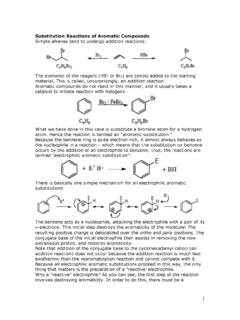
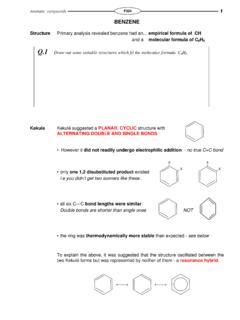
Transcription of Reactions of Benzene & Its Derivatives
1 Organic Lecture Series1 Reactions of Reactions of Benzene & Benzene & Its DerivativesIts DerivativesChapter 22 Organic Lecture Series2 Reactions of BenzeneReactions of BenzeneThe most characteristic reaction of aromatic compounds is substitution at a ring carbon:++ChlorobenzeneHalogenation:HClCl 2 FeCl3 HCl++NitrobenzeneNitration:HNO2 HNO3H2SO4H2 OOrganic Lecture Series3+Benzenesulfonic acidSulfonation:HSO3 HSO3H2SO4++An alkylbenzeneAlkylation:RRXAlX3HX++Acylat ion:An acylbenzeneHRCXAlX3 HXOCROHR eactions of BenzeneReactions of BenzeneOrganic Lecture Series4 RArenesAlkylbenzenesAlCl3 RClCarbon-Carbon Bond Formations:Organic Lecture Series5 Electrophilic aromatic SubstitutionElectrophilic aromatic substitution Electrophilic aromatic substitution :Electrophilic aromatic substitution : a reaction in which a hydrogen atom of an aromatic ring is replaced by an electrophile In this section.
2 Several common types of electrophiles how each is generated the mechanism by which each replaces hydrogen++HEE+H+Organic Lecture Series6 EAS: General MechanismEAS: General Mechanism A general mechanism Key question: What is the electrophile and how is it generated?+E+HEH+s low , ratedeterminingStep 1:Step 2:EH+fast+H+EEl e ct ro - phileResonance-stabilized cation intermed iateOrganic Lecture Series7++Organic Lecture Series8 ChlorinationChlorinationStep 1: formation of a chloronium ionStep 2: attack of the chloronium ion on the ring+++Resonance-stabilized cation intermediate.
3 The positivecharge is delocalized onto three atoms of the ring+slow , ratedeterminingClHHClHClClClClClClClFeCl ClClFeClClClFe Cl4-+-A molecular complex w ith a po sitiv e ch arg e o n ch l ori neFe rri c chl o ri de(a Lew is acid )Chlorin e(a Lew isbas e)++An ion p air contain ing a ch l oro ni um i o nOrganic Lecture Series9 Step 3: proton transfer regenerates the aromatic character of the ringChlorinationChlorinationClHCl-F eCl3 ClHClFeCl3 ChlorobenzenefastCationintermediate+++-+ Organic Lecture Series10++BromobenzeneHBrBr2 FeBr3 HBrBrominationBrominationThis is the general method for substitution of halogen onto a Benzene ring(CANNOT be halogenated by Free Radical Mechanism)Organic Lecture Series11 BrominationBromination--Why not Why not addnaddnof Brof Br22?
4 ?Regains aromatic EnergyOrganic Lecture Series12 Generation of the nitronium ion, NO2+ Step 1: proton transfer to nitric acid Step 2: loss of H2O gives the nitronium ion, a very strong electrophileHSO3 OHHONOOHSO4 ONOOHHCo n ju gate ac i dofnitric acid++SulfuricacidNitricacidThe nitro niumionONOOHHOHH+ONON itrationNitrationpKa= -3 Organic Lecture Series13 Step 1: attack of the nitronium ion (an electrophile) on the aromatic ring (a nucleophile)Step 2: proton transfer regenerates the aromatic ringONOHNO2NO2 HHNO2++++Resonance-stabilized cation intermediate+OHHOHHHHNO2NO2 OHHHOHHH++++++NitrationNitrationOrganic Lecture Series14 A particular value of nitration is that the nitro group can be reduced to a 1 amino groupCOOHNO23H2 NiCOOHNH22H2O4-Aminobenzoic acid4-Nitrobenzoic acid+(3 atm )
5 +NitrationNitrationOrganic Lecture Series15 SulfonationSulfonation Carried out using concentrated sulfuric acid containing dissolved sulfur trioxideB enzenesulfonic acidBenzene+SO3 HSO3H2SO4(SO3in H2SO4is sometimes called fuming sulfuric acid.)Organic Lecture Series16 FriedelFriedel--Crafts AlkylationCrafts Alkylation Friedel-Crafts alkylation forms a new C-C bond between an aromatic ring and an alkyl groupClAlCl3 HCl+Benzene2-Chloropropane(Iso prop yl chlo rid e)Cumene(Isopropylbenzene)+The electrophilic partner is a carbocation.
