Transcription of Safe Handling of Hazardous Drugs - BC Cancer
1 Safe Handling of Hazardous Drugs Module 1. Includes Recommended Procedures and Techniques Table of Contents Section A .. 1. Potential Hazards of Handling Hazardous Drugs .. 1. Hazardous drug List .. 2. BCCA Hazardous drug Evaluation Criteria .. 2. Medical Surveillance .. 2. Personal Exposure Records .. 3. Work Re-Assignment .. 3. Section B .. 4. International Standards Organization (ISO) Classifications .. 4. Controlled Work Area .. 4. Hazardous drug Cleanroom .. 4. Hazardous drug 5. Other Rooms in the Controlled Work Area .. 5. 5. Biological Safety Cabinets .. 5. Communication System ..14. Carts.
2 14. Section C .. 14. General Protective Guidelines .. 14. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Cleanroom Garb .. 15. Scrubs ..16. Footwear ..16. Shoe Covers ..16. Hair Covers ..17. Surgical Masks ..17. Respirators ..18. Chemotherapy Gowns ..18. Isolation Gowns ..19. Chemotherapy Gloves ..19. Eye Protection ..21. Table 1: Summary of Process for Donning Personal Protective Equipment and Cleanroom Garb .21. (For controlled work area with anteroom and cleanroom only) ..21. Table 2: Summary of Process for Donning Personal Protective Equipment and Cleanroom Garb .22. (For controlled work area with other rooms in addition to anteroom and cleanroom).
3 22. Hand Hygiene .. 23. Hand Hygiene Agents ..23. Hand Washing After Handling Hazardous Drugs ..23. Table 3: Hand Hygiene for Sterile Compounding Personnel ..24. Nails and Nail Polish ..24. Safety 25. Eyewash Stations ..25. Emergency Showers ..26. Safety Stations Section D .. 27. Supplies .. 27. Wipes/Towels ..27. BCCA PHARMACY PRACTICE STANDARDS FOR Hazardous Drugs February 2017. Preparation Pad / Sterile Drape ..27. Alcohol Swabs and Solutions ..27. Aqueous Cleaning/Decontaminating Agents ..28. Devices .. 28. Syringes ..29. Syringe Tip Caps ..29. Needles ..30. Needle Needle Cap Holders ..30. Filters.
4 31. Filter Venting Devices ..32. Syringe Fluid Dispensing Connectors/Syringe Tip NON- Hazardous Solution Dispensing Pins/Universal Spikes ..34. Solution/Intravenous Administration Sets ..34. Winged Infusion Sets ..35. Closed System drug Transfer Containers .. 37. Ampoules ..38. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Bags ..39. Non-Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (Non-DEHP) Bags ..39. Empty Sterile Infusion Bags ..40. Evacuated Ambulatory drug Delivery Infusion Devices .. 40. Elastomeric Infusion Devices ..41.. Computerized Ambulatory drug Delivery (CADD ) Pump and Medication Cassette Reservoir ..43. Section E .. 43.
5 Operational Standards for Sterile Hazardous drug Preparation .. 43. Personnel Hygiene in the Controlled Work Area ..43. Personal Protective Equipment and Cleanroom Garb in the Controlled Work Biological Safety General Procedures ..46. Removing Products from the BSC ..47. Warning Labels ..48. Exiting the Cleanroom ..48. Aseptic/Protective Routines .. 49. Critical Sites ..49. First Disinfecting Critical Sites ..50. Coring ..50. Capping Needles Safely ..51. Safe Handling Aseptic Techniques .. 51. Transfer of Hazardous drug Solution from a Syringe ..51. Removal of Bubbles/Air from a Syringe ..51. Attaching and Priming Solution / Administration Withdrawal of Excess Solution from an Infusion Solution Bag.
