Transcription of PVC Chemical Resistance Guide - ipexna.com
1 FIRST EDITIONPVC Chemical Resistance Guide Thermoplastics:Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)PVCC hemicalResistance GuideChemical Resistance GuidePolyvinyl Chloride (PVC)1st Edition 2013 by IPEX. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be used or reproduced in any manner whatsoever without priorwritten permission. For information contact: IPEX, Marketing, 2441 Royal Windsor Drive, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, L5J information contained here within is based on currentinformation and product design at the time of publication and issubject to change without notification. IPEX does not guarantee orwarranty the accuracy, suitability for particular applications, orresults to be obtained IPEX, we have been manufacturing non-metallic pipe and fittings since 1951. We formulate our own compounds andmaintain strict quality control during production. Our products are made available for customers thanks to a network ofregional stocking locations from coast-to-coast. We offer a wide variety of systems including complete lines of piping, fittings,valves and custom-fabricated importantly, we are committed to meeting our customers needs.
2 As a leader in the plastic piping industry, IPEX continually develops new products, modernizes manufacturing facilities and acquires innovative process technology. In addition,our staff take pride in their work, making available to customers their extensive thermoplastic knowledge and field personnel are committed to improving the safety, reliability and performance of thermoplastic materials. We are involved inseveral standards committees and are members of and/or comply with the organizations listed on this specific details about any IPEX product, contact our customer service Chemical Resistance Guide for PVCiThermoplastics and elastomers have outstanding Resistance to a wide range of Chemical reagents. The Chemical Resistance ofplastic piping is basically a function of the thermoplastic material and the compounding components. In general, the lesscompounding components used the better the Chemical Resistance . Thermoplastic pipes with significant filler percentages maybe susceptible to Chemical attack where an unfilled material may be affected to a lesser degree or not at newer piping products utilize a multi-layered (composite) construction, where both thermoplastic and non-thermoplasticmaterials are used for the layers.
3 Layered composite material pipe may have Chemical Resistance that differs from thechemical Resistance of the individual material. Such Resistance however, is a function both of temperatures and concentration,and there are many reagents which can be handled for limited temperature ranges and concentrations. In borderline cases, itwill be found that there is limited attack, generally resulting in some swelling due to absorption. There are also many caseswhere some attack will occur under specific conditions, but for many such applications, the use of plastic will be justified oneconomic grounds when considered against alternative materials. Resistance is often affected (and frequently reduced) whenhandling a number of chemicals or compounds containing impurities. For this reason, when specific applications are beingconsidered, it may be worthwhile to carry out tests using the actual product that will be encountered in service. The listingthat follows does not address Chemical information is based on immersion tests on unstressed coupons, experiments and, when available, actual processexperience as well as data from tests inclusive of stress from temperature and pressure.
4 The end user should be aware of thefact that actual service conditions will affect the Chemical that do not normally affect the properties of an unstressed thermoplastic may cause completely different behavior(such as stress cracking) when under thermal or mechanical stress (such as constant internal pressure or frequent thermal ormechanical stress cycles). Chemical Resistance data from immersion tests cannot be unconditionally applied to thermoplasticpiping components subjected to continuous or frequent mechanical or thermal the pipe will be subject to a continuous applied mechanical or thermal stress, or to combinations of chemicals, testingthat duplicates the expected field conditions, as closely as possible, should be performed on representative samples of thepipe product to properly evaluate plastic pipe for use in this are according to the product and absence of any class indication for any given materials, signifies the absence of data for such material(s) with respect tothe specific Chemical (s), temperature(s) and concentration(s).
5 Note: Chemical Resistance data is found in a laboratory setting and cannot account for all possible variables of an installedapplication. It is up to the design engineer or final user to use this information as guidance for a specific application a material is chemically resistant to the concentrated form of a specific Chemical , it should be resistant to the diluted formof that same Chemical Resistance data for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) contained within this manual has been provided, with writtenconsent, by Chemical Resistance Guide for PVCiiNOTES_____IPEX Chemical Resistance Guide for PVC1 POLYVINYL CHLORIDE (PVC)A pipe system may be subject to a number of aggressivechemical exposures, accidental or otherwise. Resistance ofPVC pipe to attacks by Chemical agents has been determinedthrough years of research and field experience, demonstratingthe capability to endure a broad range of both acidic andcaustic Affecting ResistanceChemical reactions can be very complex.
