Transcription of Drug Design: Functional groups / Pharmacological Activity
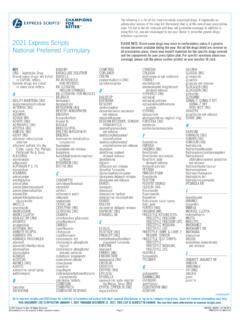
1 Drug Design: Functional groups / Pharmacological ActivityStructure - Mechanism of action (Interaction with target)Structure - Physiochemical properties (Bioavailability etc) Acid / base properties Water solubility Partition coefficient (Crystal structure) StereochemistryADMEA bsorbtion. Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion(ADMET, ADMEtox)Structure - Mechanism of actionNOOOHca. 5 Acetylcholin (Neurotransmittor)NOOH2 NCarbacholinNNHNNMeHOOA cetylcholin AgonistsNicotinePilocarpineProtonated av phys. pH (pH )Acetylcholin AntagonistsNOOOHA tropinOONOHC yclopentolatMeOOHOOOHOMeNHMeNMeMeTubocur arinCNSE ffektor celleReseptorSynapseAcetylkolinNoradrena linDet somatiske nervesystemDet autonome nervesystemCNSCNSDet sympatiskenervesystemDet parasympatiskenervesystemganglionStructu re - Mechanism of actionSAR: Structure Activity RelationshipsAcetylcholine agonists: Small N-quartenary antagonists: Larger N-quartenary (1905)NHNL idocaine/Xylocaine(1946)OAcid labile esterHydrophilicAminogroup(can be protonated)Spacer-Cn-X-X: -CO2- -CONH- -NHCO-Lipophilic(Aryl)Active compound identifiedTarget?
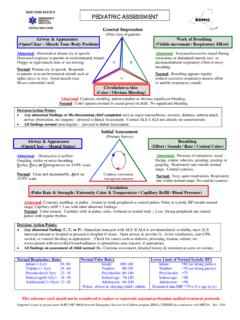
2 Target identifiedLigand?Structure - Physiochemical properties Acid / base properties Water solubility Partition coefficient (Crystal structure) StereochemistryHuman body: ca 75% waterpH blood ca (physiolog. pH)pH stomach 1 - duodenum ca. 4pH urine ca. 6 Identification of acidic / basic Functional groupspKa determines degree of ionization different places in the bodyNOOOHca. 5 Acetylcholin (Neurotransmittor)Acetylcholin AntagonistsPossible atropine analogs?OONOHC yclopentolatOONOHOONOHOONOHOC yclopentolate - tertiary amine, pKa ca. 10 [acid form][base form]At pH = + loglog[acid form][base form]= [acid form][base form]= 398; acid formOONOHH= active formOONOHH acid form + H20 OONOH baseform+ H3 OpKa = pH + log[acid form][base form]Henderson HasselbachpH=pKa; [acid]= [base]pH<pKa; acid form dominatespH>pKa; basic form dominatesAntibacterial sulfonamidesOld compoundNH2 SOOH2 NAcid form - neutralLow watersol.
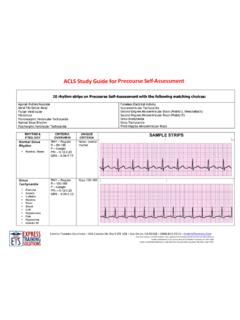
3 - crystals - Kidney damage[acid form][base form]At pH 6 (urine) = 6 + log[acid form][base form] 25000 Modern compoundArSOOHNS ulfametoksasol pKa H+ArSOONArSOONNONONONOArSOONNOAt pH 6 (urine)[acid form][base form] 1base form, ionic, water - Physiochemical properties Acid / base properties Water solubility Partition coefficient (Crystal structure) StereochemistryIonisation -permanent charge -acid / base propertiesHydrogen bondsIon - dipole bondsHNHRHA cidic form of aminesHOH - + +ROOB asic form of carboxylic acid(carboxylate)HOH + + -Intramoleculare interact. reduce water intramolec between weak organic acids and weak organic bases does not dissolve well in waterThe more H-bonds possible - the more water H-BondsOAldehyde / ketoneHHOHOH2 H-BondsRR'OEsterHHOHOH3 H-BondsRORHOHP rimary amine3 H-BondsRNHHOOHOHHHHHS econdary amine2 H-BondsRNR'HOHOHHHS econdary amine1 H-BondsRNR'R''HOHP rediction of water solubility - EmpiricalWater solubilization of Functional groupsFunctional groupMonofunctional 6 carbons3 4 carbonsPhenol6 73 4 Ether4 52 Aldehyde4 52 Ketone5 62 Amine6 73 Carboxylic acid5 63 Ester63 Amide62 - 3Ex.
