Transcription of SEMIVOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (SVOCs) Summary …
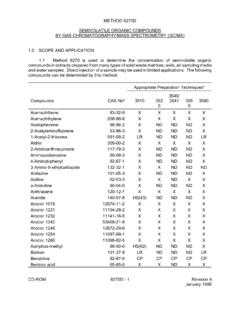
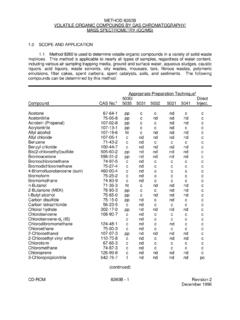
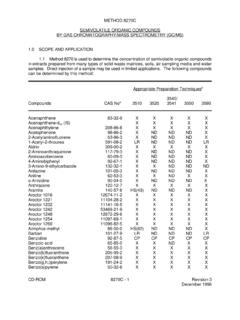
1 SEMIVOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (SVOCs) SW-846 Method 8270 Table 1A. Summary of Holding Times and Preservation for SEMIVOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Analytical Parameter a Technical and Contract Holding Times Preservation SEMIVOLATILE OrganicCompounds (SVOCs) in Water Technical for Extraction: 14 days from collection; Contract for Extraction: 10 days from receipt atlaboratory; Technical and Contract for Analysis: 40 days fromextraction Cool to 4EC 2EC; SVOCs in Soil b Technical for Extraction: 14 days from collection; Contract for Extraction: 10 days from receipt atlaboratory; Technical and Contract for Analysis: 40 days from extraction Cool to 4EC 2EC a Individual target COMPOUNDS are listed in Table Perform initial sample analysis using a 2-gram sample for mid-level analysis and a 30-gram sample for low-level analysis Data Calculations and Reporting Units: Use the mean RRF from the initial calibration to calculate the concentration of individual analytes according to Section of EPA Method 8270C, Revision Report water sample results in concentration units of micrograms per liter (Fg/L).
2 Report soil sample results on a dry-weight basis in micrograms per kilogram (Fg/kg). Report percent solid and percent moisture to the nearest whole percentage point. For rounding results, adhere to the following rules: a)If the number following those to be retained is less than 5, round down; b)If the number following those to be retained is greater than 5, round up; or c)If the number following the last digit to be retained is equal to 5, round down if the digit is even, or round up if the digit is odd. All records of analysis and calculations must be legible and sufficient to recalculate all sample concentrations and QC results. Include an example calculation in the data package. 8270 CRF 1 of 5 Revision 12/07/1999 Table 1B: Target compound List and Contract Required Quantitation Limits (CRQLs) for SEMIVOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (SVOCs) by SW-846 Method 8270 Contract RequiredQuantitation Limits PRGs Analyte Water (Fg/L) Soil (mg/kg) Industrial Soil (mg/kg) TapWater (Fg/L) 1,2-Dichlorobenzene 10 370 370 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene 10 1,700 190 1,3-Dichlorobenzene 10 140 180 1,4-Dichlorobenzene 10 2-Chloronaphthalene 10 NA NA 2-Chlorophenol 10 240 38 2-Methylnaphthalene 10 NA NA 2-Methylphenol 10 53,000 1,800 2-Nitroaniline 25 64 2-Nitrophenol 10 NA NA 2,2 -oxybis (1-Chloropropane)
3 10 NA NA 2,4-Dichlorophenol 10 3,200 110 2,4-Dimethylphenol 10 21,000 730 2,4-Dinitrophenol 25 2,100 73 2,4-Dinitrotoluene 10 2,100 73 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol 25 110,000 3,700 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol 10 270 2,6-Dinitrotoluene 10 1,100 37 3-Nitroaniline 25 NA NA 3,3 -Dichlorobenzidine 10 4-Bromophenyl-phenylether 10 NA NA 4-Chloro-3-methylphenol 10 NA NA 4-Chloroaniline 10 4,300 150 4-Chlorophenyl-phenyl ether 10 NA NA 4-Methylphenol 10 5,300 180 4-Nitroaniline 25 NA NA 4-Nitrophenol 25 66,000 2,300 4,6-Dinitro-2-methylphenol 25 NA NA Acenaphthene 10 28,000 370 Acenaphthylene 10 NA NA Anthracene 10 220,000 1,800 Benzo(a)anthracene 10 Benzo(a)pyrene 10 Benzo(b)fluoranthene 10 Benzo(g,h,i)perylene 10 NA NA Benzo(k)fluoranthene 10 36 bis(2-Chloroethoxy)-methane 10 NA NA 8270 CRF 2 of 5 Revision 12/07/1999 Table 1B.
