Transcription of Major Ions in Water - National Hydrology Project
1 World Bank & Government of The Netherlands fundedTraining module # WQ - 28 Major ions in WaterNew Delhi, September 1999 CSMRS Building, 4th Floor, Olof Palme Marg, Hauz Khas,New Delhi 11 00 16 IndiaTel: 68 61 681 / 84 Fax: (+ 91 11) 68 61 685E-Mail: Consultants BV & DELFT HYDRAULICS withHALCROW, TAHAL, CES, ORG & JPSH ydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 1 Table of text32 Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 21. Module contextThis module presents the Major inorganic ions which are significant to Water in which prior training is required to complete this module successfully and otheravailable, related modules in this category are listed in the table designing a training course, the relationship between this module and the otherswould be maintained by keeping them close together in the syllabus and placing them in alogical sequence.
2 The actual selection of the topics and the depth of training would, ofcourse, depend on the training needs of the participants, their knowledge level and skillsperformance upon the start of the titleCodeObjectives1. Basic Water quality conceptsWQ - 01 Discuss the common Water qualityparameters List important Water quality issues2. Basic chemistry conceptsaWQ - 02 Convert units from one to another Discuss the basic concepts ofquantitative chemistry Report analytical results with thecorrect number of significant Basic Aquatic ChemistryConceptsWQ - 24 Calculate ion concentrations fromionisation constantsa - prerequisiteHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 32. Module profileTitle: Major ions in WaterTarget group:HIS function(s): Q2, Q3, Q5, Q6, Q7, Q8 Duration:1 session of 60 minObjectives:After the training the participants will Know the Major ions in Water and their sources Understand the significance of Major ion concentrationsKey concepts: Sources of Major ions in Water Ion balance Hardness, SAR Health effectsTraining methods:Lecture and discussionTraining toolsRequired:Board, flipchart, OHS,Handouts:As provided in this module,Further readingand references: Water Quality Monitoring, ed.
3 J. Bartram and R. Balance Water Quality Assessment, ed. D. Chapman, E&FN SPON,LondonHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 43. Session planNoActivitiesTimeTools1 Preparations2 Introduction: Introduce the session Suggest a number of common aquatic ions andask the participants whether these would be majoror secondary constituents of groundwater Following discussion use overhead to confirm 10 min OHS 3 Introduction to Major ions Discuss Major cations and anions Talk about how ions become dissolved in Water Discuss the sources of Major ions Show how it is possible to characterise watersgraphically 10 min OHS 4 Individual Major ions Discuss calcium and magnesium and what theirpresence means in Water Discuss the concept of hardness and what thatmeans in terms of Water quality List other Major ions and ask the participants whattheir presence in Water indicates Follow up by showing overhead of various majorions Discuss sar, %Na, RSC and how it is used toassess potential irrigation waters.
4 Talk about thedifference between Indian and International SARstandards. Show USDA classification 15 min OHS 5 Ion Balancing Talk about the technique of ion balancing and whyit is so useful to the chemical analyst and waterquality expert Show how ion balancing can be done and discussthe acceptability of errors15 minOHS6 Wrap up and Evaluation10 Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 54. Overhead/flipchart masterOHS format guidelinesType of textStyleSettingHeadings:OHS-TitleArial 30-36, with bottom border line (not:underline)Text:OHS-lev1 OHS-lev2 Arial 24-26, maximum two levelsCase:Sentence case. Avoid full text in :Use occasionally and in a consistent wayListings:OHS-lev1 OHS-lev1-NumberedBig for definite series of steps. Avoidroman numbers and :None, as these get lost in photocopying andsome colours do not reproduce at of a table will ease horizontal alignmentover more lines (columns)Use equation editor for advanced formattingonlyHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 6 Major ions in Water Major and Secondary Constituents of Groundwater Sources Water Characterisation Water Quality Consequences Ion Balancing Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 7 Major constituents ( to 1000 mg/L) Secondary Constituents( to mg/L) Sodium Iron Calcium Strontium Magnesium Potassium Bicarbonate Carbonate Sulphate Nitrate Chloride Fluoride Silica Boron Hydrology Project Training Module File.
5 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 8 Major Cations and Anions in Water CATIONS ANIONS Calcium (Ca2+) Bicarbonate (HCO3-)/Carbonate (CO32-) Magnesium (Mg2+) Sulphate (SO42-) Sodium (Na+) Chloride (Cl-) Potassium (K+) Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 9 Sources (1) Atmospheric Gases Dissolved by Rain and their Reactions- Oxygen- Nitrogen- Carbon dioxide- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)- Sulphur oxides (SOx) Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 10 Sources (2) Calcium Amphiboles, feldspars, gypsum, aragonite, calcite,pyroxenes, dolomite, clay minerals Magnesium Amphiboles, olivine, pyroxenes, dolomite,magnesite, clay minerals Sodium Feldspars, clays, halite, mirabilite, industrial wastes Potassium Feldspars, feldspathoids, some micas, clays Bicarbonate/Carbonate Limestone, dolomite Sulphate Oxidation of sulphide ores, gypsum, anhydrite Chloride Sedimentary rock, igneous rockHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 11 Water Characterisation (1) MgNa + KCaClSO4CO3 + HCO3 Equivalents per million-> A B D CBar Graphs for 4 different samplesHydrology Project Training Module File.