6 There are so manyfactors affecting the reaction of a piping system to chemicalattack that it is impossible to construct charts to cover allpossibilities. Some of the factors affecting chemicalresistance are:1. Temperature2. Chemical (or mixture of chemicals) present3. Concentration of chemicals4. Duration of exposure5. Frequency of exposurePVC Pipe and FittingsThe Chemical Resistance information for PVC pipe provided inthe following tables is based on short-term immersion ofunstressed strips of PVC in various chemicals (usuallyundiluted), and may be useful in assessing the suitability ofPVC under unusual or specific operating of this type of test can be used only as a Guide toestimate the response of PVC. These tables provide guidanceto industrial users of pipe for conveying the chemicals listed,rather than design criteria for sewers that may experienceoccasional exposures or when diluted by other additional source of information on the chemicalresistance of PVC pipe is the National Association ofCorrosion Engineers publication entitled, "Corrosion DataSurvey, Nonmetals Section.
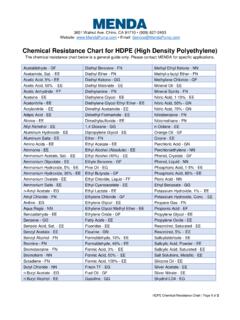
7 " For critical applications it isrecommended that testing be performed under conditionsthat approximate the anticipated field applications where exposure to harmful chemicals isfrequent, of long duration or in high concentrations, furthertesting is following Chemical Resistance legend is used in thefollowing PVC tables:All Chemical Resistance data for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) contained within this manual has been provided, with writtenconsent, by resistantCLess resistant than R butstill suitable for someconditionsNNot resistantIPEX Chemical Resistance Guide for PVC2R - Generally ResistantC - Less resistant than R but still suitable for some conditionsN - Not resistantChemical23 C(73 F)60 C(140 F)AAcetaldehydeNNAcetaldehyde, aq 40%CNAcetamide--Acetic acid, vaporRRAcetic acid, glacialRNAcetic acid, 25%RRAcetic acid, 60%RNAcetic acid, 85%RNAcetic anhydrideNNAcetoneNNAcetyleneNNAcetyl chlorideNNAcetylnitrileNNAcrylonitrileNN Acrylic acidNNAdipic acidRRAlcohol, allylRCAlcohol, amylNNAlcohol, benzylNNAlcohol, butyl (n-butanol)RRAlcohol, diacetoneNNAlcohol, ethyl (ethanol)RRAlcohol, hexyl (hexanol)RRAlcohol, isopropyl (2-propanol)RRAlcohol, methyl (methanol)RRAlcohol, propyl (1-propanol)
8 RRAlcohol, propargylRRAllyl chlorideNNAlumsRRexcept Aluminim fluorideRNAmmonia, gasRRAmmonia, liquidNNAmmonium saltsRRexcept Ammonium DichromateRNAmmonium fluoride, 10%RRAmmonium fluoride, 25%RCAmyl acetateNNAmyl chlorideNNAnilineNNPOLYVINYL CHLORIDE (PVC) Chemical Resistance DATAC hemical23 C(73 F)60 C(140 F)Aniline chlorohydrateNNAniline hydrochlorideNNAnthraquinoneRRAntimony trichlorideRRAnthraquinone sulfonic acidRRAqua regiaCNArsenic acid, 80%RRAryl-sulfonic acidRRBB arium saltsRRexcept Barium nitrateRNBeerRRBeet sugar liquorRRBenzaldehyde, 10% RNBenzene (benzol)NNBenzene sulfonic acid, 10%RRBenzene sulfonic acid, > 10% NNBenzoic acidRRBlack liquor paperRRBleach, 12% active chlorineRRBleach, 5% active chlorineRRBoraxRRBoric acidRRBrineRRBromic acidRRBromine, aqRRBromine, liquidNNBromine, gas, 