Transcription of Issued December 20, 1990 32 - ThreeBond
1 Three Bond Technical News Issued December 20, 1990 32 . Curing Agents for Epoxy Resin Introduction _____ . Epoxy resin was discovered in 1938 by with various curing agents. Pierre Castan, a chemist in Switzerland. As of This issue describes the types of curing 1989, 137,000 tons of epoxy resin had been agents for epoxy resin and their characteristics produced in Japan, and epoxy resin has been comparing to Three Bond products. used in a wide range of fields, such as paints, The epoxy resin compositions of Three Bond electricity, civil engineering, and bonds. This is currently on the market are the Three Bond because epoxy resin has excellent bonding 2000 Series (base agent for epoxy resin), the property, and also after curing, it has excellent Three Bond 2100 Series (curing agent for properties on mechanical strength, chemical epoxy resin), and the Three Bond 2200 Series resistance, electrical insulation.
2 In addition, (one-part thermal cure epoxy compound epoxy resin is able to have various different resins). properties as it is combined and cured together Contents Introduction .. 1. 1. 2. 1-1. Aliphatic amine .. 2. 1-2. Aromatic amine .. 4. 1-3. Modified amines .. 4. 2. Polyamide resin .. 5. 3. Tertiary and secondary amines .. 5. 4. Imidazoles .. 6. 5. Polymercaptan curing 6. 5-1. Liquid polymercaptan .. 6. 5-2. Polysulfide resin .. 6. 6. 8. 7. Latent curing agents .. 8. 7-1. Boron trifluoride-amine 8. 7-2. 8. 7-3. Organic acid hydrazide .. 9. 8. Photo- and ultraviolet-curing 9. Conclusion .. 10. 1. 1. Amines _____ . Amine compounds are classified into primary, agent for epoxy resin ant able to cure at room secondary, and tertiary amines, in which one, two, temperature.
3 The cured resin has excellent and three hydrogen molecule(s) of ammonia (NH3) properties, and its heat resistance is 100 C. have been substituted for hydrocarbon, respectively. Aromatic amine has been developed to achieve Amines are called monoamine, diamine, tri-amine, greater heat resistance and chemical resistance than or polyamine according to the number of amines in those of aliphatic amine. one molecule. Amines are classified into aliphatic, The curing of epoxy resin by amine curing agents alicyclic (Three Bond 2106), and aromatic amines is expressed by the formula shown below; the active according to the types of hydrocarbons involved, hydrogen in primary amine reacts with an epoxy and the all are important curing agents for epoxy group to form secondary amine, and the secondary resin.
4 Amine reacts with an epoxy group to cure. Then, the Aliphatic amine (Three Bond 2103) is curing resultant tertiary amine polymerizes epoxy groups. In general, curing agent must have more than temperature, but inner epoxy type such as three active hydrogen atoms and two amino groups cyclohexene oxide and epoxidized polybutadiene is in a molecule so that the cured resin becomes hardly cured. Glycidyl-ester type cures quite faster crosslinked polymer, according to the reaction of than glycidyl-ether type. Diglycidyl ether of the above equation. The loading of the curing agent bisphenol A (DGEBA), which is a condensation in epoxy resin becomes optimal when the number product of bisphenol A and epichlorohydrin, is of moles in epoxy groups is equal to that of active primarily cured by aliphatic amines at room hydrogen.
5 Temperature, but is slowly cured by aromatic amines The curing speed of individual amines depends and requires thermal curing. on the type and loading of amine, and the type of Table 1 shows the properties and performances of epoxy resin. The most commonly used representative polyamines used as curing agents for glycidyl-ether type resins easily cure at room epoxy resin. 1-1. Aliphatic amine (Three Bond 2103) room temperature are improved. The heat-deformation Aliphatic amine, which rapidly reacts with epoxy temperature (HDT) of cured object of DGEBA is 120 C. resin, is a representative room-temperature curing agent. at the highest. However, it generates a large quantity of heat and has a Resins that have been cured using aliphatic amines short pot life (usable time).
