Transcription of MATH 113 Section 8.1: Basic Geometry
1 Why Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionMATH 113 Section : Basic GeometryProf. Jonathan DuncanWalla Walla UniversityWinter Quarter, 2008 Why Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionOutline1 Why Study Geometry ?2 Formal Geometry3 Geometric Objects4 ConclusionWhy Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionGeometry in HistoryOur modern concept of Geometry started more than 2000 yearsago with the s AcademyTo the Greeks, what we would callmathematics was merely a tool to thestudy of Geometry . Tradition holdsthat the inscription above the door ofPlato s Academy read: Let no one ignorant of Geometry enter. Geometry is one of the fields of mathematics which is most directlyrelated to the world around us. For that reason, it is a very importantpart of elementary school Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionThe Study of ShapesOne way to look at Geometry is as the study of shapes, theirrelationships to each other, and their is Geometry Useful?
2 Measuring land for mapsbuilding plansschematics for drawingsartistic portrayalsothers?Why Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionTetris and Mathematical ThinkingGeometry is also useful in stimulating mathematics thinking. Takefor example the game of Thinking and TetrisDefining TermsWhat is a tetronimo? It is more than just four squares put together. Spatial Sense and ProbabilityWhat are good strategies for playing Tetris?StatisticsMeasure improvement by recording scores and comparing early scores to later pieces are the same and which are actually different?Problem SolvingHow many Tetris pieces are there?TessellationWhich tetronimo will cover a surface with no gaps? Geometry and AlgebraHow does the computer version of Tetris work?Why Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionTwo Types of GeometryTraditionally, Geometry in education can be divided into twodistinct of GeometryFormal GeometryThis type of Geometry is similar to that studied in ancientGreece in which everything is proven from a set of or Conceptual GeometryIn this type of Geometry focus is placed on shapes andrelationships and not on formal axioms and will spend a little time with Formal Geometry before going onto talk more about conceptual Study Geometry ?
3 Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionEuclid s PostulatesWe can not prove everything! We must have some starting pointto any formal s PostulatesOne of the most famous books in history is Euclid s Elements. In it theGreek mathematician Euclid presented his five postulates for are statements which are to be accepted as true without straight line may be drawn between any two piece of a straight line may be extended circle may be drawn with any given radius and an arbitrary right angles are a straight line crossing two straight lines makes the interior angleson the same side less than two right angles, the two straight lines, ifextended indefinitely, meet on that side on which the angles lessthan two right angles Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionEuclid s Fifth PostulateTo understand the consequences of stating postulates, considerEuclid s fifth postulate. This is often called the parallel postulateand has been to the Parallel PostulateThe following are alternatives to the parallel postulate which states that two lines which are not parallel must exists a pair of similar non-congruent exists a pair of straight lines everywhere equidistant from one exists a circle through any three non-colinear three angles of a quadrilateral are right angles, then the fourth angle is also a right a straight line intersects one of two parallel lines it will intersect the lines parallel to a third line are parallel to each straight lines that intersect one another cannot be parallel to a third is no upper limit to the area of a Study Geometry ?
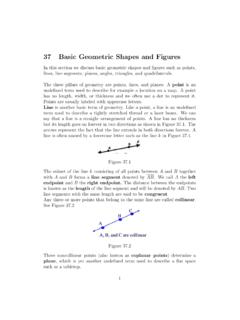
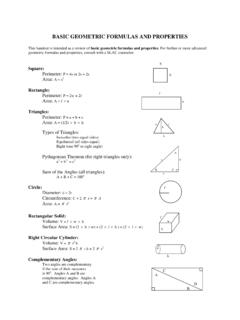
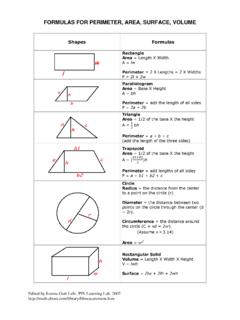
4 Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionBasic Objects in GeometryWe now turn to the more conceptual questions in Geometry . Thoseinvolving Basic objects and their Geometric ObjectsThe following objects in Geometry can not be formally defined, butwe must agree on what the terms have no dimensions but they do have a locationLineslines are straight, extend infinitely in two directions, and canbe thought of as being made up of plane is a flat surface which extends infinitely in Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionColinearityExample1 How many lines are there through a single point?2 How many lines are there through two distinct points?3 How many lines are there through three distinct points?Colinear PointsA set of points iscolinearif there is a single line through all of thepoints. (Note: Every set of two points is colinear.)ExampleDraw a set of three points which are colinear and another set ofthree points which are not Study Geometry ?
5 Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionCoplanarityQuestions line those we asked about lines can be asked aboutplanes as many planes are there through a single point?2 How many planes are there through two points?3 How many planes are there through three points?Coplanar PointsA set of points is said to becoplanarif there is a plane containingall points in the you find a set of points which are not coplanar?Why Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionFrom a Line To..Using the Basic object of a line, we can define several new SegmentAline segmentis a subset of the line which contains two pointson the line, calledendpoints, and all parts of the line betweenthese two a subset of a line that contains a specific point, called theendpoint, and all points on the line on one side of the an example of a line, line segment, and a ray and name eachobject using point Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionRelationships Between LinesTwo lines can have several different relationships to each Between LinesTwo lines can have the following relationships:1 PerpendicularThe lines form right angles at their lines intersect at a single in the same plane which do not intersect are LinesTwo lines which lie in different planes and do not intersect arecalled skew Study Geometry ?
6 Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionAnglesWhen two lines intersect they form an AngleAnangleis the union of two rays which the same endpoint, calledthevertex. Each ray is called asideof the way to think of angles is as movement or change. One raysweeps out a 45 and name two different angles using only two angle partitions the plane into three pieces: the angle itself, theinterior (the portion of the plan between the rays on the side ofleast change) and the Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionDealing with AnglesThere are several important tasks which we need to be able toaccomplish with with AnglesNaming AnglesMeasuring AnglesClassifying AnglesAngles can be classified based on their measures. Angles are:Straight- if their measure is 180 Right- if their measure is 90 Obtuse- if their measure is between 180 and 90 Acute- if their measure is between 0 and 90 Reflex- if their measure is greater than 180 Why Study Geometry ?
7 Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionClassifying Angle RelationshipsAngles can also be classified by their relationship to each RelationshipsTwo angles are:Complementary- if their measures add to 90 .Supplementary- if their measures add to 180 .Adjacent- if they share a side and if they share a vertex and sides on the same vs. EqualityTwo angles are congruent if they have the same measure. To be equalthe angles must made up of the same that vertical angles are Study Geometry ?Formal GeometryGeometric ObjectsConclusionImportant ConceptsThings to Remember from Section of Formal Geometry2 Definition of Basic Geometric Objects3 Relationships Between Basic Geometric Objects4 Working with Lines and Angles