Transcription of Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
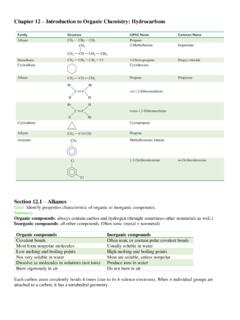
1 Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedIntroduction to Organic Chemistry: HydrocarbonsChapter 12 Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Organic Alkanes with Properties of Cis-Trans Aromatic OrganicCompoundsIdentify properties characteristic of Organic or inorganic chemistryis the study of carbon Alwayscontainscarbonandhydrogenatoms May also contain other nonmetals such as oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, or a halogen. Organiccompoundsarefoundin: Gasoline, medicines, shampoos, plastics, and perfumes Carbohydrates,fats,andproteinsFunctional Groups Organic compounds are organized by their functional groups(groups of atoms bonded in a specific way). Compoundsthat contain the same functional groups have similar physical and chemical properties.
2 Theidentificationoffunctionalgroupsallow sustoclassifyorganiccompoundsaccordingto theirstructure, to name compounds within each family, and to predict their chemical 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedOrganic vs. Inorganic In chemistry , molecules are classified as Organic or Inorganic. Inorganic compoundsare (quite expansively) anything that is not Organic . OrganicandInorganiccompoundshavedifferen tproperties. Organic compounds: Havelowmeltingandboilingpoints. Are flammable and undergo combustion. Arenotsolubleinwater. Inorganiccompounds Many inorganic compounds have high melting and boiling points. Inorganiccompoundsthatareionicareusually solubleinwater, 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedCopyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedPracticeIdentify each characteristic as most typical of compounds that are inorganic or Organic .
3 A. It has a high melting It is not soluble in It contains carbon and hydrogen It has the formula It burns easily in 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedRepresentations of Carbon Compounds Hydrocarbons are Organic compounds that consist of only carbon and hydrogen. Inorganicmolecules,everycarbonatomhas four bonds. Inmethane(CH4),thecarbonatom forms an octet by sharing its four valence electrons with four hydrogen :a)space-fillingmodel,b)ball-and-stick model, c) wedge-dash model, d) expanded structural formula, and e) condensed structural formulaCopyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedRepresentations of Carbon Compounds In ethane (C2H6), each tetrahedral carbon forms three covalent bonds to hydrogen and one to the other carbon. Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
4 All Rights ReservedAlkanesAlkanes are formed by a continuous chain of carbon atoms. are named using the IUPAC(International Union of Pure and Applied chemistry ) system. have names that end in ane. use Greek prefixes to name carbon chains with five or more carbon 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedStudy CheckIn the butane molecule (C4H10), predict the shape around each carbon 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Organic Alkanes with Properties of Cis-Trans Aromatic CompoundsCopyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights -AlkanesWrite the IUPAC names and draw the condensed or line-angle structural formulas for alkanes and 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedAlkanes More than 90% of the compounds in the world are Organic compounds.
5 Thelargernumberofcarboncompoundsis possible because the covalent bonds between carbon atoms (C-C) is very strong, allowing carbon atoms to form long, stable 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedAlkanes The alkanesare a type of hydrocarbon in which the carbon atoms are connected only by single bonds. Alkanesareformedbyacontinuouschainofcarb onatoms. The names of alkanes and in ane. SuchnamesarepartoftheIUPAC system(InternationalUnion of Pure and Applied chemistry ) used by chemists to name Organic chemistry . Alkanesmadeofcarbonchains are named based on how many carbons make up the chain. One of the most common uses of alkanes is as fuels. Methane,propane,octane, and hexane are all alkanes used as 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedIUPAC Names of AlkanesCopyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
6 All Rights ReservedLine-Angle Structural FormulasA simplified structure of Organic molecules is called the line-angle structural formula. shows a zigzag line in which carbon atoms are represented as the ends of each line and as atoms at the end are bonded to three hydrogen atoms. in the middle are bonded to two hydrogen 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedCondensed formula and Line-angle formula PentaneCopyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedCondensed formula and Line-angle formula Draw the condensed structural formula and name the molecule:Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedGuide to Drawing Structural Formulas for AlkanesStep 1: Draw the carbon 2: Draw the expanded structural formula by adding the hydrogen atoms using single bonds to each of the carbon 3: Draw the condensed structural formula by combining the H atoms with each C 4: Draw the line-angle structural formula as a zigzag line in which the ends and corners represent C 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
7 All Rights ReservedDrawing Expanded, Condensed, and Line-Angle Structural Formulas (1 of 3)Draw the expanded, condensed, and line-angle structural formula for 1: Draw the carbon chain. A molecule of pentane has five carbon atoms in a continuous 2:Draw the expanded structural formula by adding the hydrogen atoms, using single bonds to each of the carbon 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedDrawing Expanded, Condensed, and Line-Angle Structural Formulas (2 of 3)Draw the expanded, condensed, and line-angle structural formula for 3: Draw the condensed structural formula by combining the H atoms with each C 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedDrawing Expanded, Condensed, and Line-Angle Structural Formulas (3 of 3)Draw the expanded, condensed, and line-angle structural formula for 4: Draw the line-angle structural formula as a zigzag line in which the ends and corners represent C 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
8 All Rights ReservedConformations of Alkanes Single bonds can spin and rotate. Thusdifferentarrangements,known as conformations, occur during the rotation about a single bond. 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedStructural Formulas: C4H10 As butane (C4H10) rotates, sometimes theline up in front of each other, and at other times they are opposite each other. Butane can be drawn using a variety of two-dimensional condensed structural formulas:Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedStructural Formulas: C4H10 Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedCycloalkanesHydrocarbons can also form into circles or rings called: cycloalkanes have two fewer hydrogen atoms than the open chain form. are named by using the prefix cyclobefore the name of the alkane chain with the same number of carbon 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
9 All Rights ReservedFormulas of Formulas of Some Common CycloalkanesNameBLANKBLANKBLANKC yclopropaneCyclobutaneCyclopentaneCycloh exaneBall-and-Stick ModelBLANKBLANKBLANKT hree carbons single-bonded to each other in a triangular pattern, with each carbon single-bonded to 2 ball and stick model shows four carbons single-bonded to each other in a square pattern, with each carbon single-bonded to 2 ball and stick model shows five carbons single-bonded to each other in a pentagonal pattern, with each carbon single-bonded to 2 ball and stick model shows six carbons single-bonded to each other in a hexagonal pattern, with each carbon single-bonded to 2 Structural FormulaBLANKBLANKBLANKThe condensed structural formula shows a triangular ring of three C H 2 condensed structural formula shows a square ring of four C H 2 condensed structural formula shows a pentagonal ring of five C H 2 condensed structural formula shows a hexagonal ring of six C H 2 Structural FormulaBLANKBLANKBLANKThe line-angle structural formula is a line-angle structural formula shows a line-angle structural formula shows a pentagon.
10 The line-angle structural formula shows a 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedStudy CheckGive the IUPAC name for each of the following compounds: 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedStudy CheckName the following alkanes: A. Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Organic Alkanes with Properties of Cis-Trans Aromatic CompoundsCopyright 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Alkanes and SubstituentsWrite the IUPAC names for alkanes with substituents and draw their condensed and line-angle structural 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights ReservedStructural IsomersStructural isomers have the same molecular formula with a different arrangement of atoms. have the same number of atoms bonded in a different (C4H10) has two structural isomers: a straight chain and a branched 2016, 2013, 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.