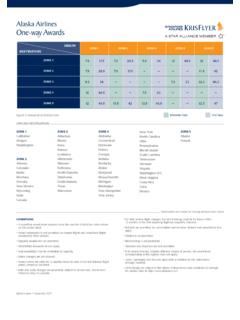
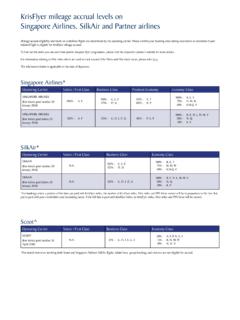
Transcription of SINGAPORE AIRLINES
1 Annual Report F Y 2016/17 SINGAPOREAIRLINESMISSION STATEMENTS ingapore AIRLINES is a global company dedicated to providing air transportation services of the highest quality and to maximising returns for the benefit of its shareholders and 70 YEARS OF EXCELLENCE: The SINGAPORE AIRLINES Group s history dates back to 1947 with the maiden flight of Malayan Airways Limited. The airline was later renamed Malaysian Airways Limited, and then Malaysia- SINGAPORE AIRLINES . In 1972, Malaysia- SINGAPORE AIRLINES split into SINGAPORE AIRLINES and Malaysian Airline System. Initially operating a modest fleet of 10 aircraft to 22 cities in 18 countries, SINGAPORE AIRLINES commitment to service excellence, product leadership and network connectivity quickly distinguished it as a world-class international airline group.
2 Today, SINGAPORE AIRLINES operates a modern passenger fleet of more than 100 aircraft. Together with wholly-owned subsidiaries SilkAir, Scoot, Tiger Airways (which operates as Tigerair) and SIA Cargo, the SIA Group fleet comprises nearly 180 aircraft. The combined passenger network covers 131 destinations in 35 countries. More than 31 million passengers were carried by the SIA Group s four SINGAPORE -based passenger AIRLINES in the 2016/17 financial year. SINGAPORE AIRLINES and its subsidiaries today employ more than 25,000 staff, with the world-famous SINGAPORE Girl as an iconic symbol of quality customer care and service.
3 CONTENTSOVERVIEW2 3-Year Financial Highlights3 SIA Group Portfolio4 Statistical Highlights6 Significant EventsSTRATEGY8 A Global Flyer 10 A Premium Full-Service Airline12 An Innovative Market Leader14 Celebrating 70 Years of Excellence16 Our Strategy for the Future18 Chairman s Letter to Shareholders20 Board of DirectorsPERFORMANCE22 The Year in Review24 Network26 Fleet Management27 Products and Services32 People Development34 Environment35 Community Engagement36 Subsidiaries44 Financial Review60 AwardsGOVERNANCE62 Statement on Risk Management63 Corporate Governance Report75 Membership and Attendance of SINGAPORE AIRLINES Limited76 Further Information on Board of DirectorsFINANCIAL80 Financial Report212 Information on Shareholdings214 Share Price and Turnover 215 Notice of Annual General MeetingIBC Corporate DataOUR JOURNEY Report FY2016/17013-Year Financial Highlights$ cents20 centsNET ASSET VALUE PER SHAREEARNINGSPER SHARETOTAL DIVIDEND PER SHARENet asset value per share is computed by dividing equity attributable to owners of the parent by the number of ordinary shares in issue excluding treasury
4 Per share is computed by dividing profit attributable to owners of the parent by the weighted average number of ordinary shares in issue excluding treasury final dividend of 11 cents per share will be paid on 16 August 2017 to shareholders as at 3 August the interim dividend of 9 cents per share paid on 24 November 2016, the total dividend for the 2016/17 financial year will be 20 cents per share.($ million)Total Group Revenue2016/172015/162014/1514,86915,239 15,566($ million)Group Operating Profit2016/172015/162014/15623681410($ million)Group Net Profit2016/172015/162014/15360804368 SINGAPORE Airlines02 SINGAPORE Airlines02 OverviewSIA Group PortfolioDuring the year in review, the SINGAPORE AIRLINES Group continued to expand its global network, leveraging its position as a leader in key markets around the SERVICELOW COSTS ingapore AirlinesSilkAirTigerairScoot18,990,166pa ssengers carried in FY2016/174,105, 576passengers carried in FY2016/175,145,835passengers carried in FY2016/173, 357.
