Transcription of Good Ventilation is Essential for a ... - WSU Energy Program
1 good Ventilation is Essential for a Healthy and Efficient building Our Mission To advance environmental and economic well-being by providing unmatched Energy services, products, education and information based on world-class research. About Us Our staff of over 100 people ( Energy engineers, Energy specialists, technical experts, software developers, Energy research librarians, and more). work out of our Olympia, Spokane and satellite offices. Operating similar to a consulting firm, the WSU Energy Program is a self-supported department within the University. Most of us spend about half of fresh air and distributes it Within WSU our waking hours in office or to people throughout the We are part of the College school buildings. It follows that building . of Agricultural, Human and the quality of air in these buildings Natural Resource Sciences. We can affect the health, productivity The information presented here is report directly to the WSU Vice and comfort of the occupants.
2 Designed to: President of Agriculture and Measures that protect air quality, Extension. Help facility managers un- such as adequate Ventilation , derstand the importance should be taken seriously. Contact of continually monitoring Rich Prill a building 's Ventilation building Science & Indoor Indoor air quality (IAQ) is rate to ensure adequate Environmental Quality determined by: IAQ is maintained as the Specialist Concentrations of con- number of people in each 509-477-6701 taminants in the air, and area of a building (or zone) changes through- Website: How effectively the out the day. Ventilation system brings in appropriate volumes of Explain how much out- side air (OSA) should be Symptoms of Ventilation problems brought into a building . Stuffy or stale conditions Noticeable odors from outdoors or other areas in Describe symptoms of the building Ventilation problems.
3 Very low or high relative humidity, dampness or window Discuss the importance of condensation assessing pressure differ- Pressure imbalances between the inside and outside, entials (inside to outside which can make it difficult to open or close doors and zone to zone). Noise or drafts from air delivery vents Provide guidance for Spillage or back-drafting of combustion equipment controlling indoor air Dust and dirt accumulation pollutants. Reports of comfort or health issues Unusually high utility costs See the companion factsheet, Measuring Carbon Dioxide Inside As workers and students come If too little OSA is brought Buildings Why is it Important? * and go throughout the day, in, the CO2 concentrations will to learn how carbon dioxide the air quality in the building rise throughout the day, as will (CO2) levels in a building can changes. People continually concentrations of pollutants be used to monitor IAQ and generate CO2, so CO2 levels can and odors.
4 These impacts are for guidance about obtaining build up throughout the day exaggerated in buildings where accurate CO2 measurements. unless OSA is brought in through the HVAC system re-circulates 70. the HVAC system to dilute the to 80 percent of the indoor air. Bringing fresh CO2. As the CO2 builds up, so can other potentially serious indoor air If just enough OSA is brought air inside pollutants. in, the levels of CO2, pollutants, Scientific studies clearly show that odors and moisture will more people who work in buildings Bringing in OSA that has been likely be within appropriate where adequate fresh air is filtered and heated or cooled to guidelines and the HVAC system provided and properly delivered the appropriate temperature is will not have to work harder to the building occupants are Essential to control odors, reduce than necessary to maintain a more productive than those exposure to indoor air pollutants, comfortable temperature.
5 Who work in buildings that are and purge moisture and contami- inadequately ventilated. nants in a building . However, Ventilation is not a cure-all for IAQ issues. Strong good Ventilation is Essential How much OSA pollutant sources in the building , for a comfortable, healthy and including occupant-created productive indoor environment, is too much? pollutants and those emitted so a top priority for facility It is important to bring only from carpets and other building managers should be to under- enough OSA into the building furnishings, can overwhelm stand and tune the building 's as needed to maintain healthy typical fresh air exchange rates, so heating, Ventilation and air conditions. To accomplish this, a practical IAQ policy that works conditioning (HVAC) system so it the facility manager needs to to limit pollutant sources should meets the needs of the building monitor and control the building 's also be implemented.
