Transcription of How to Meet ISO 17025 Requirements for Method ... - AOAC
1 PURPOSEThe purpose of the guide is to define the activities that arerequired to fulfill Method verification based on analyticalmethod performance 17025 :2005 section states: ..The laboratory shall confirm that it can properly operatestandard methods before introducing the tests orcalibrations. If the standard Method changes, theconfirmation shall be repeated. In this guide, to confirm is the same as to that a laboratory can adequately operate astandard Method requires that the laboratory provide objectiveevidence the performance parameters specified in the testmethod have been met with the matrices to which the Method is being applied. Most often, the critical Requirements are theaccuracy and the precision (generally accepted as repeatability and reproducibility) which are reflected in the measurementuncertainty.
2 The objective evidence is the accuracy andprecision obtained from actual lab AND APPROACHThe scope of this guide encompasses aoac OfficialMethodsSM, EPA, FDA and FSIS official methods, and NADA methods and methods used in Microbiological, Food andPharmaceutical industries may have differing terminology whendescribing categories of analytical methods and analyticalparameters. This guide attempts to use the terminologycommonly used by industries may have specific Requirements . Aparticular federal agency or client may have very specificcriteria for Method verification. In this case the client s oragency s Requirements would override those in this guide. The analytical test methods are grouped according to thecategory of Method based on its purpose.
3 The lab can identifythe category of test Method it is verifying and find thecorresponding parameters that need to be a Method is verified, the laboratory is required todemonstrate that it can achieve certain specific performancecharacteristics/parameters established during the validationstudy. The validation study must contain all pertinentperformance characteristics. Certain performancecharacteristics, such as linearity, will not vary from lab to laband do not need to be verified. Other parameters, such asrepeatability, are specific to the lab performing the Method andneed to be verified. Thus, the performance characteristics thatneed to be verified are a subset of the performancecharacteristics included in a Method guide treats chemical test methods and microbiologymethods METHODSC ategories of Chemical MethodsChemical analytical methods fulfill many differentpurposes, from quantifying an analyte at a low concentration toidentifying a material.
4 With such a variety of methods, it islogical that different test methods require varying ease of discussion, the test methods can be divided into sixdifferent categories based on their purpose. The categories are listed below. For each of the categories of test methods onlyrelevant performance characteristics need to be included in amethod verification. The approach of this guide is to list allperformance characteristics needed for verification, andexplain the reason for verifying the performance six categories of chemical analytical methods are:1. Confirmation of Identity, a Method that ensures amaterial is what it purports to be or confirms the detection of the target Quantifying an analyte at a low Determining if an analyte is present above or below aspecified, low concentration (often called a Limit Test).
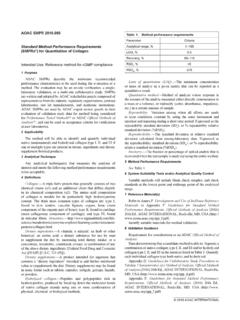
5 Thespecified concentration is close to the Quantifying an analyte at a high Determining if an analyte is present above or below aspecified, high concentration (often called a Limit Test).The specified concentration is substantially above Qualitative the activities needed for Method verification are asubset of those needed for validation, the requiredperformance characteristics for validation will be presentedfirst. The performance characteristics needed for the validationof each of six main categories of chemical test methods areidentified in Table 1. If a performance characteristic is notneeded for validation, it is not needed for verification. In Table1, Yes means the performance characteristic must beincluded for validation and No means the performancecharacteristic does not need to be included for ALACC Project1 How to Meet ISO 17025 Requirements for Method VerificationRequirements of Method Verification for the SixCategories of Chemical Test MethodsIn Tables 2 5, Yes means the performance characteristic must be included for verification and No means theperformance characteristic does not need to be included 6.
6 Qualitative Tests:Qualitative tests are used to identify a specific element orcompound (analyte) based on the response of a material to thetest. The most important characteristic of a qualitative test is itsability to reliably identify the analyte in the presence of othersubstances. This is referred to as the specificity. Method validation includes determining any cross reactivity with other known entities. The lack of cross reactivitydemonstrates the specificity of the Method . If samples areidentical to those for which the Method is intended, noverification of specificity is required. If any matrix componentsare unique to the lab s samples, the lab will need todemonstrate there is no impact on Method precision of qualitative tests is generallyexpressed as false-positive/false-negative rates and isdetermined at several concentration levels.