5 174passengers carried in FY2016/17106 aircraft in fleet30 aircraft in fleet23 aircraft in fleet12aircraft in fleet3new destinations introduced3new destinations introduced12cities served in China5new destinations introduced70years of operation in 201752destinations in 14 countries13years of operation in 20178additional Dreamliners on firm orderAnnual Report FY2016/1703 Annual Report FY2016/1703 Statistical HighlightsFinancial Statistics not meaningfulR1 SINGAPORE AIRLINES financial year is from 1 April to 31 March. Throughout this report, all figures are in SINGAPORE Dollars, unless otherwise Return on equity holders funds is profit attributable to owners of the parent expressed as a percentage of the average equity holders funds.
6 R3 Total debt : equity ratio is total debt divided by equity attributable to owners of the parent as at 31 March. R4 Earnings per share (basic) is computed by dividing profit attributable to owners of the parent by the weighted average number of ordinary shares in issue excluding treasury Earnings per share (diluted) is computed by dividing profit attributable to owners of the parent by the weighted average number of ordinary shares in issue excluding treasury shares, adjusted for the dilutive effect on the exercise of all outstanding share options. R6 Net asset value per share is computed by dividing equity attributable to owners of the parent by the number of ordinary shares in issue excluding treasury shares at 31 Dividend cover is profit attributable to owners of the parent divided by total ChangeThe GroupFinancial Results ($ million)Total revenue14, 15, expenditure14, 14, profit before attributable to owners of the Position ($ million)Share capital1, 1, Treasury shares( )( )+ Capital reserve( )( ) Foreign currency translation reserve( )( )+ Share-based compensation Fair value reserve( )
7 ( )+ General reserve11, 11, Equity attributable to owners of the parent13, 12, + Return on equity holders funds (%) pointsTotal assets24, 23, + Total debt 1, 1, + Total debt : equity ratio (times) + timesValue added4, 5, Per Share DataEarnings basic (cents) Earnings diluted (cents) Net asset value ($) + DividendsInterim dividend (cents per share) centsFinal dividend (cents per share) centsDividend cover (times) timesThe CompanyFinancial Results ($ million)Total revenue11, 11, Total expenditure10, 11, Operating Profit before Profit after Value added3, 3, SINGAPORE Airlines04 SINGAPORE Airlines04 OverviewSingapore AirlinesRevenue passenger-km = Number of passengers carried x distance flown (in km)Available seat-km = Number of available seats x distance flown (in km)
8 Passenger load factor = Revenue passenger-km expressed as a percentage of available seat-kmPassenger yield = Passenger revenue from scheduled services divided by revenue passenger-kmPassenger unit cost = Operating expenditure (less bellyhold revenue from SIA Cargo) divided by available seat-kmPassenger breakeven load factor = Passenger unit cost expressed as a percentage of passenger yield. This is the theoretical load factor at which passenger revenue equates to the operating expenditure (less bellyhold revenue from SIA Cargo)SilkAirRevenue passenger-km = Number of passengers carried x distance flown (in km)Available seat-km = Number of available seats x distance flown (in km)Passenger load factor = Revenue passenger-km expressed as a percentage of available seat-kmPassenger yield = Passenger revenue from scheduled services divided by revenue passenger-kmPassenger unit cost = Operating expenditure (less cargo and mail revenue)
9 Divided by available seat-kmPassenger breakeven load factor = Passenger unit cost expressed as a percentage of passenger yield. This is the theoretical load factor at which passenger revenue equates to the operating expenditure (less cargo and mail revenue)Budget Aviation HoldingsRevenue passenger-km = Number of passengers carried x distance flown (in km)Available seat-km = Number of available seats x distance flown (in km)Passenger load factor = Revenue passenger-km expressed as a percentage of available seat-kmRevenue per revenue seat-km = Passenger revenue from scheduled services divided by revenue passenger-kmCost per available seat-km = Operating expenditure divided by available seat-kmBreakeven load factor = Cost per available seat-km expressed as a percentage of revenue per revenue seat-km.
10 This is the theoretical load factor at which passenger revenue equates to the operating expenditureSIA CargoCargo load = Cargo and mail load carried (in tonnes) x distance flown (in km)Gross capacity = Cargo capacity production (in tonnes) x distance flown (in km)Cargo load factor = Cargo and mail load (in tonne-km) expressed as a percentage of gross capacity (in tonne-km)Cargo yield = Cargo and mail revenue from scheduled services divided by cargo load (in tonne-km)Cargo unit cost = Operating expenditure (including bellyhold expenditure to SINGAPORE AIRLINES ) divided by gross capacity (in tonne-km)Cargo breakeven load factor = Cargo unit cost expressed as a percentage of cargo yield.