess than (125 mol/L) (125 250 mol/L) (251 440 mol/L)Greater than (440 mol/L)CanineFelineLess than (140 mol/L) (140 250 mol/L) (251 440 mol/L)Greater than (440 mol/L)SDMA* in g/dL Less than1818 3536 54 Greater than 54 CanineFelineLess than1818 2526 38 Greater than 38 UPC ratioCanineNonproteinuric < Borderline proteinuric Proteinuric > < Borderline proteinuric Proteinuric > blood pressure in mm HgSubstage based on blood pressureNormotensive <140 Prehypertensive 140 159 Hypertensive 160 179 Severely hypertensive >_180 Stage based on stable creatinineStage based on stable SDMAS ubstage based on proteinuria Note.
5 In the case of staging discrepancy between creatinine and SDMA, consider patient muscle mass and retesting both in 2 4 weeks. If values are persistently discordant, consider assigning the patient to the higher 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 treatment recommendationsUse nephrotoxic drugs with cautionCorrect prerenal and postrenal abnormalitiesFresh water available at all times Monitor trends in creatinine and SDMA to document stability or progression Investigate for and treat underlying Disease and/or complicationsTreat hypertension if systolic blood pressure persistently >160 or evidence of end-organ damageTreat persistent proteinuria with renal therapeutic diet and medication (UPC > in dogs.)
6 UPC > in cats)Keep phosphorus < mg/dL (< mmol/L) If required, use renal therapeutic diet plus phosphate binderSame as Stage 1 Renal therapeutic dietTreat hypokalemia in catsSame as Stage 2 Keep phosphorus < mg/dL (< mmol/L)Treat metabolic acidosisConsider treatment of anemia Treat vomiting, inappetence, and nauseaIncreased enteral or subcutaneous fluids may be required to maintain hydrationConsider calcitriol therapy in dogsSame as Stage 3 Keep phosphorus < mg/dL (< mmol/L)Consider feeding tube for nutritional and hydration support and ease of medicatingStep 3: Treat CKDSee for more detailed staging, therapeutic, and management guidelines.