Transcription of e.g. older Oxfordshire HbA1c is 75mmol/mol (9%) …
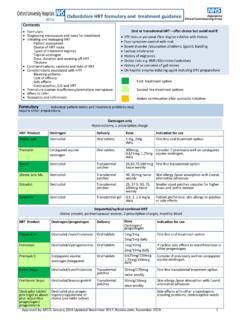
1 Oxfordshire Clinical Commissioning Group Insulin initiation and Adjustment in Type 2 Diabetes Primary Care Guideline This updated guideline is for use by clinicians who have professional competence in insulin initiation and adjustment attendance at Oxfordshire Primary Care Diabetes Courses on insulin initiation and intensification (page 5). Insulin initiation should be considered in line with NICE CG87, for patients with type 2 diabetes, whose individual targets for glycaemic control are not achieved on optimum oral treatments. NICE recommendations are to intensify treatment for patients with an HbA1c concentration greater than 58mmol/mol ( ); consider a range of options to achieve this. Prioritise insulin initiation for those patients at highest risk especially of microvascular complications over time, especially for younger patients with the highest HbA1c concentrations.
2 Individual treatment targets should be agreed but ideally aim for HbA1c of 53mmol/mol (7%), avoiding hypoglycaemia. Patient to receive structured diabetes education (Box B). Consider referral to Enhanced Diabetes Dietetic Service for weight management, via eRS. (tel 01865 264933). Re-evaluate oral therapy. Provide and update patient's self-management plan. 1. Initial 3. introduction to Intensification insulin for all 2. Intensification from from regime 1. patients and regime 1 but Basal Plus not or 2 and active ideal long term required and reasonably lifestyle where regime in less active but fairly habitual flexibility is active lifestyle lifestyle OR consider if important and older HbA1c is 75mmol/mol (9%) manageable patients or greater. Regime 1. Regime 2. Regime 3. overleaf overleaf overleaf Basal Plus Background Twice daily Insuman Basal or insulin human mixture Humulin I.
3 Insuman Basal or Humulin M3 or PLUS Insuman R or Humulin I Insuman Comb 25 Humulin S. Regular review and education Patient self-management titration plans and education checklist examples are available. Box A Individual targets for blood Box B Structured education glucose should be agreed. Structured patient education should be provided in line with NICE (TA 60). See page 5 for competencies Local adult education courses, Diabetes2gether and Diabetes4ward, are available. Version 2, November 2015. Approved by Area Prescribing Committee Oxfordshire (APCO) November 2015. Review date November 2017 1. Regime 1. Background human insulin regime Insuman Basal or Humulin I. In combination with oral hypoglycaemic agents (see Box D for use of insulin analogues). Start evening dose after individual assessment (see Box A). Up to 10 units usually given in the evening/at bedtime.
4 Monitor blood glucose daily Self test 3-4 times a week fasting glucose before breakfast AND 2-3 times a week once a day at different times AND 4 point profile every 5-6 weeks Adjust dose: Increase by 2 units (or 10%) every 3 days to achieve pre-breakfast target. If all readings are greater than 10mmol/l increase by 4 units (or up to a maximum of 20%). If pre-evening meal blood glucose remains high OR HbA1c remains high despite good fasting blood glucose Start morning dose Up to 10 units If fail to achieve individual targets or encountering Monitor and titrate: as above to achieve challenges pre-evening meal target Consult competent*. colleagues NB If blood glucose is less than 4 Consider intensification mmol/l on 2 consecutive days to regimes 2 or 3. reduce by 2 units or 10% Contact CDS**. Box C. Hypoglycaemia: It is essential that the person starting insulin and their immediate family know what symptoms to expect, how to reduce the risks of hypos and how to treat them.
5 Hypoglycaemia is defined as blood glucose below 4 mmol/l. Too many hypos can lead to loss of hypo awareness. Examples of patient hypoglycaemia leaflets are available. Sick day rules: Patients require education on sick day rules'. *see page 5 for competencies **Community Diabetes Service, tel: 01869 604089, email: Version 2, November 2015. Approved by Area Prescribing Committee Oxfordshire (APCO) November 2015. Review date November 2017 2. Regime 2. Twice daily human mixture regime Humulin M3 or Insuman Comb 25 (see Box D for use of insulin analogues) Insulin to be injected 20 minutes before food. Stop sulfonylureas. Starting dose after individual Intensification from Regime 1. assessment (see Box A): Split total daily units into 2 appropriate Up to 10 units before breakfast doses; pre-breakfast and pre-evening Up to 8 units before evening meal meal*.
