Transcription of Section 5 The Charging System - Autoshop 101
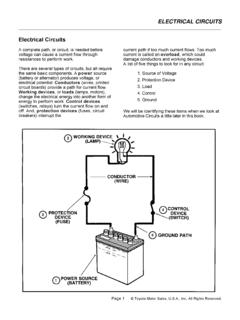
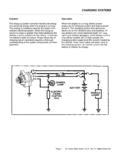
1 Electrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-1 The Charging System has two essential functions: Generate electrical power to run the vehicle's electrical systems Generate current to recharge the vehicle's batteryElectrical power - At low engine speeds, the battery may supplysome of the power the vehicle needs. At high engine speeds, thecharging System handles all of the vehicle's electrical - Alternator (generator) output is higher than batteryvoltage to recharge the SystemThe alternator suppliespower for the vehiclewhen the engine isrunning and engine speedis above 5-01TL623f501 Section 5 The Charging SystemChargingSystemSection 55-2 toyota Technical TrainingThese components make up the Charging System .
2 Alternator Voltage regulator Battery Charging indicatorCharging SystemComponentsThis figure shows themajor components of thecharging 5-02TL623f500 Charging SystemComponentsThe Charging SystemElectrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-3 The alternator contains these main components: Stator (attached to alternator housing, remains stationary) Rotor (spins inside the stator) Rectifier Voltage regulatorSlip rings and brushes make an electrical connection to the spinning alternator generates electricity through these steps: Engine power drives the alternator rotor through a pulley anddrive belt.
3 The alternator rotor spins inside the windings of the stator. The stator windings generate an alternating current. Rectifier diodes change the alternating current (AC) into directcurrent (DC).AlternatorExploded view of thealternator s 5-03TL623f503 AlternatorSection 55-4 toyota Technical TrainingThe voltage regulator controls the alternator's output current to preventover- Charging and under- Charging of the battery. It does this byregulating the current flowing from the battery to the rotor's field 's IC voltage regulator is a fully electronic device, using resistorsand RegulatorThe voltage regulatorcontrols the alternator soutput 5-04TL623f504 Voltage RegulatorThe Charging SystemElectrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-5 The battery supplies current to energize the alternator field coil.
4 Thebattery also acts as a voltage stabilizer. The battery must alwaysremain attached to the electrical System while the engine is battery suppliescurrent to energize thealternator s field 5-05TL623f505 BatterySection 55-6 toyota Technical TrainingThe Charging indicator is usually an ON/OFF warning lamp. When thesystem is running, the light should be OFF. The lamp lights when thecharging System is not providing sufficient Charging indicatorlights when the chargingsystem is not supplyingenough power to chargethe 5-06TL623f506cCharging IndicatorThe Charging SystemElectrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-7 Current in the Charging System changes for these three differentoperating conditions.
5 Ignition switch to ON - engine stopped Ignition switch to ON - engine running alternator output belowdesired voltage Ignition switch to ON - engine running alternator output abovedesired voltageIgnition switch to ON - engine stopped: As soon as the ignition switch is turned to ON, the IC regulatorcauses a current of about amps through the rotor's field coil. The IC regulator turns on the Charging indicator. There is no output from the stator because the rotor is not Switchto ON - EngineStoppedThe IC regulator causes asmall current through thealternator rotor field 5-07TL623f507cCharging SystemOperationSection 55-8 toyota Technical TrainingIgnition switch to ON - engine running, alternator outputbelow desired voltage: The windings in the stator generate a voltage any time the rotor isenergized and spinning.
6 Voltage generated in the stator is applied to the voltage regulator. If the alternator output voltage is below volts, the voltageregulator responds by increasing current through the field coil ofthe rotor. This causes the voltage to increase. A Charging current is sent to the ON- Output VoltageBelow voltsThe windings in the statorgenerate a voltage, and acharging current is sentto the 5-08TL623f508cThe Charging SystemElectrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-9 Ignition switch to ON - engine running alternator outputabove desired voltage:When the voltage regulator senses alternator output at or above volts: It reduces current through the rotor field coil.
7 This reduces alternator output voltage. No Charging current goes to the ON- OutputVoltage HighThe regulator reducescurrent through the fieldcoil; no Charging currentgoes to the 5-09TL623f509cSection 55-10 toyota Technical TrainingSafeguards are built into the alternator in case the connection toTerminal B or Terminal S is lost: Terminal S is an input to the regulator to monitor voltage levels. Terminal B is alternator S disconnected: The voltage regulator does not detect voltage. The voltage regulator regulates voltage at Terminal B to 16 voltsand lights the Charging SDisconnectedThe voltage regulatorregulates voltage atTerminal B to 16 voltsand lights thecharging 5-10TL623f510cThe Charging SystemElectrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-11 Terminal B disconnected: No Charging voltage available for battery.
8 This condition could result in voltage regulator BDisconnectedAn open circuit in theB terminal results in nocharging output forthe battery andcould damage thevoltage 5-11TL623f511cSection 55-12 toyota Technical TrainingThe Charging System requires little maintenance. The battery shouldbe fully charged and connections kept clean and of Charging System problems is typically may be electrical or troubleshooting flow diagram on the next page lists the mostcommon Charging System problems, the possible cause, andrecommended actions to resolve the with a thorough visual inspection.
9 If this fails to turn up thepossible cause, several tests are available to help you find the problem: Alternator output test (no load) Alternator output test (with load) Voltage drop tests Charging current relay test Diode testsDiagnosisand TestingThe Charging SystemElectrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-13 Use this flow diagram to troubleshoot Charging systems with compact,high speed DiagramFig. 5-12TL623f512 TroubleshootingFlow DiagramSection 55-14 toyota Technical TrainingInclude the following items in a visual inspection of the Charging System :1. Battery2.
10 Fusing3. Alternator Drive Belt4. Alternator Wiring5. Noise6. Charging IndicatorItem 1: BatteryInspect the battery forthe defects shownin this 5-13TL623f513cCharging SystemVisual InspectionThe Charging SystemElectrical Circuit Diagnosis - Course 6235-15 Other Battery ChecksState of Charge - Check the specific gravity of the electrolyte todetermine the battery's state of charge. Specific gravity should be between and (at 80 C).Condition - Check overall battery condition with a battery BatteryChecksA hydrometer can tellyou the battery s stateof 5-14TL623f514 Section 55-16 toyota Technical TrainingItem 2: Fusing Refer to the EWD to identify fuses and fusible links in the chargingsystem for the vehicle under test.