Transcription of Introduction to the Finite Element Method
1 ME280 AIntroduction to the Finite Element MethodPanayiotis PapadopoulosDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringUniversity of California, Berkeley2015 editionCopyrightc 2015 by Panayiotis PapadopoulosContents1 Introduction to the Finite Element Historical perspective: the origins of the Finite Element Method .. Introductory remarks on the concept of discretization .. Structural analogue substitution Method .. Finite difference Method .. Finite Element Method .. Particle methods .. Classifications of partial differential equations .. Suggestions for further reading ..112 Mathematical Sets, linear function spaces, operators and functionals .. Continuity and differentiability .. Norms, inner products, and completeness .. Norms .. Inner products .. Banach and Hilbert spaces .. Linear operators and bilinear forms in Hilbert spaces .. Background on variational calculus .. Exercises.
2 Suggestions for further reading ..343 methods of Weighted Introduction .. Galerkin methods .. Collocation methods .. Point-collocation Method .. Subdomain-collocation Method .. Least-squares methods .. Composite methods .. An interpretation of Finite difference methods .. Exercises .. Suggestions for further reading ..694 Variational Introduction to variational principles .. Variational forms and variational principles .. Rayleigh-Ritz Method .. Exercises .. Suggestions for further reading ..845 Construction of Finite Element Introduction .. Finite Element spaces .. Completeness property .. Basic Finite Element shapes in one, two and three dimensions .. One dimension .. Two dimensions .. Three dimensions .. Higher dimensions .. Polynomial Element interpolation functions .. Interpolations in one dimension .. Interpolations in two dimensions.
3 Interpolations in three dimensions .. The concept of isoparametric mapping .. Exercises ..1336 Computer Implementation of Finite Element Numerical integration of Element matrices .. Assembly of global Element arrays .. Algebraic equation solving in Finite Element methods .. Finite Element modeling: mesh design and generation .. Symmetry .. Optimal node numbering .. Computer program organization .. Suggestions for further reading .. Exercises ..1537 Elliptic Differential The Laplace equation in two dimensions .. Linear elastostatics .. A Galerkin approximation to the weak form .. On the order of numerical integration .. The patch test .. Best approximation property of the Finite Element Method .. Error sources and estimates .. Application to incompressible elastostatics and Stokes flow .. Suggestions for further reading .. Exercises ..1878 Parabolic Differential Standard semi-discretization methods .
4 Stability of classical time integrators .. Weighted-residual interpretation of classical time integrators.. Exercises ..2059 Hyperbolic Differential The one-dimensional convection-diffusion equation .. Linear elastodynamics .. Exercises ..219iiiivList of Galerkin .. R. Courant .. Clough (left) and J. Argyris (right) .. infinite degree-of-freedom system.. simple example of the structural analogue Method .. Finite difference Method in one dimension.. one-dimensional Finite Element approximation.. one-dimensional kernel functionWlassociated with a particle Method .. depiction of a setV.. of a set that does not form a linear space.. between two sets.. function of classC0(0,2) .. between two points in the classical Euclidean sense.. The neighborhoodNr(u) of a pointuinV.. A continuous piecewise linear function and its derivatives .. linear operator mappingUtoV.. bilinear form onU V.
5 Functional exhibiting a minimum, maximum or saddle point atu=u .. open and connected domain with smooth boundary written as the unionof boundary regions i.. domain of the Laplace-Poisson equation with Dirichlet boundary uand Neumann boundary q.. Linear and quadratic approximations of the solution to the boundary-valueproblem in .. point-collocation Method .. point collocation Method in a square domain.. subdomain-collocation Method .. interpolation functions used for region(xl x2,xl+ x2]in theweighted-residual interpretation of the Finite difference Method .. interpolation functions used for region[0,x1+ x2]in the weighted-residual interpretation of the Finite difference Method .. functions for a Finite Element approximationof a one-dimensionaltwo-cell domain.. linear interpolations functions in one dimension.. of exact and approximate solutions.. interpretation of Fourier coefficients.. Finite Element mesh.)
