Transcription of SPECIFICATIONS - DEL METALS
1 1|P a g eSPECIFICATIONSTo assist our customers we have compiled the following data sheets which provide technicalinformation frequently required by designers and are combined into three groups:a) ) ) and other suggested cold forming radii for the various grades of steel should, in our opinion, beattainable when using normal press brake practices. Greater care in the preparation of materials andbending practice could result in smaller radii being obtained. More generous radii may be required forrolling establishment of specific welding techniques depends upon many factors such as temperature ofthe work piece and/or atmosphere, the welding process employed, the thickness and chemistry ofthe materials being joined, joint restraint etc. As a result only generalized welding information can beoffered. In general, an electrode is employed whose strength is equal to that of the materials beingjoined. Suggested preheat and interpass temperatures are tabulated on the following steels-page steels-page 143 These are appreciably in agreement with those stipulated by both the and the covering welded structures and should be adequate to avoid weld cracking.
2 However,higher preheat and interpass temperatures may be required depending upon the actual weldingconditions associated with specific |P a g eGuide to Structural steel SelectionCSA SteelCSA ofSimilar Steel1 ASTM Designation ofSimilar Steel1 Max. ShapeGroupMaximum ThicknessPlate or BarHSS ; A283 1/4--400G60G-3301 1/4--260W38WA364401 1/2--300W42W*, 44WA572 Gr. 42 Gr. 453 & HSS401 1/2165/8350W50WA572 & HSS401 1/2165/8380W*55W*A572 KFG51004--300T44TA572 KFG51004--350T50TA441 K; A572 & HSS1004165/8380T*55T*A572 KFGHSS--165/8400T60TA572 KFG2203/4--480T70TA572 KFG1203/4--350R50RA2421141/2--350A50AA24 2A; A5885 & HSS1004165/8400A60A-2401 1/2--480A70A--203/4--700Q100QA514-502--* These grades are available in hollow structural sections only.(1) Similarity in yield strength, description and application; not necessarily in chemical composition ortest requirements; see the individual SPECIFICATIONS for details.(2) Assumessuitable welding technique is used.(3) Refers to steel without paint or other protective coating.
3 (4) Atmospheric corrosion resistance can be enhanced to FAIR by specifying copper |P a g eWeld-ability2 Low to F--}4 Carbon-manganesesteels, SemiKilledBolted structures------VG-G--}4 Weldablecarbon-manganesesteels, Semi-KilledGeneral useweldedconstructionVG-G--VG-G--VG-G--} 4VG-G--VG-G--VG-GVG-}4 Welded carbon-manganesesteels, Killed FineGrain (KFG)practice, for lowtemperatureserviceWelded bridgesVG-GVG-VG-GVG-VG-GVG-}4VG-GVG-VG- GVG-G-VGLow-alloycorrosionresisting steel ,KilledExposedunpaintedcladding and lightstructuralmembersVG-GVGVGLow-alloyc orrosionresisting steel ,KFG for lowtemperatureserviceExposedunpaintedbri dgesVG-GVGVGVG-GVGVGG withpropertechnique--Low-alloy, KFG,Quenched andTempered highstrength steelBridges andspecialapplications4|P a g eShape Size GroupingsFor Tensile Property ClassificationShapeGroup 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Wide Flange ShapesW610 x82,W920 x 201W920 x 342W360 x 347W360 x 900(Nominal depth in mm92to 313 446 818 1086 Mass in )W530 x 66W840 x 176W840 x 299W310 x 313to 85 226 359 500 incl.