6 It will arrange to the most stable ion: allylic>3o>2o>1oOrganic Lecture Series17 Step 1: formation of an alkyl cation as an ion pairStep 2: attack of the alkyl cation on the aromatic ringStep 3: proton transfer regenerates the aromatic ring+R+RHRHRHA resonance-stabilized cation+++HRCl A lCl3 RAlCl3 HCl+++RClClAlClClRClClClAl ClR+ AlCl4-A n ion pair contain ing a carbo catio n+-+A molecular co mp l e xFriedelFriedel--Crafts AlkylationCrafts AlkylationOrganic Lecture Series18 There are two major limitations on Friedel-Crafts alkylations:1.
7 Carbocation rearrangements are common:+Isobutylchloridetert-Butylbenzen eBenzeneAlCl3+HClClCH3 CHCH2-ClCH3 AlCl3CH3C- C H2-Cl-AlCl3CH3 HCH3C+AlCl4-CH3CH3I sobutyl chl ori de+-+amolecularcompl exan i on pai rFriedelFriedel--Crafts AlkylationCrafts AlkylationOrganic Lecture Series192. F-C alkylation fails on Benzene rings bearing one or more of these stronglyelectron-withdrawing groupsYRXAlCl3SO3 HNO2NR3+CF3 CCl3 CNCHOCROCO HOCOROCNH2O+ N o reacti o nWhen Y Equals Any of These Groups, the BenzeneRing Does Not Undergo Friedel-Crafts AlkylationFriedelFriedel--Crafts AlkylationCrafts AlkylationOrganic Lecture Series20 Organic Lecture Series21 The The DeDe--activationactivation of of aromatic SystemsAromatic SystemsNote.
8 Deactivation refers to the rateof EASO rganic Lecture Series22 Friedel-Crafts acylationacylationforms a new C-C bond between a Benzene ring and an acylgroup:OClCH3 CClOAlCl3 AlCl3 OOHClHCl+BenzeneAcetophenoneAcetylch l ori de4-Phenylbutanoylchl o ri d e -Tetralon e++FriedelFriedel--Crafts Crafts AcylationAcylationOrganic Lecture Series23 The electrophile is an acyliumacyliumionionR-C ClOClClAl-ClOR-CClAl ClClClOR-C+AlCl4-AluminumchlorideAn acylchlorideA molecular complexwith a positive charge charge on chlorineA n ion pair containing an acylium ion+- +(1)(2)
9 FriedelFriedel--Crafts Crafts AcylationAcylationOrganic Lecture Series24 an acylium ion is a resonance hybrid of two major contributing structures F-C acylations are free of a major limitation of F-C alkylations; acyliumions do not rearrange.:++complete valence shellsThe more importantcontributing structureOOR-CR-C::FriedelFriedel--Craft s Crafts AcylationAcylationOrganic Lecture Series25A special value of F-C acylations is preparation of unrearrangedalkylbenzenes:+AlCl3N2H4, KOHdiethylene glycolIsobutylbenzene2-Methyl-1-phenyl-1 -propanone2-Methylpropanoyl chlorideClOOFriedelFriedel--Crafts Crafts AcylationAcylationOrganic Lecture Series26 DiDi--and and PolysubstitutionPolysubstitutionOnly a traceOrganic Lecture Series27 DiDi--and and PolysubstitutionPolysubstitutionOrientat ion on nitration of monosubstitutedbenzenes:OCH3 ClBrCOOHCNNO2orthometaparaortho + bstitu entCH358438964 Organic Lecture Series28 Orientation: certain substituents direct preferentially to ortho & parapositions.
10 Others to meta positions substituents are classified as either orthoortho--paraparadirectingdirecting or meta meta directing directing toward further substitutionDiDi--and and PolysubstitutionPolysubstitutionOrganic Lecture Series29 Rate certain substituents cause the rate of a second substitution to be greater than that for Benzene itself; others cause the rate to be lower substituents are classified as activatingactivatingor deactivatingdeactivatingtoward further substitutionDiDi--and and PolysubstitutionPolysubstitutionOrganic Lecture Series30 Organic Lecture Series31 -OCH3is ortho-para directing.