25%RRBromobenzeneNNBromotolueneNNButadie neRRButaneRRButynediolRNButyl acetateNNButyl stearateRNButyl phenolRNButylene, liquidRRButyric acidRNIPEX Chemical Resistance Guide for PVC3R - Generally ResistantC - Less resistant than R but still suitable for some conditionsN - Not resistantChemical23 C(73 F)60 C(140 F)CCadmium CyanideRRCalcium saltsRRexcept Calcium bisulfideNNCalcium hypochlorite, 30%RRCalcium hydroxideRRCalcium NitrateRRCalcium OxideRRCalcium SulfateRRCamphorRNCane sugar liquorsRRCarbon disulfideNNCarbon dioxideRRCarbon dioxide, aqRRCarbon monoxideRRCarbitolRNCarbon tetrachlorideRNCarbonic AcidRRCastor oilRRCaustic potash, (potassium hydroxide), 50%RRCaustic soda, (sodium hydroxide)
9 , < 40%RRCellosolveRNCellosolve acetateRNChloral hydrateRRChloramine, diluteRNChloric acid, 20%RRChlorine, gas, dryCNChlorine, gas, wetNNChlorine, liquidNNChlorine waterRRChloracetic acid, 50%RRChloroacetyl ChlorideRNChlorobenzeneNNChlorobenzyl chlorideNNChloroformNNChloropicrinNNChlo rosulfonic acidRNChromic acid, 10%RRChromic acid, 30%RRChromic acid, 40%RCPOLYVINYL CHLORIDE (PVC) Chemical Resistance DATAC hemical23 C(73 F)60 C(140 F)Chromic acid, 50%NNChromium potassium sulfateRNCitric acidRRCoconut oilRRCoffeeRRCoke oven gasRRCopper acetateRNCopper salts, aqRRCorn oilRRCorn syrupRRCottonseed oilRRCresoteNNCresol, 90%NNCresylic acid, 50%RRCroton aldehydeNNCrude oil, sourRRCupric Salts, aqRRCyclohexaneNNCyclohexanolNNCyclohexa noneNNDD etergents, aqRRDextrinRRDextroseRRDibutoxyethyl phthalateNNDiesel fuelsRRDiethylamineNNDiethyl EtherRNDisodium phosphateRRDiglycolic acidRRDioxane -1,4 NNDimethylamineRRDimethyl formamideNNDibutyl phthalateNNDibutyl sebacateRNDichlorobenzeneNNDichloroethyl eneNNIPEX Chemical Resistance Guide for PVC4R - Generally ResistantC - Less resistant than R but still suitable for some conditionsN - Not resistantChemical23 C(73 F)60 C(140 F)
10 EEtherNNEthyl etherNNEthyl halidesNNEthylene halidesNNEthylene glycolRREthylene oxideNNFF atty acidsRRFerric saltsRRFish OilRRFluorine, dry gasRNFluorine, wet gasRNFluoboric acidRRFluosilicic acid, 50%RRFormaldehydeRRFormic acidRNFreon - F11, F12, F113, F114 RRFreon - F21, F22 NNFructoseRRFurfuralNNGG allic acidRRGas, coal, manufacturedNNGas, natural, methaneRRGasolinesCCGelatinRRGlucoseRRGl ue, animalRRGlycerine (glycerol)RRGlycolic acidRRGlycolsRRGrape SugarRRGreen liquor, paperRRPOLYVINYL CHLORIDE (PVC) Chemical Resistance DATAC hemical23 C(73 F)60 C(140 F)HHeptaneRRHexaneRNHexanolRRHydraulic OilRNHydrobromic acid, 20%RRHydrochloric acidRRHydrofluoric acid, 30%RNHydrofluoric acid, 50%RNHydrofluoric acid, 100%NNHydrofluosilic acidRRHydrocyanic acidRRHydrogenRRHydrogen cyanideRRHydrogen fluorideNNHydrogen phosphideRRHydrogen peroxide, 50%RRHydrogen peroxide, 90%RRHydrogen sulfide, aqRRHydrogen sulfide, dryRRHydroquinoneRRHydroxylamine sulfateRRHydrazineNNHypochlorous acidRRII odine, aq, 10%NNJJet fuels, JP-4 and JP-5 CCKK eroseneRRKetonesNNKetchupRNKraft paper liquorRRIPEX Chemical Resistance Guide for PVC5R - Generally ResistantC - Less resistant than R but still suitable for some conditionsN - Not resistantChemical23 C(73 F)60 C(140 F)