Transcription of Names for ABO (ISBT 001) Blood Group Alleles
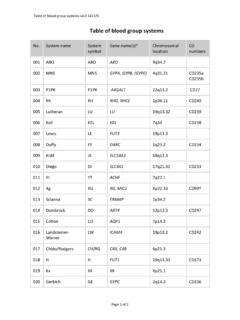
1 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles v1. 1 171023 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles General description: The ABO system was discovered as in 1900 and is considered the first and clinically most important system. The ABO gene and its 7 coding exons give rise to one of two principally different glycosyltransferases. The A glycosyltransferase (GTA) catalyzes the addition of a donor substrate, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine, to an acceptor substrate known as the H antigen. The B glycosyltransferase (GTB) differs by only four amino-acid substitutions from GTA and performs the same enzymatic reaction but uses UDP-galactose as donor substrate.
2 In this way, genetic polymorphism gives rise to two related antigens in this system. Any polymorphism or mutation that changes the activity or specificity of the encoded enzyme may therefore alter the ABO phenotype. Alterations that completely abolish enzymic activity give rise to the Blood Group O phenotype, in which the H antigen remains unconverted and no A or B antigen can be detected. If the genetic alteration decreases the activity of the enzyme, or alters its subcellular location and thereby decreases conversion of H to A or B, a weak A or B subgroup phenotype can result.
3 Furthermore, certain polymorphisms result in promiscuous enzymes that can synthesize both A and B antigen, thereby resulting in the so-called cisAB or B(A) phenotypes. The A phenotype is divided into A1 and A2. The former is more prevalent in all populations and has approximately 5 times more A epitopes per red cell. The GTA1 is also better than GTA2 at synthesizing certain forms of A, . A type 3 and 4. In addition to the A and B antigens, two other antigens are included in the ABO system, namely A,B and A1.
4 The former is a joint epitope on A or B antigen and is therefore present in both A, B and AB phenotypes. The exact biochemical nature of the A1 antigen has been more controversial but has been proposed to represent A type 4. Gene name: ABO Number of exons: 7 Init iation codon: Wit hin exon 1 Stop codon: Within exon 7 Entrez Gene ID: 28 LRG sequence: (genomic) (transcript) Reference allele: ABO* (shaded) Page 1 of 17 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles v1. 1 171023 Molecular bases associated with the A1, A2 and weak A phenotypes Reference allele ABO* encodes A glycosyltransferase that synthesizes A antigen.
5 Phenotype Allele name Nucleotide change Exon Predicted amino acid change A1 ABO* A1 ABO* >T 7 A2 ABO* >T; 7 ; *23 A2 ABO* >T 7 A2 ABO* >G 7 A2 ABO* >G; >G; >T; >A; >T; >A 6 7 ; ; A2 ABO* >T; >G 7 ; A2 ABO* 7 *23 A2 ABO* >C 7 A2 ABO* >T; >C 7 ; A2 ABO* >T; >A; 7 ; ; *23 A2 ABO* >C; >T 6 7 ; A2 ABO* >T; >T 6 7 ; A2 ABO* >A; >A; 4 7 ; ; *23 A2 ABO* >T; >T 7 ; A2 ABO* >T; >A; >T; >T; 3 4 7 ; ; ; *23 A2 ABO* >T; >T 7 ; A2 ABO* >T; >A 7 ; A2 ABO* >T; >A 7 ; Page 2 of 17 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles v1.
6 1 171023 Phenotype Allele name Nucleotide change Exon Predicted amino acid change A2 ABO* >T; >A 7 ; A3 ABO* >A 7 A3 ABO* >A; 7 ; *23 A3 ABO* >T 7 A3 ABO* >T; >A; 7 ; ; *23 A3 ABO* >A 7 A3 ABO* >T; >A 7 ; A3 ABO* >T; >T 7 ; Aweak ABO* >T; >T; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >C; >T; 6 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >C; >T; 4 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T 7 Aweak ABO* >G 7 Aweak ABO* >G 7 Aweak ABO* >T; >T; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >G; >T; >G; >A 5 6 7 ; ; ; Aweak ABO* >A; >T; >A; >T; >T; 2 3 4 5 7 ; ; ; ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >A 7 Aweak ABO* >A; >T 7 ; Page 3 of 17 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles v1.
7 1 171023 Phenotype Allele name Nucleotide change Exon Predicted amino acid change Aweak ABO* >T; >G 7 ; Aweak ABO* >C 1 Aweak ABO* >T; >A 7 ; Aweak ABO* +4A>T Intron 6 Altered splicing Aweak ABO* >G; >T; 1 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >T; 5 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >C; >T; 6 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >G; >T; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >A; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >C; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >A; 7 ;Val212 Met; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >A; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >T; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >A; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >T; >A; 7 ; ; *23 Aweak ABO* >A; 7 ; *23 Aweak ABO* +2T>C Intron 1 Altered splicing Aweak ABO* >A 6 Ax/Aweak ABO* >A 7 Ax/Aweak ABO* >A; >A 7 Page 4 of 17 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles v1.
8 1 171023 Phenotype Allele name Nucleotide change Exon Predicted amino acid change Ax/Aweak ABO* >G; >A; >A; >T; >A 6 7 ; Ax/Aweak ABO* >A; >A; >T; >A 7 ; Ax/Aweak ABO* >A 7 Ax/Aweak ABO* >T; >T 7 ; Ax/Aweak ABO* >T; >A; >G 7 ; ; Ax/Aweak ABO* >T; >T 7 ; Ax/Aweak ABO* >A 7 Ax/Aweak ABO* >G 7 Ax/Aweak ABO* >C 7 Ax/Aweak ABO* >C 7 Ax/Aweak ABO* >T 7 Ax/Aweak ABO* >G 6 Ax/Aweak ABO* >T; >G 7 ; Ax/Aweak ABO* >T; >T 7 ; Afinn/Aweak ABO* +4A>G Intron 6 Altered splicing Abantu/Aweak ABO* +1delG; >T; Intron 4 7 Altered splicing Am ABO* >T; >T 7 ; Am ABO* >A 7 Ael ABO* 7 *124 Ael ABO* >T; >A; >A 7 ; Ael ABO* 7 *20 Ael ABO* +5G>A Intron 6 Altered splicing Ael ABO* >T; >C 7 ; Ael ABO* >C; >T 7 ; Ael ABO* >T; 681G>A; 771C>T; >A 7 ; Page 5 of 17 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles v1.
9 1 171023 Phenotype Allele name Nucleotide change Exon Predicted amino acid change Ael ABO* >T; 7 ; *124 The A103-A107 Alleles in dbRBC do not give rise to an altered amino acid sequence compared to other Alleles , and so are not included here. A108 and A109 are listed as unpublished, and had no phenotype registered in dbRBC. A214 and A215 represent the same coding sequence as ABO* , but have been registered under other Names due to intron polymorphisms. Also, their phenotypes are not given in dbRBC.
10 Some Alleles listed above are unpublished, but have been submitted to GenBank/dbRBC. It is also noteworthy that many of the Alleles registered as associated with the rare A2 phenotype in Asia ( , , , and ) cause amino acid substitutions that have been associated with weaker A subgroups in other studies. In the case of and , the phenotype was given as A, not A2. Page 6 of 17 Names for ABO ( isbt 001 ) Blood Group Alleles v1. 1 171023 Molecular bases associated with the B and weak B phenotypes The seven B-associated polymorphisms are only shown for the first allele but are present in all the others except ABO* , which uses Differences compared to ABO* , that encodes B glycosyltransferase, are given.