Transcription of SI: INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM of UNITS (a.k.a. METRIC)
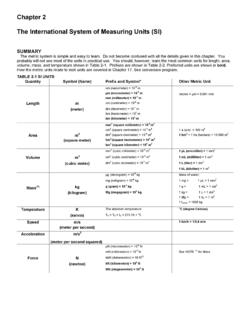
1 1 CHEM 1711 & 1811 Lecture # 1 7/27/16SI: INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM of UNITS ( METRIC) used universally in science convenient decimal structure quantity : a number and UNITS ; may be measured, calculated, or derived from other quantities JAG height = base UNITS : fundamental UNITS from which all others in the SYSTEM derive SHOW overhead of base SI UNITS mass : quantity of matter (base = kg) representing its inertia; similar to weight, which is a measure of gravity's effect on mass length : quantity of distance (base = m) along a line in 3-D space time : the fourth dimension (base = s) ; other non-SI UNITS include min, h, day, yr, .. temperature : a measure of internal energy in matter (base = K) ; properly not "degrees Kelvin" 0 K is the absolute zero of temp. ; negative K temps.
2 Do not exist 2 CHEM 1711 & 1811 Lecture # 1 7/27/16 other T scales: 1) Celsius ( centigrade) C = K - 2) Fahrenheit F = C x + 32 conversion "room temperature" = 70 F in K T = ? = (70 - 32) / + = K SI DECIMAL PREFIXES use upper or lower case letter to represent a power of ten need to memorize: G, M , k , d , c , m , , n , p SHOW overhead of prefixes scientists develop an ability to mentally process decimal pts. EXAMPLE Convert cm to m 17 J/mol to kJ/mol unit CONVERSIONS English - Metric equivalents must memorize: 1 lb = 454 g 1 in = cm 1 qt = L 1 mL = 1 cm3 use unit -factor method to convert 3 CHEM 1711 & 1811 Lecture # 1 7/27/16- (given quantity) / (same quantity) = unity 1 in / cm = 1 or 1000 mg / 1 g = 1 - multiplying a quantity by 1 does not change it - both the number and the UNITS change 1 in3 = ( cm)3 = ( )3 cm3 = cm3 EXAMPLE converting UNITS for an area: ft2 = ?
3 Cm2 area (cm2) ? = ( ft2) (12 in / 1 ft)2 ( cm / 1 in)2 = 929 cm2 ** check dimensions ** EXAMPLE density conversion (density = mass/volume) The density of copper is g/cm3; what is the density in lb/ft3 ? density (lb/ft3) ? = ( g/cm3) (1 lb / 454 g) ( cm / 1 in)3 x (12 in / 1 ft)3 = 557 lb/ft3 ** check dimensions ** ** does this make sense ?? ** MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTY accuracy vs. precision random vs. systematic error significant figures and rounding (in lecture typically 3 or 4) THESE TOPICS WILL BE COVERED IN LAB