Transcription of Synthesis and Intrinsic Viscosity-molecular Weight ...
1 Chemical Science International Journal 20(1): 1-9, 2017; Article ISSN: 2456-706X. (Past name: American Chemical Science Journal, Past ISSN: 2249-0205). Synthesis and Intrinsic Viscosity-molecular Weight Relationship of Poly(ethylene adipate). Liwei Chen1, Weilan Xue1* and Zuoxiang Zeng1. 1. Institute of Chemical Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, 200237, Shanghai, China. Authors' contributions This work was carried out in collaboration between all authors. Authors LC and WX designed the study. Author LC performed the experiment and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Author ZZ. managed the analyses of the study and revised the first draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
2 Article Information DOI: Editor(s): (1) Georgiy B. Shul'pin, Semenov Institute of Chemical Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia. Reviewers: (1) Ogah Anselm Ogah, Ebonyi State University, Nigeria. (2) M. Siddiq, Quaid-I-Azam University, Pakistan. (3) Jana Tothova, Technical University in Kosice, Slovakia. Complete Peer review History: Received 3rd July 2017. th Original Research Article Accepted 24 July 2017. st Published 1 August 2017. ABSTRACT. In this work, two series of poly (ethylene adipate) (PEA) samples with broad and narrow molecular Weight distribution (MWD) were prepared by the polymerization between adipic acid and ethylene glycol. An accurate and swift method, one-point method, was used to determine the Intrinsic viscosity of PEA samples.
3 On the basis of Mark-Houwink-Sakurada (MHS) equation, the relationship between the Intrinsic viscosity and molecular Weight was built for PEA (Mw 11000) in tetrahydrofuran at 298K. The average molecular weights (Mn, Mv, Mw and Mz) were determind by using Gel-Permeation chromatography (GPC). The constants, a and K of MHS equation for the PEA. samples dissolved in tetrahydrofuran at 298K were determined by a numerical method, and the influence of polydispersity correction factor (qMHS) on the relationships were studied for PEA with narrow MWD ( ) and broad MWD ( ). Keywords: One-point method; Poly(ethylene adipate); Intrinsic viscosity; molecular Weight ; Mark- Houwink-Sakurada. _____. *Corresponding author: E-mail: Chen et al.
4 ; CSIJ, 20(1): 1-9, 2017; Article NOMENCLATURES Where K and a are constants for a certain solvent and temperature. By determining of PEA : Poly(ethylene adipate) PEA samples with different molecular Weight , we MWD : Molecular Weight distribution may obtain the values of K and a. qMHS : Polydispersity correction factor a : Viscometric constants In the traditional way, the Intrinsic viscosity of K : Viscometric constants (dL/g) polymer is determined by dilution extrapolation Mn : Average molecular Weight (g/mol) method which means we need to determine Mz : Average molecular Weight (g/mol) the specific viscosity of the polymer with Mw : Average molecular Weight (g/mol) four different concentrations for each sample. Mv : Viscosity-average molecular Weight Cheng, et.
5 Al [16] proposed an accurate (g/mol) and swift method (one-point method) for : Intrinsic viscosity (dL/g) determining the Intrinsic viscosity of polymer : Relative viscosity (dL/g) samples. : Specific viscosity (dL/g). : PEA solution concentration (g/dL) Thus, in this work, two series of PEA samples AD : Absolute deviation (%) with broad and narrow MWD were prepared by the polymerization of adipic acid and ethylene 1. INTRODUCTION glycol. GPC was used to determine the molecular Weight of the Intrinsic As one of the main raw materials used in the viscosities of the PEA samples dissolved in polyurethane industry, poly(ethylene adipate) tetrahydrofuran at 298K were determined by one- (PEA) with different molecular Weight is widely point method and verified by the dilution used in the production of flexible or rigid extrapolation method.
6 Lastly, the MHS constants polyurethane foam, polyurethane rubber, (K and a) for PEA were obtained. polyurethane elastomer and hot melt adhesives [1-4]. Especially, when used as a raw material for 2. EXPERIMENTAL. hot melt adhesives, the higher the molecular Weight of PEA, the faster the setting speed of hot Materials melt adhesives [5], and the setting speed can affect the bonding rateof the hot melt adhesives. The PEA samples were prepared by Thus, it is significant to determine the molecular polycondensation between adipic acid and Weight of PEA by an easy and effective method. ethylene glycol. Adipic acid (Sinopharm), Han, G. C et. al [6] studied the properties of Ethylene Glycol (Wuxi Jani chemical Co. LTD). poly(1,4-butylene adipate).
