Transcription of GBD PROFILE: PAPUA NEW GUINEA - Institute for Health ...
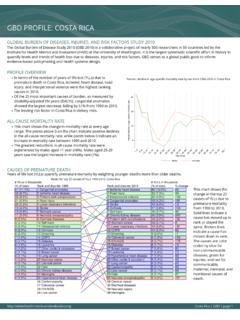
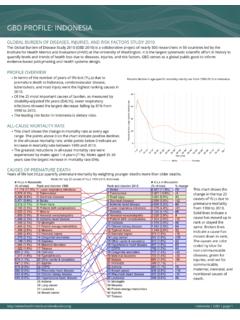
1 global burden OF DISEASES, INJURIES, AND RISK FACTORS STUDY 2010 The global burden of disease Study 2010 (GBD 2010) is a collaborative project of nearly 500 researchers in 50 countries led by theInstitute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington. It is the largest systematic scientific effort in history toquantify levels and trends of Health loss due to diseases, injuries, and risk factors. GBD serves as a global public good to informevidence-based policymaking and Health systems OVERVIEWlIn terms of the number of years of life lost (YLLs) due topremature death in PAPUA New GUINEA , lower respiratoryinfections, diabetes mellitus, and diarrheal diseases were thehighest ranking causes in the 25 most important causes of burden , as measured bydisability-adjusted life years (DALYs)
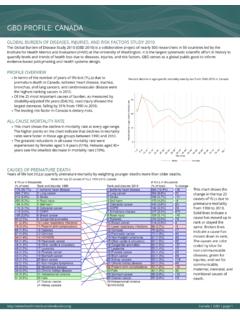
2 , protein-energymalnutrition showed the largest decrease, falling by 42% from1990 to leading risk factor in PAPUA New GUINEA is high fastingplasma MORTALITY RATElThis chart shows the decline in mortality rate at every age higher points on the chart indicate that declines in mortalityrates were faster in those age groups between 1990 and greatest reductions in all-cause mortality rate wereexperienced by females aged 1-4 years (64%). Females aged 80+years saw the smallest decrease in mortality rate (4%).Percent decline in age-specific mortality rate by sex from 1990-2010 in PAPUA NewGuineaCAUSES OF PREMATURE DEATHY ears of life lost (YLLs) quantify premature mortality by weighting younger deaths more than older chart shows thechange in the top 25causes of YLLs due topremature mortalityfrom 1990 to lines indicate acause has moved up inrank or stayed thesame.
3 Broken linesindicate a cause hasmoved down in causes are colorcoded by blue fornon-communicablediseases, green forinjuries, and red forcommunicable,maternal, neonatal, andnutritional causes profile : PAPUA NEW New GUINEA | GBD | page 1015304560 Percent decline in age specific mortality rate 1 45 910 1415 1920 2425 2930 3435 3940 4445 4950 5455 5960 6465 6970 7475 7980+Age groupMalesFemales# YLLs in thousands(% of total)Rank and disorder 1990 Rank and disorder 2010# YLLs in thousands(% of total)% change32 ( )17 Acute hepatitis A42 ( )11 Asthma24 ( )21 Chronic kidney disease32 ( )15 Cirrhosis35 ( )13 Congenital anomalies48 ( )9 Diabetes180 ( )2 Diarrheal diseases24 ( )23 Drowning28 Drowning27 ( )19 Fire26 Fire31 ( )16 Ischemic heart disease20 ( )24 Leukemia554 ( )1 Lower respiratory infections167 ( )3 Malaria50 ( )10 Maternal disorders81 ( )
4 4 Meningitis39 ( )12 Neonatal encephalopathy36 ( )14 Neonatal sepsis72 ( )8 Poisonings74 ( )7 Preterm birth complications86 ( )5 Protein-energy malnutrition25 ( )20 Road injury30 ( )22 Stroke21 ( )25 Syphilis41 Syphilis33 ( )18 Tetanus47 Tetanus82 ( )6 Tuberculosis30 ( )24 Acute hepatitis A-752 ( )13 Asthma2726 ( )25 COPD3526 COPD66 ( )9 Chronic kidney disease16560 ( )10 Cirrhosis8450 ( )14 Congenital anomalies40130 ( )2 Diabetes171116 ( )3 Diarrheal diseases-3881 ( )5 HIV/AIDS2,79160 HIV/AIDS57 ( )11 Ischemic heart disease8632 ( )22 Leukemia5644 ( )21 Liver cancer16031 Liver cancer449 ( )1 Lower respiratory infections-21108 ( )8 Malaria-3651 ( )16 Maternal disorders-177 ( )7 Meningitis-644 ( )19 Neonatal encephalopathy1343 ( )20 Neonatal sepsis2156 ( )12 Poisonings-2179 ( )6 Preterm birth complications851 ( )15 Protein-energy malnutrition-4344 ( )18 Road injury7331 ( )23 Self-harm7029 Self-harm52 ( )17 Stroke7393 ( )
5 4 Tuberculosis11 Ranks for top 25 causes of YLLs 1990-2010, PAPUA New GuineaCCCommuni cabl e, maternal , neonatal , and nutri ti onalCCNon-communi cabl eCCInj uri es020,00040,00060,00080,000 YLDs0 6 days7 27 days28 364 days1 4 years5 9 years10 14 years15 19 years20 24 years25 29 years30 34 years35 39 years40 44 years45 49 years50 54 years55 59 years60 64 years65 69 years70 74 years75 79 years80+ yearsWar & disasterIntentional injuriesUnintentional injuriesTransport injuriesOther non communicableMusculoskeletal disordersDiabetes/urogen/blood/endoMenta l & behavioral disordersNeurological disordersDigestive diseasesCirrhosisChronic respiratory diseasesCardio & circulatory diseasesCancerOther communicableNutritional deficienciesNeonatal disordersMaternal disordersNTD & malariaDiarrhea/LRI/other infectiousHIV/AIDS & tuberculosisLOWER RESPIRATORY
6 INFECTIONSDIABETESTUBERCULOSISDIARRHEAL DISEASESMALARIAHIV/AIDSPRETERM BIRTH COMPLICATIONSMENINGITISASTHMACHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASEMAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDERISCHEMIC HEART DISEASECIRRHOSISROAD INJURYLOW BACK PAINCONGENITAL ANOMALIESPOISONINGSCOPDMATERNAL DISORDERSIRON-DEFICIENCY ANEMIAPROTEIN-ENERGY MALNUTRITIONNEONATAL ENCEPHALOPATHYSTROKENEONATAL SEPSISLIVER CANCER12 34 56 789 10 11 12 13 14 15 161718 19 202122 23 24 25-200-150-100-50050100150200 New GUINEA | GBD | page 2 Percent change 1990-2010 YEARS LIVED WITH DISABILITY (YLDs)Years lived with disability (YLDs) are estimated by weighting the prevalence of different conditions based on severity.