7 Verification of alab s ability to properly operate a qualitative Method can bedemonstrated by analyzing populations of negative andpositive fortified samples. For example, for each differentsample matrix, duplicate samples are analyzed at three levels are blanks (no analyte), low level (near the2007 ALACC Project2 How to Meet ISO 17025 Requirements for Method VerificationTable 1. Categories of Chemical Test Methods: Since the activities needed for Method verification are a subset of those needed forvalidation, the required performance characteristics for validation are presented in this tablePerformanceCharacteristicPerformanc e Characteristics Included in a ValidationIdentification 1 Analyte at LowConcentrationQuantitative 2 Analyte at LowConcentrationLimit Test 3 Analyte at HighConcentrationQuantitative 4 Analyte at HighConcentrationLimit Test 5 Qualitative 6 AccuracyNoYesNoYesYesNoPrecisionNoYesNoY esYesNoSpecificityYesYesYesYesYesYesLODN oYesYesYes/NoNoNoLOQNoYesNoYes/NoNoNoRug gednessNoYesNoYesNoNoLinearity/RangeNoYe sNoYesNoNoTable 2.)
8 Category 1: Confirmation of Identity A Method that ensures a material is what it purports to be or confirms the detection ofthe target analytePerformance CharacteristicVerificationVerification ActivitiesReason for VerificationSpecificityNo if the lab s samples are identicalto those in the standard Method and if any differences in instrumentation donot impact the samples have the same matrix,the specificity which is based onbasic principles, will not be principles are chemicalreactions, reaction of Ag with Clto create a if the lab s samples differ fromthose in the standard as those required forvalidation. Yes if differences betweeninstruments could affect specificity. The activity need only deal with theunique aspect s of the lab s samplesor can be impacted bydifferences in range of the Method ) and high level (near the high end ofthe range).
9 Standard additions can be used to obtain thecorrect concentration levels. Rates comparable to those statedin the validated Method demonstrate the labs ability to operatethe MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY IN METHODVERIFICATION OF CHEMICAL TESTSThe estimate of measurement uncertainty (MU) for ameasurand is the indicator of precision, and the MU is one ofthe components that can be used to verify a lab can perform the Method there is no validation data available, the MU may bethe only parameter that can be compared to the specification toensure the Method comparison of a lab s performance (bias andprecision) can be compared to those from the collaborativestudy using the approach as described in ISO TechnicalSpecification ISO/TS 21748, Guidance for the use ofrepeatability, reproducibility and trueness estimates inmeasurement uncertainty guidance, including examples of using theapproach suggested in ISO/TS 21748 will be posted on theAOAC ALACC Project3 How to Meet ISO 17025 Requirements for Method VerificationTable 3.
10 Category 2: Analyte at Low Concentration, QuantitativePerformance CharacteristicVerificationVerification ActivityReason for VerificationAccuracyYesIf the concentration range for which the Method isvalidated is narrow (<1 order of magnitude),analyze one reference material/standard/spike atone concentration. Otherwise, demonstrateaccuracy at each concentration level (low, middleand high) by analyzing one referencematerial/standard/spike at each a narrow concentration range, the accuracyand precision should not vary, therefore, thedemonstration at one concentration is a wide concentration range, the accuracyand precision can vary, thus they need to beverified at the different concentration the repeatability test once. If the methodcovers a concentration range >1 order ofmagnitude, then the repeatability test must includelow, middle and high a narrow concentration range, the accuracyand precision should not vary, therefore, thedemonstration at one concentration is a wide concentration range, the accuracyand precision can vary, thus they need to beverified at the different concentration precision, between analysts, ishandled by making sure the analysts are trainedand can adequately perform the Specificity in General RequirementsSee Specificity in General RequirementsLODYesRun a sample close to LODLOD is very likely to be matrix and instrumentspecificLOQYesRun a sample close to LOQLOQ is very likely to be matrix and instrumentspecificTable 4.