Transcription of Eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval
1 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDE. Eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval NSW Referral Guide SEPTEMBER 2019. Stroke Network Agency for Clinical Innovation 67 Albert Avenue Chatswood NSW 2067. PO Box 699 Chatswood NSW 2057. T +61 2 9464 4666 | F +61 2 9464 4728. E | Produced by: Stroke Network Further copies of this publication can be obtained from the Agency for Clinical Innovation website at Disclaimer: Content within this publication was accurate at the time of publication. This work is copyright. It may be reproduced in whole or part for study or training purposes subject to the inclusion of an acknowledgment of the source.
2 It may not be reproduced for commercial usage or sale. Reproduction for purposes other than those indicated above, requires written permission from the Agency for Clinical Innovation. Preferred citation: NSW Agency for Clinical Innovation. Eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval : NSW Referral Guide. Sydney: ACI; 2019. SHPN (ACI) 190421. ISBN 978-1-76081-224-9. Version: V1; ACI_0191 [08/19] Date amended: September 2019. Cover image credit: Trim: ACI/D19/1844. State of New South Wales (NSW Agency for Clinical Innovation) 2019. Creative Commons Attribution No derivatives licence. Eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval NSW Referral Guide September 2019.
3 Contents endovascular clot retrieval referral pathway at a glance 1. Patient selection endovascular clot retrieval 2. Introduction 3. Section 1: Patient journey perspective 5. The stroke patient journey key stages 5. Section 2: Clinical considerations for hyper-acute stroke management 7. Pre-morbid function 7. Anterior and posterior circulation selection 8. Brain imaging for suspected stroke 8. Section 3: Requirements for the delivery of hyper-acute stroke care 9. Minimum clinical requirements to support assessment for ECR Eligibility 9. References 11. Key supporting documents 12. Appendices 13.
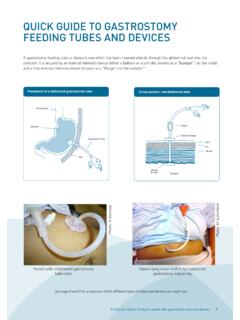
4 Appendix 1: modified rankin Scale (mRS) 14. Appendix 2: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale 15. Appendix 3: NSW Ambulance Stroke Process sheet 19. Glossary 21. Acknowledgements 22. Agency for Clinical Innovation . Eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval NSW Referral Guide September 2019. endovascular clot retrieval referral pathway at a glance Triage Category 2 This guide is intended to support EMERGENCY Neurological Assessment and evidence based patient selection. It does con rm time of onset not replace clinical decision making for appropriate patient selection. YES Patients not meeting the inclusion criteria but may benefit from intervention may be accepted for ECR after consultation with Direct to CT scanner a capable centre.
5 IMAGING. Noncontrast head CT rules out intracerebral haemorrhage Local intracerebral CT angiography + CT perfusion NO haemorrhage (essential for cases that are 6-24 hrs pathway post onset). YES. EITHER < 6 hours Blocked vessel Local ischaemic OR 6-24 hours NO TO BOTH. stroke pathway Blocked vessel with signi cant Tissue plasminogen activator can commence if eligible volume of salvageable tissue YES TO EITHER. Consider tissue Independent premorbid NO plasminogen function modi ed rankin Scale activator if eligible, (mRS) 2. NEUROLOGICAL local stroke pathway ASSESSMENT. YES. Stroke Physician review on-site or via Telestroke ABC Neuro exam history Neurological de cit present Consider tissue NIH Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS) plasminogen NO.
6 5 activator if eligible, local stroke pathway YES. REFERRAL endovascular clot retrieval referral Agency for Clinical Innovation 1. Eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval NSW Referral Guide September 2019. Patient selection for endovascular clot retrieval Inclusion criteria This guide is intended to support evidence based 1. Ischaemic stroke with confirmed large vessel patient selection. It does not replace clinical occlusion on computed tomography angiography decision making for appropriate patient selection. (C TA). internal carotid artery Patients not meeting the above inclusion criteria middle cerebral artery but may benefit from intervention may be accepted M1 segment for ECR after consultation with a capable centre proximal M2 for example: basilar artery.
7 Patients with low NIHSS but large vessel occlusion may fluctuate clinically and should be 2. Previously independent with minimal reviewed by an ECR capable centre stroke team. assistance. Able to manage own affairs, should consider independence in driving, shopping and Patients with improving symptoms but large banking. High prospect of meaningful functional volume of tissue at risk from large vessel recovery based on premorbid function occlusion. Such patients may be at significant modified rankin scale (mRS) 2. (Appendix 1). risk of subsequent deterioration (the risk of deterioration and significant disability in such 3.)
8 Patients with a significantly disabling patients with initially rapidly improving neurological deficit (National Institutes of symptoms is probably significantly greater than Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) 5, or major the peri-procedural risk). aphasia).(Appendix 2). Patients with a higher mRS due to mobility but 4. Time window: Ability to start endovascular independent with good quality of life. mRs = 3. clot retrieval (ECR) within 24 hours from Any distal occlusion site outside of the inclusion symptom onset. criteria with a clinically significant deficit. Under six hours procedure can be started with blocked vessel and broad clinical and A local process should review all patients who are imaging criteria.
9 Treated outside of the guidelines. A regular formal cross-district review meeting is recommended to Between 6 to 24 hours blocked vessel with regularly discuss these patients. significant volume of salvageable tissue on computed tomography perfusion (CTP) as per national and international guidelines. Basilar artery revascularisation may be considered up to 48 hours. 5. Intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). should be administered to all eligible patients in parallel with CTA, perfusion acquisition and ECR decision making to avoid delays. Agency for Clinical Innovation 2. Eligibility for endovascular clot retrieval NSW Referral Guide September 2019.
10 Introduction Over the past two decades, treatment for ischaemic ECR is not appropriate for all stroke patients and stroke has been transformed from a management it is not a procedure that can be performed in approach that primarily provided supportive care, non-specialist settings. This document provides to one that actively seeks to restore blood flow to information and advice on ECR services from the brain, reducing mortality and disability. three perspectives. Intravenous thrombolysis, the use of clot busting A patient perspective describing the drugs, was first trialled in the late 1990s and patient journey in stroke and placing ECR in represented a step change in stroke care.