6 52. Section F .. 52. Clean Up and Waste Disposal .. 52. Biological Safety Cabinet Waste Cleanup ..52. BCCA PHARMACY PRACTICE STANDARDS FOR Hazardous Drugs February 2017. Hazardous Waste Disposal ..53. Section G .. 54. Safe Handling of Oral, Topical and Pre-Packaged Hazardous drug Dosage Forms .. 54. Oral Preparations ..54. Topical Preparations ..54. Pre-filled Syringes ..55. Section H .. 55. Hazardous drug 55. Recommended Spill Kit Contents ..55. Accidental Exposure to Hazardous Drugs .. 56. Inhalation ..56. Ingestion ..56. Absorption/Skin Contact ..57. Accidental Injection/Skin Section 58. Receipt and Unpacking.
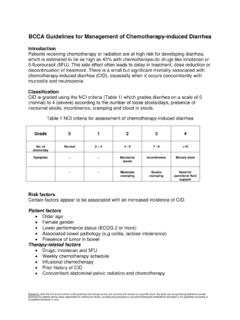
7 58. Receipt ..58. Receipt of a Damaged Shipment ..58. Storage .. 59. Packaging and Transportation .. 59. References .. 61. BCCA PHARMACY PRACTICE STANDARDS FOR Hazardous Drugs February 2017. Section A. Potential Hazards of Handling Hazardous Drugs Hazardous Drugs used to treat Cancer may cause temporary or permanent changes in a patient's health. Temporary adverse effects that patients may experience during or after treatment are well documented - immunosuppression, nausea/vomiting, hair loss, etc. and may be reversible. Cancer treatment regimens that may cause permanent health problems include cardiotoxicity after cumulative doses of DOXO rubicin and peripheral nerve damage after high doses of vinCRIS tine.
8 In therapeutic doses, some Hazardous Drugs can lead to 1,2. reproductive problems such as decreased fertility, fetal malformations, and spontaneous abortions. Adverse effects similar to those seen in treated Cancer patients may occur in healthcare workers who handle 3,4. Hazardous Drugs regularly, especially if protective garb and equipment are not used. Various studies have 5. demonstrated possible links between occupational exposure to Hazardous Drugs and menstrual dysfunction , 6 1 7. infertility , miscarriages and stillbirths , low birth weights and congenital abnormalities. Many of the studies investigating occupational exposure to chemotherapy in healthcare workers were conducted prior to the development of safe Handling standards for the preparation and administration of Hazardous Drugs .
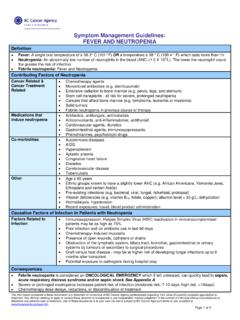
9 In the mid-1980's, international standards regarding sterile preparation rooms (cleanrooms), personal protective equipment, biological safety cabinets, etc. were developed. Given the changes in the Handling procedures for 8. Hazardous Drugs , the risk of acute and long-term toxic effects in healthcare workers may have declined. Nevertheless, the potential health risks for hospital staff still exist as suggested by recent environmental contamination studies showing the presence of Hazardous drug contamination on multiple surfaces in the 9-11. workplace. Standard: Hazardous drug (HD) safe Handling policies and procedures must be developed to address the following:12,13.
10 Receipt12-14. Storage12-15. Preparation12,13. Labelling12,14,15. Safety equipment16. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)14,17. Emergency procedures for treating accidental contact and spills13,14. Packaging12,15. Transport12,14,15. drug administration13. Disposal12-14. All pharmacy staff must be informed of HD policies and procedures, and receive training for Handling Hazardous Drugs safely, cleaning up spills, and using all equipment and PPE ,14. There must be established work practices related to both drug manipulation techniques and to general hygiene Workplace procedures must be developed for using and maintaining all equipment that functions to reduce Hazardous drug Warning signs, which are clearly visible and clearly state the identified hazards, must be posted in all areas where Hazardous Drugs are received,18 stored,13 prepared13 and BCCA PHARMACY PRACTICE STANDARDS FOR Hazardous Drugs February 2017.