4 Monofuctional - pentanol/hexanol are solubileCharge: 1 charge - 20-30 CNTerbinafineAntifungal agent21 C-atom, tertiary amine solubilize 6 - 7 C atomsInsolubile (neutral form)Corresponding acid (cationic) solubile(solubile: >10 mg/mL)Water solubilization of Functional groupsFunctional groupMonofunctional 6 carbons3 4 carbonsPhenol6 73 4 Ether4 52 Aldehyde4 52 Ketone5 62 Amine6 73 Carboxylic acid5 63 Ester63 Amide62 - 3Ex. polyfunctional : 1 charge - 20-30 COONHOHB etaxololBetablokker18 C-atomerEther: 2 Ether: 2 Alchohol: 3-4 Amine 2 Tot: 9 - 10(not solubile)logPExperimental: MlogP or logPmeasP: Partition coefficient between n-octanol and waterFragment -valueC (aliphatic+ + + + (carboxyl) (amide) (hydroxyl, ether) (amine) (aliphat.))
5 (aromat.) x C aliphat: + : + x O: : + (SciFinder): -value: hydrophilic - lipophilic valuelogP Rt (HPLC, TLC reverse phase)Structure - Physiochemical properties Acid / base properties Water solubility Partition coefficient (Crystal structure) StereochemistryCalcd: ClogPAbsorbtion of Bioactive CompoundsAbsorbtion from GI tractStomachpH 1-3 DuodenumpH 5-7 JejunumIleumpH 7- 8 Small intestine+ digestive enzymesDrugGI-tractBloodMembraneAcidic / Enzymatic break downOften rate limitingBinding to biomoleculesMost drugs: Passive diffusionStomachpH 1 - 3 BloodLipophilic MembraneR-HR-HR-CO2HR-CO2HR-NH3 Amount un ionized drugpKapHpKa = pH + log[acid form][base form]Henderson HasselbachLow lipophilicity unionized form - low absorbtionlogP - P: Partition coefficient between n-octanol and water Water phase - extracellular fluidLipophilic phase - cell membraneCrossing the membraneHigh proteinPassive transport / diffusionRate Conc.
6 Absortion site (1. order kinetics)% Drug absorbed lipophilicitySize of moleculeCertain ionic compounds may go thru as ion-pairActive transport / Carrier mediated transport Less common Structural recemblanse with for instance nutritional compound Transport against conc. gradient Mechanism saturated at high conc. Competition for carrier molecules, compounds with structural resemblanceEnergyThe Lipinski "Rule of Five" states that compounds are likely to have good absorption and permeation in biological systems and are more likely to be successful drug candidates if they meet the following criteria:five or fewer hydrogen-bond donors ten (2 x 5) or fewer hydrogen-bond acceptors molecular weight less than or equal to 500calculated logP less than or equal to 5*Compound classes that are substrates for biological transporters are exceptions to the too polarNot too bigNot too hydrophobicBiomolecules (reseptors, enzymes): AsymmetricEnantiomers may behave differently.
7 Absorbtion (membrane selectivity) Metabolism Binding to other reseptors than target (loss, side effects) Binding to target reseptorStructure - Physiochemical properties Acid / base properties Water solubility Partition coefficient (Crystal structure) StereochemistryABCDDrugBiomolecular targetDesired responceDBCANo desired resonceSide effects??Restricted rotation - optically active rotamersPP(R)-(+)-BINAPPP(S)-(-)-BINAPII INH2 OCO2H*Chiral C-atomChiral axis (restrict. tot.)4 stereoisomersX-ray contrast agent Screening/Design/Serendipity/Natural products Lead compound Structure Optimisation Actual DrugRefinement of lead structure: Determining pharmacophore Functional group modificationPharmacophore: The part of the molecule that contains the Functional groups that actually binds to the reseptorMorfinOOHNOHNOOP etidineNOOD extropropoxypheneNNNNOClLead compoundNNNNArXYZRel high activityNNNNORR CH2 PhNNNNRR=H, alkylInactiveNNNNArPharmacophore?
8 ?Azapurines??Deazapurines??NNNArR??NNAr? ?Antimycobacterials??XArImprovement of lead by Functional group modification Activity Toxicity Bioavailability MetabolismIsosters: Functional groups that results in approx. the same propertiesSteric and electronic similaritiesSbp 81 oCbp 84 oC-CH=CH- and -S- are isostersNbp 116 oC-C= and -N= not isosters(at least with respect to bp)Bioisosters: Functional groups that results in approx. the same biological propertiesClassical bioisostersSteric and electronic similaritiesMonovalent-F, -H-OH, -NH2-H, -F, -OH, -NH2, -CH3-SH, -OH-Cl, -Br, -CF3 Divalent-C=S, -C=O, -C=NH, -C=C-Trivalente-CH=, -N=TetravalenteRingsNSONCNNNNOX-X p% Inhib g/mLMIC( g/mL) > > > > > > > : electronic effects; >0 electron withdrawing, <0 electron donating : Lipophilicity, >0 increased lipophil.
9 Rel to HNon-classical bioisostersNot strong steric or electronic similaritiesNNNNHOONNNNNHNOHO2 CAngiotensin II antagonists(Hypertention)NNHpKa karboksylsyrer