4 Target compound List and Contract Required Quantitation Limits (CRQLs) for SEMIVOLATILE ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (SVOCs) by SW-846 Method 8270 Contract RequiredQuantitation Limits PRGs Analyte Water (Fg/L) Soil (mg/kg) Industrial Soil (mg/kg) TapWater (Fg/L) bis(2-Chloroethyl) ether 10 bis(2-Ethylhexyl)phthalate 10 21 Butylbenzylphthalate 10 930 7,300 Carbazole 10 150 Chrysene 10 360 Di-n-butylphthalate 10 NA NA Di-n-octylphthalate 10 10,000 730 Dibenz(a,h)anthracene 10 Dibenzofuran 10 3,200 24 Diethylphthalate 10 100,000 29,000 Dimethylphthalate 10 100,000 370,000 Fluoranthene 10 37,000 1,500 Fluorene 10 22,000 240 Hexachlorobenzene 10 Hexachlorobutadiene 10 38 Hexachlorocyclopentadiene 10 7,100 260 Hexachloroethane 10 210 Indeno(1,2,3-cd)pyrene 10 Isophorone 10 3,200 71 N-Nitroso-di-n-propylamine 10 N-nitrosodiphenylamine 10 610 14 Naphthalene 10 190 Nitrobenzene 10 100 Pentachlorophenol 25 15 Phenanthrene 10 NA NA Phenol 10 100,000 22,000 Pyrene 10 26,000 180 Notes: Fg/Lmg/kgNA = = = micrograms per per available.
5 PRG = EPA Preliminary Remediation Goals, Region 9 May 1, 8270 CRF 3 of 5 Revision 12/07/1999 cTable 2. Summary of Calibration Procedures for SVOCs by SW-846 Method 8270C Calibration Element Frequency Acceptance Criteria Corrective Action GC/MS Tuning with decafluorotriphenyl phosphine (DFTPP) Beginning of each 12 hour period duringwhich standards samples are analyzed Ion abundance criteria in Table 3 of Method 8270C, Revision 1. Identify the problem. 2. MS tune criteria must be met before any calibration standards, samples, blanks, orQC samples are analyzed Initial Calibration (minimum blank + 5 points for eachanalyte) (ICAL)a, b, c Initially; wheneverrequired, due to failure of CCV RSD for RRFs #30%; or correlation coefficient (r) generated by thelinear regression must be for all analytes 1.
6 Terminate analysis2. Recalibrate and verify before sample analysis ContinuingCalibration Verification (CCV) d Beginning of every12-hour period, and end of run %D between RRF of CCV and avg RRFs from ICAL #30%; or 30% of true value for linear regressiion 1. Re-calibrate and verify2. Re-analyze samples back to last good CCV Integrated areas ofInternal Standards Each analysis Area must be within -50 to 100 percent. 1. Re-analyze samples withinternal standard -50 percent and greater than 100 percent Retention time evaluation of all standard, surrogate, and sample analytes Each analysis 3 x the SD of the avg ICAL RT for each analyte 1. Re-calibrate and verify 2. Re-analyze samples outcontrol limits a The ICAL low standard must be above but near the CRQL. The low ICAL standard must have a signal to noiseratio $5:1.
7 If this requirement cannot be met, the laboratory must submit a MDL study as part of the data ICAL and continuing CAL standards must contain all target analytes listed in Table the retention time window for each analyte. Determine retention time windows as 3 x the standard deviation of the average initial calibration retention time for each If some COMPOUNDS are beyond the control limits of the CCV and these target COMPOUNDS are detected in samples and 10 percent or less of these analytes are beyond control limits, a single point calibration maybe used to quantify the out-of-control analytes. 8270 CRF 4 of 5 Revision 12/07/1999 Table 3. Summary of Internal Quality Control Procedures for SVOCs by SW-846 Method 8270C QC Element Frequency Acceptance Criteria b Corrective Action Method Blank (MB) Each 12-hour time period, minimum ofone per SDG a < CRQL for each compound 1.
8 Investigate the source of contamination and document. 2. Re-analyze all samples processed with a blank that isout of control. Matrix Spike and Matrix Spike Duplicate (MS/MSD) One MS/MSD set per batch or SDG (1MS/MSD set per 20 samples minimum) Water Sample: MS and MSD recoveries and RPD between within laboratory limits Soil Sample: MS and MSD recoveries and RPD between within laboratory limits 1. Report in case narrative Surrogate Spikes Every sample, standard and method blank Water Sample: Surrogate recoveries within laboratorylimits Soil Sample: Surrogate recoveries within laboratorylimits 1. Re-analyze all samples with non-compliant surrogaterecoveries LaboratoryControl Sample (LCS) One per SDG Water Sample: LCS recoveries within laboratory limits Soil Sample: LCS recoveries within laboratory limits 1.
9 Investigate the source ofproblem and document. 2. Re-analyze all samplesprocessed with a LCS that is out of control. a SDG - Sample Delivery Group - each case of field samples received; or each 20 field samples within a case; or each 14 calendar day period during which field samples in a case are within 3 sigma of laboratory control charts. The laboratory should submit the control charts. Dilute and reanalyze samples which contain one or more target analytes at concentrations above the initial calibration range. Results for such reanalyses should fall within the mid-range of the calibration results and submit documentation for both analyses. 8270 CRF 5 of 5 Revision 12/07/1999