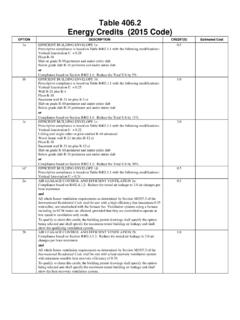
6 Occupants throughout the day. Ventilation rate. If too much OSA is brought in, Recommended The Ventilation rate is the flow of outside air (OSA) into the HVAC system will have to Ventilation rates a building per unit of time. work harder to heat or cool the building codes and guidance, OSA to the appropriate temper- such as American Society of ature, resulting in wasted Energy Heating Refrigerating and Air * Available on the Washington State University Energy Program website: and excessive utility payments. Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE). Standard , define Ventilation rates and dictate that adequate Supply and return systems Ventilation should be provided are both at ceiling level. ASHRAE recommends that either naturally or mechanically. HVAC system does not indoor CO2 levels not exceed Ventilation recommendations are circulate the air down to the outdoor concentration.
7 Continually evolving; it is a good the occupant level during which is about 380 ppm by idea to check codes that apply to heating mode, such as more than about 650 ppm. your building . with a variable air volume or multi-zone system. Meeting and maintaining Ventilation rates can be deter- mined and maintained through prescribed air exchange Prescriptive methods can be rates can be difficult without prescriptive or controlled methods. difficult to employ because they: practical and effective OSA. The prescriptive Ventilation Require direct measure- monitoring strategies. method requires specific volumes ments of the OSA flow of OSA in cubic feet per minute rates per balancing of OSA per person (cfm/p) plus standards, which can be difficult, time-consuming The controlled Ventilation a prescribed volume of OSA per and subject to significant method recommends using square foot of the space (cfm/.)
8 Errors. sensors to control the Ventilation sqft). These two values are rate. The most common system combined to determine the total Assume full occupancy of this type is Demand Controlled Ventilation rate for the space at all the time, which may Ventilation (DCV). full occupancy. result in overventilation. For this reason, the pre- DCV systems use CO2 sensors to The prescriptive method also scriptive method is likely continually adjust the Ventilation requires up to 20 percent more not as Energy efficient as rate to meet the actual occupant OSA if the: the controlled method. loads and activity levels in the building . DCV systems are especially useful for spaces that Relationship between measured CO2 and experience variable occupancy Ventilation rate per person rates, such as conference rooms, The CO2 values in this table are approximate.* classrooms, auditoriums, dining rooms and open workspaces.
9 CO2 (ppm) Outside Air ( Ventilation rate) As more people occupy a space, they exhale more CO2. When the 2,400 5 cfm/p Unacceptable DCV system senses that CO2 levels 1,400 10 cfm/p Poor are rising, it increases the volume 1,000 15 cfm/p Classrooms of OSA that is brought in through the HVAC system so the CO2 level 800 20 cfm/p Offices is controlled to a pre-set value. 600 25 cfm/p ~ 380 <------> Outdoors According to the Department of Energy 's Federal Energy The figures given assume: Management Program , DCV. A constant number of occupants over an extended systems have been demonstrated period, to save 5 to 27 percent of HVAC. Occupants are sedentary adults, Energy usage in a typical office The Ventilation rate is constant (although occupied environment (see Resources #16. spaces are rarely at full occupancy for more than a and 17). The cost to implement fraction of an hour), and this feature is minimal and usually The OSA CO2 concentration is about 380 ppm.
10 Results in a very good payback. The return on investment for * Check code requirements for your building ; codes and guidance continually evolve. larger HVAC systems can be less than one year. The greater the Ventilation rate (volume of OSA per person . cfm/p), the more the CO2 will be diluted. To maintain an optimal CO2 level in classrooms and offices (approximately 1,035 ppm of CO2), the Ventilation system should be set to bring in OSA at a rate of 15 to 20 cfm/p. Assessing pressure differentials Proper air pressure analysis is also important for maintaining an Energy efficient and adequately ventilated space. Pressure differentials are created by the HVAC system and/or air Make sure air filters are not clogged so the Ventilation system can work properly. Photo: Rich Prill leakage through the building envelope. When differential Many indoor air pollutants are Test ducts to determine pressure in one part of a building generated by materials used in if they are meeting is greater than in an adjacent area, the building itself, such as carpets, design tightness criteria.