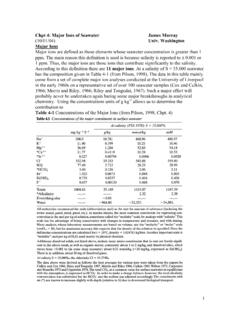
6 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 12 Water Characterisation (2) Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 13 Water Characterisation (3) Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 14 Water Quality Consequences Calcium and Magnesium- Cause hardness when combined with HCO-3, CO2-3, SO2-4 etc- Ca2+ normally below 15 mg/l- Ca2+ can be above 100 mg/l in carbonate-rich rocks- Mg2+ normally between 1 and 50 mg/l depending upon rock typeHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 15 Hardness Classification Hardness (mg/Las Ca CO3) Classification 0 - 75 Soft 75 - 150 Moderately hard 150 - 300 Hard Over 300 Very hard Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 16 Other Major ions Major ions in Water - Sodium high levels often associated with pollution- Potassium generally low (<10) in natural fresh waters- Bicarbonate normally ranges from 25 to 400 mg/l- Carbonate in fresh waters is normally dilute (<10 mg/l)- Sulphate is normally between 2 and 80 mg/l- Chloride is normally less than 40 mg/l in unpolluted waters- Nitrate is significant in some areasHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 17 Health Effects- Nitrate- Fluoride- Sodium- Potassium- ChlorideHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 18 Irrigation Water Quality (1) Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) - in milliequivalents/L ()SARNaCaMg=++++222 International SAR Standards Indian SAR Standard SAR < 3.
7 Suitable for irrigation SAR > 26 unsuitable for irrigation SAR 3 9: use may be restricted SAR > 9 unsuitable for irrigation Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 19 Irrigation Water Quality (2) Percent Sodium = Na+/ (Ca++ + Mg++ + Na+ + K+) x 100- should be less than 60 Residual Sodium CarbonateRSC = (CO3-- + HCO3-) - (Ca++ + Mg++)> not - marginal< safeHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 20 Irrigation Water Quality (3) Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 21 Major ions in Water Ion Balancing + =anionscationsanionscationserrorbalance% - concentrations in milliequivalents. Error should be < 10% for surface and ground watersHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 225.
8 Evaluation sheetsHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 23 Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 246. HandoutHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 25 Major ions in Water Major and Secondary Constituents of Groundwater Sources Water Characterisation Water Quality Consequences Ion Balancing Major constituents ( to 1000 mg/L) Secondary Constituents( to mg/L) Sodium Iron Calcium Strontium Magnesium Potassium Bicarbonate Carbonate Sulphate Nitrate Chloride Fluoride Silica BoronMajor Cations and Anions in Water CATIONS ANIONS Calcium (Ca2+) Bicarbonate (HCO3-)/ Carbonate (CO32-) Magnesium (Mg2+) Sulphate (SO42-) Sodium (Na+) Chloride (Cl-) Potassium (K+) Sources (1) Atmospheric Gases Dissolved by Rain and their Reactions- Oxygen- Nitrogen- Carbon dioxide- Nitrogen oxides (NOx)- Sulphur oxides (SOx)Sources (2)
9 Calcium Amphiboles, feldspars, gypsum, aragonite, calcite,pyroxenes, dolomite, clay minerals Magnesium Amphiboles, olivine, pyroxenes, dolomite, magnesite,clay minerals Sodium Feldspars, clays, halite, mirabilite, industrial wastes Potassium Feldspars, feldspathoids, some micas, clays Bicarbonate/Carbonate Limestone, dolomite Sulphate Oxidation of sulphide ores, gypsum, anhydrite Chloride Sedimentary rock, igneous rockHydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 26 Water Quality Consequences Calcium and Magnesium- Cause hardness when combined with HCO-3, CO2-3, SO2-4 etc- Ca2+ normally below 15 mg/l- Ca2+ can be above 100 mg/l in carbonate-rich rocks- Mg2+ normally between 1 and 50 mg/l depending upon rock typeHardness Classification Hardness (mg/L as Ca CO3) Classification 0 - 75 Soft 75 - 150 Moderately hard 150 - 300 Hard Over 300 Very hard Other Major ions Major ions in Water - Sodium high levels often associated with pollution- Potassium generally low (<10) in natural fresh waters- Bicarbonate normally ranges from 25 to 400 mg/l- Carbonate in fresh waters is normally dilute (<10 mg/l)
10 - Sulphate is normally between 2 and 80 mg/l- Chloride is normally less than 40 mg/l in unpolluted waters- Nitrate is significant in some areasHealth Effects- Nitrate- Fluoride- Sodium- Potassium- ChlorideIrrigation Water Quality (1) Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) - in milliequivalents/L ()SARNaCaMg=++++222 International SAR Standards Indian SAR Standard SAR < 3: suitable for irrigation SAR > 26 unsuitable for irrigation SAR 3 9: use may be restricted SAR > 9 unsuitable for irrigation Hydrology Project Training Module File: 28 Major ions in Version 05/11/02 Page 27 Irrigation Water Quality (2) Percent Sodium = Na+/ (Ca++ + Mg++ + Na+ + K+) x 100- should be less than 60 Residual Sodium CarbonateRSC = (CO3-- + HCO3-) - (Ca++ + Mg++)> not - marginal< safe Major ions in Water Ion Balancing + =anionscationsanionscationserrorbalance% - concentrations in milliequivalents.