4 (WShapes)W460 x 52W760 x 147W360 x 216to 106 314 314 x 39W690 x 125W310 x 179to 85 265 283 x 33W610 x 101to 79 241 x 21W530 x 92to 86 219 x 18W460 x 113to 67 177 x 15W410 x 100to 71 149 x 13W360 x 91to 37 196 x 24,W310 x 9728to 158 x 19W250 x 73to 167 x 8610 Light Miscellaneousto 56 Kg/mBeams and Columns(M Shapes)Standard I Beamsto 52 Kg/mOver 52Kg/m(S Shapes)HBearing Pilesto 152 Kg/mOver 152Kg/m(HP Shapes)Standard Channelsto (C Shapes)Miscellaneous Car &to Channels(MC Shapes)Angles, Bulb Angles,to 13 13 mmto 20 20 and Rolled Tees(1)Shape size grouping of rolled shapes is in accordance with CSA G40-20-M19785|P a g eCSA and (1976)Structural Quality SteelsThis Standard includesmaterials having a number of different types, defined as follows:Type G-General Construction of this type meet minimum strength requirements;however, the chemical control is not such that all of these steels may be welded satisfactorily undernormal field conditions.
5 They are primarily designed for applications involving bolted connections or forwelding under carefully controlled shop conditions;Type W-Weldable of this type meet minimum strength requirements andare suitable forgeneral welded construction where notch toughness at low temperatures is not a prime may include buildings, compression members of bridges, T-Weldable of this type are suitable for welded construction and may be specifiedwhen low-temperature notch toughness is a prime consideration in design. In such cases Charpy V-notchtesting should be specified by the purchaser to ensure that the impact requirements are R-AtmosphericCorrosion-Resistant Structural of this type display an atmosphericcorrosion resistance approximately four times that of plain carbon steels.* These steels may bereadily welded up to the maximum thickness covered by thisStandard. Applications includeunpainted siding, unpainted light structural members, etc., where notch toughness at low temperaturesis not a A-Atmospheric Corrosion-Resistant Weldable Structural of this type displayanatmospheric corrosion resistance of approximately four times that of plain carbon steels.
6 * These steelsmay be welded readily under normal conditions and are often used in structures in the unpaintedcondition. These steels may be specified when low-temperature notch toughness is a primeconsideration in design. In such cases, Charpy V-notch testing should be specified by the purchaser toensure that the impact requirements are met.*Copper content not exceeding per Q-Quenched and Tempered Low Alloy steel of this type display a very high yieldstrength and good resistance to brittle fracture and are especially suited for bridges and similarstructures. While these steels may be readily welded, the welding and fabrication techniques are offundamental importance and must not adversely affect the properties of the plate , especially the heat-affected number of strength levels are available under this Standard, and are designated by theapproximate yield strength which is incorporated in the Grade Number, similar to thefollowing examples:Metric 230G-(Yield Strength 230 MPa-Type G).
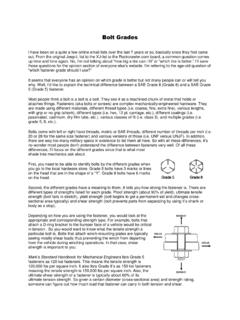
7 Imperial (1976)-Grade 33G-(Yield Strength 33 Ksi-Type G).The grades, types, and strength levels normally available are shown on the following |P a g eCSA FORMINGP lates and bars of all CSA grades can be satisfactorily formed on a press brake or otherconventional coldbending equipment There is a considerable difference in the formability of thedifferent grades due to the strength level and chemical composition differences; because of this, caremust be exercised when forming is following table summarizes the results of research and experience and is offered as a guide to theminimum bend radius that can be expected for different grades and thicknesses. These criteria applystrictly to longitudinal bends, , where the bend line is transverse tothe rolling direction. Transversebends may require up to twice the indicated radius. It is assumed that the bend is not carried out on anedge that has been flame-hardened by gas cutting, on heavily burred or work hardened by shearingunless some special edge preparation, such as grinding or chipping has been carried MINIMUM BEND RADIUS: Longitudinal BendsGradeUp to 6 Over 6 to 12 Over 12 to 25 Over 25 to 40 Over 40 to 50230G1t1t2t3t4t350G2 1/2t3 1/2t---400G3t5t---260W1 1/2t1 1/2t2t3t-300W1 1/2t2t3t4t-350W2 1/2t2 1/2t4t--400W3 1/2t3 1/2t6t--480W5t5t---260T1 1/2t2t3t4t4t300T1 1/2t2t3t4t5t350T2 1/2t3t4t--400T3 1/2t3 1/2t6t--480T4t5t6t--350R2t3t---350A2t3t5 t--400A3t4t6t--480A4t5t6t--T = thickness in mmHOT FORMING-is recommended for all thicknesses not showing a value.
