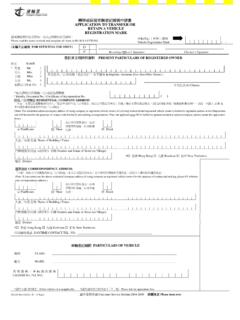
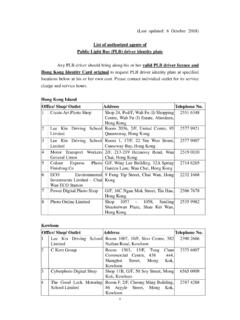
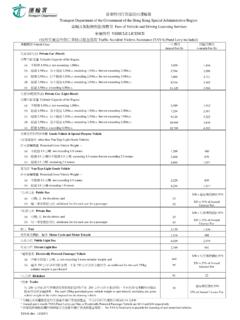
Transcription of Public Transport Strategy Study - Transport Department
1 Transport and Housing BureauPublic TransportStrategy StudyJune 2017 Public Transport Strategy Study Final Report Chapter 1 Introduction Since 1976, the Government conducted three comprehensive Transport studies ( CTS ) to map out the strategic plans for Transport planning and overall development, as well as formulate development plans for infrastructures so as to cater for the socio-economic development of Hong Kong. The mass transit railway system was put in place following the recommendations of the CTS-1 completed in 1976.
2 Subsequently, following the recommendations of the CTS-21 completed in 1989, the Government took forward a number of road and railway infrastructural projects, including the North Lantau Expressway and Lantau Link, Airport Express/Tung Chung Line, Tseung Kwan O Line, and West Rail Lin, to tie in with the development of the airport at Chek Lap Kok, the Metroplan and various reclamation studies. The CTS-3, completed in 1999, has laid down a number of broad directions. Key ones include: (a) better use of railway as the backbone of our passenger Transport system; (b) provision of better Public Transport services and facilities; (c) wider use of advanced technologies in Transport management; and (d) implementation of more environmentally-friendly Transport measures.
3 The CTS-3 also sets out a hierarchy of the roles and positioning of the different Public Transport services having regard to their efficiency and functions. At the top of this hierarchy is heavy rail as it operates on dedicated rail corridor, providing high-capacity, convenient and emission-free services. The next level comprises franchised buses and Light Rail. They serve as mass carriers and provide feeder services to heavy rail. Other Public Transport services basically play a supplementary role.
4 For instance, Public light buses are used for routes with a relatively lower patronage, taxis offer personalised and point-to-point services for commuters who are willing to pay a higher fare, while ferries provide outlying island passengers with essential Transport services and cross harbour passengers with another modal choice through inner harbour routes. These broad directions as well as the roles and positioning of different Public Transport services remain applicable today.
5 Public Transport services are closely related to the daily life of the Public . Every day, over 12 million passenger trips are made through different Public Transport services in Hong Kong. This accounts for over 90% of the total passenger trips each day, which is the highest in the world2. Given that Hong Kong is a small and densely-populated city with limited road space, and the Public are concerned about the impact of road traffic on air quality, it is appropriate to continue to adopt the Public Transport -oriented policy and the policy to use the railway as the backbone of the Public Transport system.
6 1 The Study was updated in 1993. 2 According to a Study conducted by the Land Transport Authority of Singapore in November 2014, the Public Transport usage rate in Hong Kong was the highest among 27 major cities. For other major cities, the Public Transport usage rate was around 60% in Singapore, 70% in Seoul, 50% in Tokyo, 30% in London and New York. - 2 - In September 2014, the Government announced the Railway Development Strategy 2014 ( RDS-2014 ). The RDS-2014 reaffirmed the policy of using railway as the backbone of our Public Transport system and mapped out the development and planning blueprint of our heavy rail network up to 2031.
7 Upon full implementation of the 7 recommended projects3 which are subject to detailed feasibility studies, our railway network will cover areas accommodating some 75% of the local population and some 85% of job opportunities. A highly-efficient railway network with comprehensive coverage would not only facilitate the daily commute of the Public and address passenger demand, but also promote the further development of the community, new towns and new development areas as well as facilitate passenger flow and goods flow.
8 This would bring economic benefits and strengthen community ties. Our Public Transport services have generally been working well. Operating on a commercial basis, Public Transport operators are able to maintain efficient and quality service and provide multi-modal choices for the community. In fact, Hong Kong was ranked first in terms of Public Transport services among 84 cities in an international survey4. However, having regard to the expansion of the heavy rail network, we consider it necessary to carry out a systematic review on the overall strategic arrangements of the Public Transport system in order to maintain the quality and diversified Public Transport services and to draw up strategies conducive to the healthy and sustainable development of the trades, with a view to improving people s livelihood, facilitating development and maintaining efficiency.
9 Meanwhile, we strive to ease traffic congestion through various means. We are taking forward progressively the series of short-, medium- and long-term recommendations by the Transport Advisory Committee in its earlier Report on Study of Road Traffic Congestion in Hong Kong to ease the traffic congestion. For instance, upon completion of the first stage Public consultation on the Central District Electronic Road Pricing Pilot Scheme this year, the Transport Department ( TD ) will appoint a consultant to conduct an in-depth feasibility Study .
10 TD will also commence a two-year consultancy Study on the parking for commercial vehicles to formulate appropriate measures to meet the parking demand of commercial vehicles. The Government will continue to Study measures to contain private cars growth and to combat illegal parking and other illegal activities that create traffic congestion. For Public Transport services that need to share road space, the alleviation of traffic congestion can help enhance their service reliability and attract more people to commute by Public Transport .