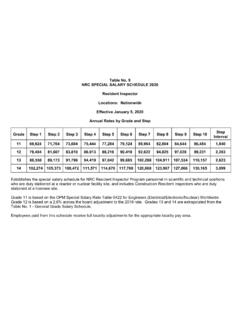
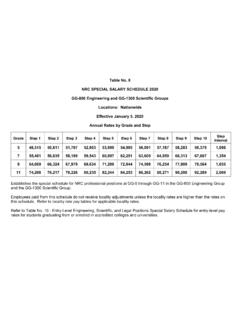
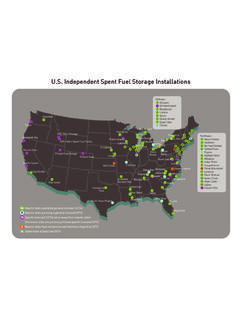
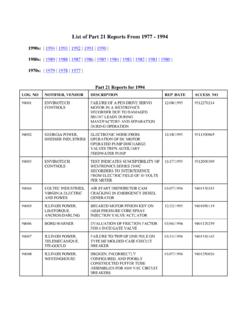
Transcription of Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology for the ...
1 May 2003 Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology for the Petroleum and Petrochemical IndustriesMay 2003 American Petroleum Institute1220 LStreet, NWWashington, DC20005-4070 National Petrochemical &Refiners Association1899 LStreet, NWSuite 1000 Washington, DC20036-3896 Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology for the Petroleum and Petrochemical Industries PREFACE The American Petroleum Institute (API) and the National Petrochemical & Refiners Associa-tion (NPRA) are pleased to make this Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology avail-able to the petroleum industry. The information contained herein has been developed incooperation with government and industry, and is intended to help refiners, petrochemicalmanufacturers, and other segments of the petroleum industry maintain and strengthen and NPRA wish to express sincere appreciation to their member companies who havemade personnel available to work on this document.
2 We especially thank the Department ofHomeland Security and its Directorate of Information Analysis & Infrastructure Protectionand the Department of Energy s Argonne National Laboratory for their invaluable contribu-tions. The lead consultant in developing this Methodology has been David Moore of AcuTechConsulting, whose help and experience was instrumental in developing this document in sucha short time. This Methodology constitutes one approach for assessing Security vulnerabilities at petroleumand petrochemical industry facilities. However, there are several other Vulnerability assess-ment techniques and methods available to industry, all of which share common risk assess-ment elements. Many companies, moreover, have already assessed their own Security needsand have implemented Security measures they deem appropriate.
3 This document is notintended to supplant measures previously implemented or to offer commentary regarding theeffectiveness of any individual company efforts. The focus of this first edition was on the needs of refining and petrochemical manufacturingoperations. In particular, this Methodology was field tested at two refinery complexes, includ-ing an interconnected tank farm, marine terminal and lube plant. It is intended that future edi-tions of this document will address other segments of the petroleum industry such as liquidpipelines and marketing terminals. API and NPRA are not undertaking to meet the duties of employers, manufacturers, or suppli-ers to train and equip their employees, nor to warn any who might potentially be exposed, con-cerning Security risks and precautions. Ultimately, it is the responsibility of the owner oroperator to select and implement the Security Vulnerability Assessment method and depth ofanalysis that best meet the needs of a specific location.
4 American Petroleum InstituteNational Petrochemical & Refiners AssociationApril 30, 2003 iii CONTENTS Page CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION.. to Security Vulnerability Assessment .. , Intended Audience and Scope of the Guidance .. Vulnerability Assessment and Security Management Principles .. 2 CHAPTER 2 Security Vulnerability Assessment CONCEPTS.. to SVA Terms .. Definition for SVA.. Attractiveness .. Approach .. of a Sound SVA Approach .. Strengths and Limitations .. Recommended Times for Conducting and Reviewing the SVA.. Validation and Prioritization of risks .. Risk Screening .. 8 CHAPTER 3 API/NPRA Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology .. of the API/NPRA SVA Methodology .. Methodology .. 1: Assets Characterization .. 2: Threat Assessment .. Step 3: Vulnerability Analysis.. 4: Risk Analysis/Ranking .. 5: Identify Countermeasures.