8 Since temperature can be a majorcause of bend failure , in no case should bending be carriedout at a metal temperature below 15 of 350 MPa and higher yield strength will require greater bending and hold down force than lowerstrength steels and provisions must be made for a greater than usual degree of cold bending ofstructural shapes is a most difficult task and the steel producer should be consulted beforecold bending of any degree of severity is carried |P a g eCSA grades of CSA steels can be readily welded with the exception ofGrades350G and 400G which can be welded under carefully controlled conditions. It is urged that therequirements of CSA Standard W59-1977 "Welded steel Construction (Metal Arc Welding)" be followedas a suggestions set forth in this guide areintended to meet these requirements. However, theapplicable standard or code should be consulted before establishing any FILLER MATERIALS:GradeManual Electrodes(SMAW) CSA , (SAW) Metal Arc(GMAW) Metal Arc(FCAW) CSA , 11, 13, 20, 27F6Z-ELXXE70-X, E70U-XE60T-8, E70T-X260W, 260TE7015, 16, 18, 28, 38F70-EMXXE70-X, E70U-IE60T-8, E70T-X(a)300W, 300TE7015, 16, 18, 28, 38F70-EMXXE70-X, E70U-IE70T-X (a)350G, 350W350R, 350AE8015-B4L61+(b)E70T-G2400AE8016-B2, C1-3 XXX10 FluxE8018-82, C1-3400G, 400WW8015, 16, 18F80-EMXXE80SE80T400T480W, 480TE8015, 16, 18F90-EMXXE90E90T480AE9018M(b)(b)(b)(a)E xclusive of E70T-2, E70T-3, E70T-G.
9 (b) Consult consumable steel :When steels of Types Rand A are used in the exposed, bare, unpainted condition, the electrodes suggested orothers producing a similar alloy composition in thedeposited metal should be used, For applications where thematerial is not boldly exposed, where colour match is not important, for all but capping passes in multipasswelds and for narrow single pass welds, the electrodes suggested for Grades 300T, 400T and 480T may be MINIMUM PREHEAT AND INTERPASS TEMPERATURES:Welding should not be carried out when the ambient temperature is below-20 C. When the base metaltemperature is below the temperature listed for the welding processand thickness it should be preheated insuch a manner that the surface of the material on which the weld is to be deposited is at or above the suggestedminimum temperature for a distance equal to the thickness of the material but not less than 75mm bothlaterally and in advance of the welding.
10 When the base metal temperature is below 0 C, it should be brought up toand maintained at 10 C during welding, for all grades. Temperatures higher than the minimum suggested may berequired for highly restrained of theShielded Metal Arc (other thanShielded Metal Arc with Basic Electrodes,Thickness PartBasic Electrodes)Submerged Arc Welding, Gas Metal Arc Welding,atFlux-Cored Arc WeldingFlux-Cored Arc WeldingPoint of Welding230G, 300W, 300T260W 260T 350R350G 400W 400T300W 300T 350A400G 480W 480T350W 350T 400A480 AUp to 20 mmnonenone10 COver 20 to 38 mm65 C10 C65 COver 38 to 63 mm110 C65 C110 COver 63 mm150 C110 C150 C8|P a g eCSA (1976)Type G General Construction SteelDISCUSSIONType G steels are basically carbon-manganese steels, usually produced to a semikilled steel -makingpractice and have minimum controls placed upon the chemical composition. The steels are designedto provide the required strength levels with the lowest possible cost of materials. Steels of this typehave found considerable usagein bolted structures, such as transmission towers, microwave towers,material handling equipment etc.