7 The top five leadingcauses of YLDs in PAPUA New GUINEA are major depressive disorder, low back pain, iron-deficiency anemia, tuberculosis, and size of the coloredportion in each barrepresents the number ofYLDs attributable to eachcause. The height of each barshows which age groups hadthe most YLDs in 2010. Thecauses are aggregated. Forexample, musculoskeletaldisorders include low backpain and neck New GUINEA YLDs by cause and age 2010 DISABILITY-ADJUSTED LIFE YEARS (DALYs)Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) quantify both premature mortality (YLLs) and disability (YLDs) within a population. In PAPUA NewGuinea, the top three causes of DALYs in 2010 were lower respiratory infections, diabetes mellitus, and tuberculosis.
8 Two causes thatappeared in the 10 leading causes of DALYs in 2010 and not 1990 were HIV/AIDS and chronic kidney top 25 causes of DALY sare ranked from left to rightin order of the number ofDALYs they contributed in2010. Bars going up show thepercent by which DALYs haveincreased since 1990. Barsgoing down show the percentby which DALYs havedecreased. Globally,non-communicable diseasesand injuries are generally onthe rise, while communicable,maternal, neonatal, andnutritional causes of DALY sare generally on the causes of DALYs and percent change 1990 to 2010 for PAPUA New New GUINEA | GBD | page 3 101234567% DALYs attributable to risk factorsUnimproved waterHigh total cholesterolSanitationIron deficiencyOccupational risksPhysical inactivityHigh blood pressureSuboptimal breastfeedingAlcohol useChildhood underweightDietary risksHigh body mass indexHousehold air pollutionSmokingHigh fasting plasma glucoseWar & disasterIntentional injuriesUnintentional injuriesTransport injuriesOther non communicableMusculoskeletal disordersDiabetes/urogen/blood/endoMenta l & behavioral disordersNeurological disordersDigestive
9 DiseasesCirrhosisChronic respiratory diseasesCardio & circulatory diseasesCancerOther communicableNutritional deficienciesNeonatal disordersMaternal disordersNTD & malariaDiarrhea/LRI/other infectiousHIV/AIDS & tuberculosisAge-standardized death rates, YLL rates, YLD rates, and life expectancy at birth and Health -adjusted life expectancy at birth for 1990 and 2010, both sexes combinedCountryAge-standardized death rate(per 100,000)Age-standardized YLL rate(per 100,000)Age-standardized YLD rate(per 100,000)Life expectancy at birthHealth-adjusted lifeexpectancy at birth19902010199020101990201019902010199 02010 Rate Rank Rate Rank Rate Rank Rate Rank Rate Rank Rate Rank LE Rank LE Rank HALE Rank HALE RankMoldova1,000 49125 26,698 3 22,769 3 11,653 1 11,362 25,101 2 16,911 1 12,459 3 11,835 23,225 1 18,413 2 12,827 5 12,639 ,12079826 41,231 6 33,518 8 12,877 6 12,323 ,361 12 1,0689 47,661 10 32,041 7 15,157 13 14,318 14 29,477 4 26,063 4 12,381 2 12.
10 150 Islands1,707 14 1,510 14 47,851 11 40,489 12 13,5209 12,482 106212 New GUINEA 1,990 15 1,700 15 64,195 15 49,553 15 14,891 12 13,793 9 15 15 15 13 Djibouti1,18081,129 11 45,440 8 38,655 11 13,493 8 14,182 ,532 13 1,094 10 56,031 13 34,746 9 13,297 7 12,323 13 ,047 59997 33,446 5 30,037 6 12,606 4 12,336 ,11067993 41,735 7 28,295 5 15,584 15 14,781 15 ,296 10 1,277 13 51,072 12 49,262 13 14,617 11 13,891 11 12 15 Nigeria1,343 11 1,159 12 60,604 14 49,276 14 14,273 10 13, 14 Mauritania1,24491,031 8 45,799 9 36,003 10 15,248 14 14,30713 10 RISK FACTORSO verall, the three risk factors that account for the most disease burden in PAPUA New GUINEA are high fasting plasma glucose, tobaccosmoking, and household air pollution from solid fuels.