Transcription of Supporting Breastfeeding and Lactation: The Primary Care ...
1 Updated 9/2009 Supporting Breastfeeding and Lactation: The Primary Care Pediatrician s Guide to Getting PaidBreastfeeding support can often be quite time-intensiveinitially but pays off in a healthier patient population. It is inyour insurers best interests that you provide theseservices, and be reimbursed pamphlet is a guide to help pediatric practitioners getpaid appropriately for their time as they incorporate morebreastfeeding support into their for problems with Breastfeeding and lactation is justlike billing for any other pediatric and other billable licensed practitioners(nurse practitioners* and physician assistants*) may.
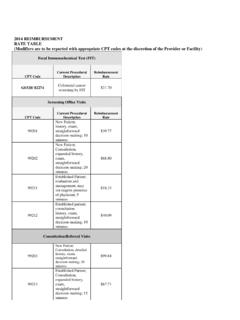
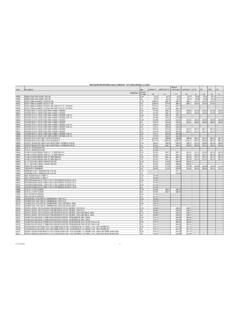
2 Use standard CPT codes, , 99212 99215 Use standard ICD-9-CM codes, , Code based on time, if greater than 50% of time isspent in counseling,education, or coordination of care Use modifier 25 appended to a separately reportedoffice or other outpatient service to bill for extendedtime spent on feeding problems at a well baby visit. Bill for care provided for the mother, often as a newpatient, in addition to billing for the baby, if history,exam, diagnosis and treatment are done for practice can also, under specific circumstances,charge for services provided by nurses and such alliedhealth professionals as lactation consultants, healtheducators, and nutritionists.
3 Using a variety of used ICD-9-CM for billing the three-to-five day for extra time spent at well baby of time-based for for care provided for the for allied health professional services*Unless restricted by their state or payors scope of practice pamphlet does NOT discuss the detailed, important and specificguidelinesaffecting decisions about billing for nurse practitioners andphysician assistants, , whether credentialed and billed under theirown names vs. billing for their services incident to physician care andthus billed under the physician s name.
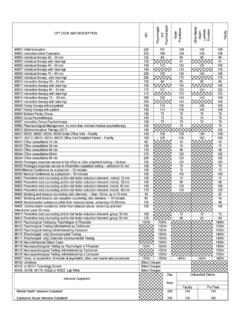
4 That topic is beyond the scopeof this pamphlet. However, all physicians employing such allied healthcare providers need to be aware of, and understand, the applicablebilling rules, and apply them carefully whether billing for feedingproblems, or for any othermedical services in the pediatric used ICD-9-CM codesBabyFeeding problemsFeeding problems/ slow feeding, vomiting in vomiting in problem, infant (> 28 days) , infant (>28 days) jaundice, and hydrationDehydration, to thrive, weight gain, FTT, infant (>28 days)
5 Well as all the diagnoses associatedwith size and crying, colic or intestinal issuesAbnormal in bowel arched specified follow-up (When the original reason for visit has resolved)MotherBreast& NippleissuesAbscess, breast/ Mastitis, milk duct/ Mastitis, engorgement, , or axillary breast specified nipple/breast specified nipple/breast , cracks or , nipple, (staph), nipple684 Candidiasis, nipple or sleep , failure to , , specified disorders of of specified follow-up (When the original reason for visit has resolved)Updated 9/2009 The three-to five-day visitThe AAP recommends1,2,3this visit to assess jaundice in ALL infants, regardless offeeding method.
6 To address other early feeding issuesFor Breastfeeding infants, the purpose of this visit is to assess weight, hydration and jaundice and to address the ability of the infant hydration growth and activity and maintain maternal assessment usually : Infant feeding, sleep and activity patterns,urine and stool output; maternal lactogenesis,comfort and : Weight, and exam for dehydration, sleepinessand level of indicated, observation of a feeding, includingweights before and after , interventions, and counseling if indicatedThe visit may be billed as either a first routine well visit OR a follow-up visit, for a problem noted earlierBilling as a well visitIf the infant s previous record does not document afeeding problem, and no other health problem has beenidentified.
7 Then this first office visitshould be coded andbilled as an established patient well-child visit. CPT code 99391 ((and any other indicateddiagnosis codes, , for jaundice or feedingproblem)In any well visit, the clinician is expected to spend timeaddressing routine feeding issues. When unusual timebeyond the usual is required, there are two ways ofbilling for this extra extratime is required:If, a feeding problem exists which requiresmorethan anordinary amount of time to address, the physician may,depending on the circumstances, choose one or both ofthe following options, as clinically appropriate: Prefer to spend extratime at this visit to address theproblem immediately.)
8 This may then be billedseparately using the 99212-99215 codes appendedwith the modifier 25, following the guidelinesdescribed on the next page Schedule a follow-up visit, for example, within a fewdays, or at one to two weeks of age. That follow-upvisit would then be billable using the office follow-upcodes (99211-99215) related to that feeding and billing as a follow-up visitFor this to be billed as a follow-up visit,the reason forfollow-up must be clearly established on the precedinghealth or hospitalrecord.
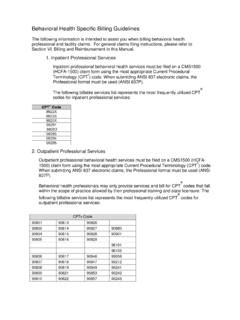
9 The earlier chart must document the unresolved problemthat requires a follow-up visit. An appropriatediagnosis code, , newborn feedingproblem ( ), or jaundice ( ) must beincluded with thehospital or birth center sdischargediagnoses, to establish the reason for the follow-up visit. Alternatively, telephone chart notes document that, sincedischarge, a new problem ofearlyproblems requiring follow-up include, butare not limited to: Jaundice Infrequent and/or dark stools Ability to transfer milk not established Infrequent Breastfeeding Weight loss exceeds 7% Breastfed infant being fed formulaOptions for coding and billingas a follow-up routinely with physician or billablelicensed health care provider ( , NP or PA).
10 Use office follow-up codes99212 99215 andappropriate ICD-9-CM codes: Ifthe feeding problem persists, use an ICD-9-CMsuch as , , , etc. If, however, the feeding problem has resolved, useinstead ICD-9-CM code , just as you wouldfor a follow-up resolved otitis visit with possible triage to physician orother billable licensed health care providerThis is aweight check and quick screen for feeding,sleep, and stool patterns. It is only billable to the nurseas a 99211 if it is NOT triaged to the doctor.