7 Harris, R. F et. al [7] are all of chemically pure-grade. Tetrahydrofuran investigated polyurethane elastomers based on is all of analytical grade. Distilled water was also molecular Weight advanced poly(ethylene ether used. carbonate) diols. However, no research work about the properties of PEA has been reported. Synthesis of PEA. Now in the polyurethane industry, many ways The Synthesis of PEA consists of two main including Gel-Permeation chromatography (GPC) stages: esterification and polymerization. [8-9], end-group analysis [10], lighting-scattering [11], H-NMR [12] and viscometry can be used to In the first stage, the esterification reaction of determine the molecular Weight of PEA. But adipic acid and ethylene glycol (molar during polyurethane production, determination of ratio=1 ~ ) was carried out at the molecular Weight (Mn, Mw and Mz) should be fast temperature of 413K-423K in a 250 ml four-neck and simple, and among these methods above, flask (200 rpm) which was equipped with a only viscometry can satisfy the requirements.
8 Single-blade, a platinum sensor and a fractionating column allowing the withdrawal of According to Mark-Houwink-Sakurada (MHS) water during the reaction. Nitrogen (50 ml/min). equation [13-15], the relationship between was continuously bubbled through the reactor for viscosity-average molecular Weight (Mv ) and the further removal of water from the Intrinsic viscosity ( ) can be described as reactor was heated with the oil jacket, and the follows: reaction temperature was controlled automatically by adjusting the oil temperature = (1) which was maintained within 2. Chen et al.; CSIJ, 20(1): 1-9, 2017; Article After the esterification reaction of 3 to 4 hours, Polydispersity Correction Factor (qMHS). the polymerization reaction was started by raising the reaction temperature to 493K-503K Generally, Mv is not experimentally accessible, via temperature programmed mode at Pa.
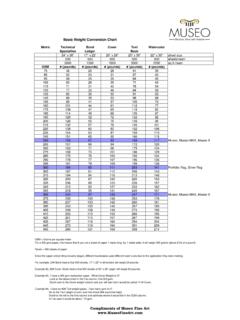
9 And in many reports, average molecular weights The polymerization reaction lasted for about 8 (Mn, Mw and Mz) are used in the MHS equation hours until the designed molecular Weight was instead of equation can be modified obtained. Then the products were extracted by [18,19] as follows: multistage precipitation fractionation [17] to obtain the PEA samples with broad and narrow = = ( / ) = (3). MWD. Where and ( / ) are polydispersity Gel-permeation Chromatography correction factors. The value of is a statistical function of MWD and it can be A GPC equipment (Waters-1515) connected to a calculated [20-22] as follows: refractive index detector was used to determine the average molecular weights (Mn:number = ( / ) ( / ) (4).)
10 Average Weight ; Mv:viscosity-average molecular Weight ; Mw: Weight -average molecular Weight ; Mz: Where b and c can be calculated [22, 23] as Z-average molecular Weight ) of the PEA samples. follows: Separation was carried out at 303K using tetrahydrofuran of chromatographic grade as c = ( (5). eluentwith a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The average molecular weights and areas of fractions of b = *+ + *( ( / ) 1 -. (6). various molecular weights were calculated with Breeze 2 software. *+ = + (. &0 (7). Intrinsic Viscosity *( = + In this work, the Intrinsic viscosities of PEA ( (8). samples were determined by the Dilution extrapolation method and the one-point method *0 = + respectively. ( (9). Dilution extrapolation method In the light of the consecutive steps, the estimation of requires prior knowledge of The Intrinsic viscosity of PEA samples dissolved the viscometric constant iterative procedure in tetrahydrofuranat 298K was determined in the proposed by Kasaai [11] can be used to Ubbelohde viscometer by extrapolation to zero circumvent the difficulty.)))))












![ABSTRACT arXiv:1409.1556v6 [cs.CV] 10 Apr 2015](/cache/preview/4/e/0/e/4/4/2/c/thumb-4e0e442c20fc4f8e108fa20a1095af07.jpg)