6 Loading of amines are strong, and are excellent in bonding properties. They containing no tertiary amine is made at the exact or very have resistance to alkalis and some inorganic acids, and closed amount that is said in stoichiometry, and use have good resistance to water and solvents, but they are amount of amines containing tertiary amine is made less not so good to many organic solvents. Aliphatic amine than that. If latter curing is performed at high irritates the skin and possesses toxicity. Although those temperature, properties of curing agents that cure at that have high molecular weight and low vapor pressure are less toxic, good cares for handling are required.
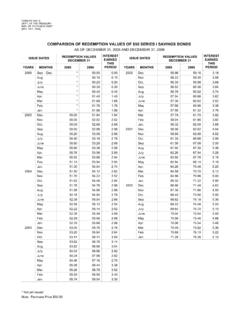
7 2. Table 1. Properties and performance of amine based curing agents Active - Loading Specific Curing conditions Heat Applicability Viscosity hydrogen amount to Pot life Name of curing gravity deformation Class Subclass Appearance cps equivale liquid (100 g) Temperature Time Remark agent (25 C) nt (amine epoxy (g/ml). (batch). temperature Bonding Lamination Casting Paint (20 C) ( C) (minutes) ( C). value) resin (phr). 5 - 10. Transparent 20 Normal to 30 minutes Diethylenetriamine (DTA). liquid Standard minutes 100 to 4 days 115. value: 8. 6 - 12. Triethylenetetramine Transparent 20 to 30 Normal to 30 minutes (TTA) liquid Standard minutes 100 to 4 days 115. value: 9.
8 7 - 14. Tetraethylenepentamine Transparent 30 to 40 Normal to 30 minutes (TEPA) liquid Standard minutes 100 to 7 days 115. Chain value: 12. aliphatic polyamine Diproprenediamine Transparent 20 to 30 Normal to 30 minutes (DPDA) liquid 12 - 15. minutes 200 to 7 days 110. 4-8. Bonding = 8, Diethylaminopropylamine Transparent 1 to 4 65 - 115 1 - 4 hours (DEAPA) liquid Casting hours 85. = 4, Lamination =6. Transparent 1000 - 30 Normal to 30 minutes AMINE 248. liquid 3000 35 minutes 100 to 4 days 92 Rare Hexamethylenediamine N-aminoethylpiperazine Transparent 43 20 - 22 20 to 30 Normal to 30 minutes (N-AEP) liquid minutes 200 to 3 days 103. Transparent 31 - 33 31 - 33 80+150 2 hours + 2.
9 Lamiron C-260. liquid 60 hours 150. Transparent 15 - 20 120 Normal 7 days Araldit HY-964. liquid 70 minutes Transparent 80 - 130 30 minutes Menthane diamine (MDA) 22 6 hours to 2 hours 158. Aliphatic liquid 130 - 200 2+3 hours Alicyclic polyamine polyamine Isophoronediamine Transparent 41 24 1 hour 80+150 4+1 hours 149. (IPDA) liquid Transparent 17 - 21 30 Normal to 2 hours to 7. S Cure 211 47. liquid minutes 70 days Transparent 12 - 16 40 Normal to 2 hours to 7. S cure 212 48. liquid minutes 70 days m p Wandamin HM 53 30 60+150 3+2 hours 150. 40 C. BAC m-xylenediamine Crystalline 16 - 18 20 Normal to 1 hour to 7. (m-XDA) liquid minutes 60 days 115. 20 Normal to 1 hour to 7.
10 Sho-amine X Liquid 68 33 - 34 16 - 18 minutes 60 days 113 Xylylenediamine (50 C). Viscous 2000 40 Normal to 1 hour to 7. Aliphatic Amine black liquid - 30 - 60 minutes 60 days Xylylenediamine trimer aromatic 6000. amine 6000. Viscous 40 Normal to 1 hour to 7. Sho-amine black liquid - 25 - 35 minutes 60 days 116 Xylylenediamine trimer 10000. 80 Normal to 1 hour to 7. Sho-amine N Liquid 5 (690) 25 minutes 60 days 81 Xylylenediamine derivative Normal to 1 hour to 7. Sho-amine 1001 Liquid 27 60 days 73 Xylylenediamine derivative Normal to 1 hour to 7. Sho-amine 1010 Liquid 27. 60 days 70 Xylylenediamine derivative Metaphenylene diamine mp62. Solid 34 14 - 16 6 hours 80+150 2+4 hours 150.