6 Monitor blood glucose twice daily: breakfast and one other appropriate time. Adjust one dose at a time to achieve Pre-breakfast target: increase evening insulin by 2 units (or 10%) every 3 days Pre-evening target: increase morning insulin by 2 units (or 10%) every 3 days If all readings are greater than 12 mmol/l increase insulin by 4 units (or up to a maximum of 20%). NB If blood If fail to achieve individual targets or glucose is less encountering challenges than 4 mmol/l Consult competent* colleagues decrease nearest Consider changing pre-mix preceding insulin proportions dose by 2 units or Consider intensification to regime 3. 10% Contact CDS**. Box C. Hypoglycaemia: It is essential that the person starting insulin and their immediate family know what symptoms to expect, how to reduce the risks of hypos and how to treat them.
7 Hypoglycaemia is defined as blood glucose below 4 mmol/l. Too many hypos can lead to loss of hypo awareness. Examples of patient hypoglycaemia leaflets are available. Sick day rules: Patients require education on sick day rules'. *see page 5 for competencies **Community Diabetes Service, tel: 01869 604089, email: Version 2, November 2015. Approved by Area Prescribing Committee Oxfordshire (APCO) November 2015. Review date November 2017 3. Regime 3. Basal Plus; Insuman Basal or Humulin I as background AND Insuman R or Humulin S as pre-meal bolus Stop sulfonylureas. (see Box D for use of insulin analogues). Patient on Regime 1 Patient on Regime 2. requiring intensification requiring intensification Starting bolus dose: 2 6 units Split total daily units*. 30minutes before meals. Adjust basal insulin if appropriate Monitor blood glucose up to four times a day Adjust bolus dose Post meal target: increase/decrease by 2 units NB If blood glucose is less than 4.
8 Mmol/l on 2 If fail to achieve individual targets or consecutive days encountering challenges reduce by 2 units or Consult competent* colleagues 10% Contact CDS**. Box C. Hypoglycaemia: It is essential that the person starting insulin and their immediate family know what symptoms to expect, how to reduce the risks of hypos and how to treat them. Hypoglycaemia is defined as blood glucose below 4 mmol/l. Too many hypos can lead to loss of hypo awareness. Examples of patient hypoglycaemia leaflets are available. Sick day rules: Patients require education on sick day rules'. *see page 5 for competencies **Community Diabetes Service, tel: 01869 604089, email: Version 2, November 2015. Approved by Area Prescribing Committee Oxfordshire (APCO) November 2015. Review date November 2017 4. Health Care Professional Education and Competence Primary Care Insulin initiation and Intensification courses: 11th Feb 2016 (more to be confirmed).
9 Contact the Community Diabetes Service, Tel 01869 604089 or email HCP initiating and adjusting insulin should have competences as described by Skills for Health; improving blood glucose control, assessment of need to start insulin, starting insulin, continuing insulin and minimising hypoglycaemia risks. Insulin Safety Safety recommendations should be followed regarding prescribing, storage, patient and health professional education, and patient leaflet and insulin passport. Extra care is required for high strength and biosimilar insulins. Prescribing Insulins must always be prescribed clearly by brand, including presentation, strength and correct device with no abbreviations. Also prescribe Pen needles (GlucoRx Finepoint). Blood glucose monitoring strips (GlucoRx Nexus or similar cost-effective strip, < 10 per 50).
10 Lancets sterile, single use. Sharps bin Sharpsafe or Sharpsguard 1litre Re-usable pen if needed Re-usable pens are expected to last between 2 to 3 years. Refer to table on page 7 for compatible pen choice. A clinical tool and patient information leaflet are available to support appropriate self-monitoring of blood glucose. Appropriate insulins for prescribing are listed on page 7. The first line choices are highlighted. Patients may be considered for switching to first line options if current treatment requires review to improve glycaemic control, compliance or other patient/clinical factors. Needle length and injection technique The Forum for Injection Technique states that there is no clinical reason for recommending needles longer than 8mm in adults. The majority of patients will require 4, 5 or 6 mm needles.