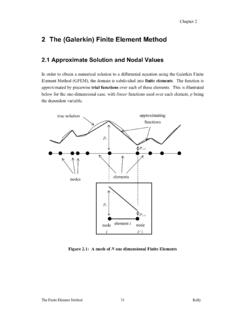
6 Finite Element -based interpolation function.. Element vs. exact domain.. in the enforcement of Dirichlet boundary conditions due to the differencebetween the exact and the Finite Element domain.. potential violation of the integrability (compatibility) requirement.. functionuand its approximationuhin the domain( x, x+h) .. triangle.. Element domains in one dimension.. Element domains in two dimensions.. Element domains in three dimensions.. Element interpolation in one dimension.. Finite Element mesh with piecewise linear interpolation.. quadratic Element interpolations in one dimension.. quadratic Element interpolations in one dimension.. interpolation functions in one dimension.. 3-node triangular Element .. triangular elements (left: 6-node Element , right: 10-node Element ) transitional 4-node triangular Element .. coordinates in a triangular domain.. rectangular Element .. functionNe1fora=b= 1(a hyperbolic paraboloid).
7 Members of the serendipity family of rectangular elements .. s triangle for two-dimensional serendipity elements (before accountingfor any interior nodes).. members of the Lagrangian family of rectangular elements .. s triangle for two-dimensional Lagrangian elements .. general quadrilateral Finite Element domain.. Finite elements made of two or four joined triangular simple potential 3- or 4-node triangular Element for the casep= 2(u, u s, u ndofs at nodes1,2,3and, possibly,udof at node4).. of violation of the integrability requirement for the 9- or 10-doftriangle for the casep= 2 .. 12-dof triangular Element for the casep= 2(u, u s, u ndofs at nodes1,2,3and u nat nodes4,5,6).. triangular Element for the casep= 2(u, u s, u ndofs at nodes1,2,3and u nat nodes4,5,6).. 4-node tetrahedral Element .. 10-node tetrahedral Element .. 6- and 15-node pentahedral elements .. 8-node hexahedral Element .. 20- and 27-node hexahedral elements .
8 Of a parametric mapping from e to e.. 4-node isoparametric quadrilateral.. interpretation of one-to-one isoparametric mapping in the 4-nodequadrilateral.. and non-convex 4-node quadrilateral Element domains.. between area elements in the natural and physical domain.. 6-node triangle and 8-node quadrilateral.. 8-node hexahedral Element .. Gauss quadrature rules forq1,q2 1(left),q1,q2 3(cen-ter), andq1,q2 5(right).. rules in triangular domains forq 1(left),q 2(center), andq 3(right). At left, the integration point is located at the barycenter ofthe triangle and the weight isw1= 1; at center, the integration points arelocated at the mid-edges and the weights arew1=w2=w3= 1/3; at right,one integration point is located at the barycenter and has weightw1= 27/48,while the other three are at points with coordinates( , , ),( , , ),and( , , ), with associated weightsw2=w3=w4= 25 .. Element mesh depicting global node and Element numbering, as well asglobal degree of freedom assignments (both degrees of freedom are fixed at node1 and the second degree of freedom is fixed at node 7).
9 Of a typical Finite Element stiffness matrix ( denotes a non-zero entryor a zero entry having at least one non-zero entry below and above it in thecolumn to which it belongs).. examples of symmetries in the domains of differential equations(corresponding symmetries in the boundary conditions, loading, and equationsthemselves are assumed).. possible ways of node numbering in a Finite Element mesh.. domain of the linear elastostatics problem.. modes for the 4-node quadrilateral with1 1 Gaussian modes for the 8-node quadrilateral with2 2 Gaussian of the patch test (Form A).. of the patch test (Form B).. of the patch test (Form C).. interpretation of the best approximation property as a closest-pointprojection fromutoUhin the sense of the energy norm.. of volumetric locking in plane strain when using 3-node triangularelements.. simplest convergent planar Element for incompressibleelastostatics/Stokes flow.
10 Depiction of semi-discretization (left) and space-time discretization(right).. of( )in the domain(tn,t] .. factorras a function of tfor forward Euler, backward Eulerand the exact solution of the homogeneous counterpart of( ) .. of the solution( )of the steady-state convection-diffusion equation forL= 1, u= 1and P eclet numbersPe= .. Element discretization for the one-dimensional convection-diffusion equa-tion.. Element solution for the one-dimensional convection-diffusion equationforc= 0 .. Element solution for the one-dimensional convection-diffusion equationforc >0 .. schematic depiction of the upwind Petrov-Galerkin methodfor the convection-diffusion equation (continuous line: Bubnov-Galerkin, broken line: Petrov-Galerkin)..212ixIntroductionThis is a set of notes written as part of teaching ME280A, a first-year graduate course onthe Finite Element Method , in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the Universityof California, , 2015xChapter 1 Introduction to the Finite Historical perspective: the origins of the Finite el-ement methodThe Finite Element Method constitutes a general tool for the numerical solution of partialdifferential equations in engineering and applied science.)