5 To the SVA .. 28 ATTACHMENT 1 EXAMPLE API/NPRA SVA Methodology FORMS .. 29 GLOSSARY OF TERMS .. 40 ABBREVIATIONS AND ACRONYMS .. 43 APPENDIX ASVA SUPPORTING DATA REQUIREMENTS .. 45 APPENDIX BSVA COUNTERMEASURES CHECKLIST .. 49 APPENDIX CAPI/NPRA SVA INTERDEPENDENCIES AND INFRASTRUCTURE CHECKLIST .. 81 REFERENCES .. 152 v Page API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Risk Definition .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , SVA Risk Variables .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Asset Attractiveness Factors .. API/NPRA SVA Process Overall Asset Screening Approach .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Recommended Times for Conducting and Reviewing the SVA .. API/NPRA Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology .. API/NPRA Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology Step 1.. API/NPRA Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology Step 2 .. API/NPRA Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology Steps 3 5.
6 API/NPRA SVA Methodology Timeline .. API/NPRA SVA Team Members .. SVA Sample Objectives Statement .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Security Events of Concern .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Description of Step 1 and Substeps .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Example Candidate Critical Assets .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Possible Consequences of API/NPRA SVA Security Events .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Example Definitions of Consequences of the Event .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Description of Step 2 and Substeps .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Threat Rating Criteria .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Target Attractiveness Factors (for Terrorism) .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Attractiveness Factors Ranking Definitions (A) . API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Description of Step 3 and Substeps .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Vulnerability Rating Criteria.
7 API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Description of Step 4 and Substeps .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Risk Ranking Matrix .. API/NPRA SVA Methodology , Description of Step 5 and Substeps .. 28 vi 1 Security Vulnerability Assessment Methodology for the Petroleum and Petrochemical Industries Chapter 1 Introduction INTRODUCTION TO Security Vulnerability Assessment The first step in the process of managing Security risks is toidentify and analyze the threats and the vulnerabilities facinga facility by conducting a Security Vulnerability Assessment (SVA). The SVA is a systematic process that evaluates thelikelihood that a threat against a facility will be successfuland considers the potential severity of consequences to thefacility itself, to the surrounding community and on theenergy supply chain. The SVA process is a team-basedapproach that combines the multiple skills and knowledge ofthe various employees to provide a complete picture of thefacility and its operations.
8 Depending on the type and size ofthe facility, the SVA team may include individuals withknowledge of physical and cyber Security , process safety,facility and process design and operations, emergencyresponse, management and other disciplines as necessary. The objective of conducting a SVA is to identify securityhazards, threats, and vulnerabilities facing a facility, and toevaluate the countermeasures to provide for the protection ofthe public, workers, national interests, the environment, andthe company. With this information Security risks can beassessed and strategies can be formed to reduce vulnerabili-ties as required. SVA is a tool to assist management in mak-ing decisions on the need for countermeasures to address thethreats and vulnerabilities. OBJECTIVES, INTENDED AUDIENCE AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDANCE This document was prepared by the American PetroleumInstitute (API) and the National Petrochemical & RefinersAssociation (NPRA) Security Committees to assist the petro-leum and petrochemical industries in understanding securityvulnerability Assessment and in conducting SVAs.
9 The guide-lines describe an approach for assessing Security vulnerabili-ties that is widely applicable to the types of facilities operatedby the industry and the Security issues they face. During thedevelopment process it was field tested at two refineries, twotank farms, and a lube plant, which included typical processequipment, storage tanks, marine operations, infrastructure,pipelines, and distribution terminals for truck and rail. Basedon these trials and the generic nature of the overall methodol-ogy, its use at other types of petroleum and petrochemicalfacilities is expected to be suitable. In future editions of thisguidance, it is intended that specific attention will be devotedto other operations within the petroleum industry such as liq-uid pipelines and marketing Methodology constitutes one approach for assessingsecurity vulnerabilities at petroleum and petrochemicalindustry facilities.
10 However, there are several other vulnera-bility Assessment techniques and methods available to indus-try, all of which share common risk Assessment companies, moreover, have already assessed their ownsecurity needs and have implemented Security measures theydeem appropriate. This document is not intended to supplantmeasures previously implemented or to offer commentaryregarding the effectiveness of any individual company efforts. Ultimately, it is the responsibility of the owner/operator tochoose the SVA method and depth of analysis that best meetsthe needs of the specific location. Differences in geographiclocation, type of operations, and on-site quantities of hazard-ous substances all play a role in determining the level of SVAand the approach taken. Independent of the SVA methodused, all techniques include the following activities: Characterize the facility to understand what criticalassets need to be secured, their importance and theirinterdependencies and supporting infrastructure; Identify and characterize threats against those assetsand evaluate the assets in terms of attractiveness of thetargets to each adversary and the consequences if theyare damaged or stolen; Identify potential Security vulnerabilities that threatenthe asset s service or integrity; Determine the risk represented by these events or con-ditions by determining the likelihood of a successfulevent and the consequences of an event if it were tooccur; Rank the risk of the event occurring and, if high risk,make recommendations for lowering the risk.