Transcription of Tax and Estimated Withholding - irs.gov
1 's New for 1. Tax Withholding for and Fringe and 2. Estimated Tax for Does Not Have To Pay Estimated Must Pay Estimated To Figure Estimated To Pay Estimated To Figure Each To Pay Estimated 3. Credit for Withholding and Estimated Tax for Social Security or Railroad Retirement Tax 4. Underpayment Penalty for Your Required Annual Payment (Part I)..50 Short Method for Figuring the Penalty (Part III)..50 Regular Method for Figuring the Penalty (Part IV)..50 Annualized income Installment Method (Schedule AI)..53 Farmers and of To Get Tax federal income tax is a pay-as-you-go tax. You must pay the tax as you earn or receive in-come during the year. There are two ways to pay as you If you are an employee, your employer probably withholds income tax from your pay.
2 In addition, tax may be with-held from certain other income , such as pensions, bonuses, commissions, and gambling winnings. The amount withheld is paid to the IRS in your tax. If you don t pay your tax through Withholding , or don t pay enough Department of the TreasuryInternal Revenue ServicePublication 505 Cat. No. 15008 ETaxWithholdingand EstimatedTaxFor use in 2018 Get forms and other information faster and easier at: (English) (Espa ol) ( ) ( ) (Pусский) (Ti ngVi t) Userid: CPMS chema: tipxLeadpct: 100%Pt. size: 8 Draft Ok to PrintAH XSL/XMLF ileid: .. tions/P505/2018/A/XML/Cycle03/source(Ini t. & Date) _____Page 1 of 59 7:56 - 16-Apr-2018 The type and rule above prints on all proofs including departmental reproduction proofs. MUST be removed before 16, 2018tax that way, you might have to pay esti-mated tax.
3 People who are in business for themselves generally will have to pay their tax this way. You may have to pay estima-ted tax if you receive income such as divi-dends, interest, capital gains, rents, and royalties. Estimated tax is used to pay not only income tax, but other taxes such as self-employment tax and alternative mini-mum publication explains both of these meth-ods. It also explains how to take credit on your return for the tax that was withheld and for your Estimated tax you didn t pay enough tax during the year, either through Withholding or by making estima-ted tax payments, you may have to pay a pen-alty. Generally, the IRS can figure this penalty for you. This underpayment penalty, and the ex-ceptions to it, are discussed in chapter aliens. Before completing Form W-4, Employee's Withholding Allowance Certificate, nonresident alien employees should see the Instructions for Form 8233, Exemption From Withholding on Compensation for Inde-pendent (and Certain Dependent) Personal Services of a Nonresident Alien Individual.
4 Also see chapter 8 of Pub. 519, Tax Guide for Aliens, for important information on and suggestions. We welcome your comments about this publication and your suggestions for future can send us comments from you can write to:Internal Revenue ServiceTax Forms and Publications1111 Constitution Ave. NW, IR-6526 Washington, DC 20224 Although we cannot respond individually to each comment received, we do appreciate your feedback and will consider your comments as we revise our tax forms and publications. Visit to download forms and publications. Otherwise, you can go to to order current and prior-year forms and instructions. Your order should arrive within 10 business questions. If you have a tax question not answered by this publication, check and How To Get Tax Help at the end of this 's New for 2018 Use your 2017 tax return as a guide in figuring your 2018 Estimated tax, but be sure to consider the in tax rates.
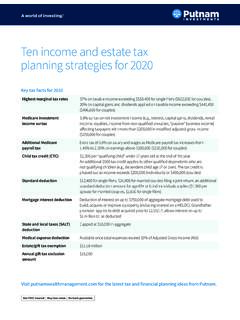
5 For 2018, most tax rates have been reduced. The 2018 tax rates are 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35% and 37%.Moving expenses no longer deductible. For 2018, you can no longer deduct your moving expenses unless you are a member of the Armed Forces on active for personal exemptions sus-pended. For 2018, you can t claim a personal exemption deduction for yourself, your spouse, or your tax credit and additional child tax credit. For 2018, the maximum credit is in-creased to $2,000 per qualifying child. The maximum additional child tax credit is increased to $1,400. In addition, the income threshold at which the credit begins to phase out is in-creased to $200,000 ($400,000 if married filing jointly).Credit for other dependents. A new credit of up to $500 is available for each of your depend-ents who does not qualify for the child tax credit.
6 In addition, the maximum income thresh-old at which the credit begins to phase out is in-creased to $200,000 ($400,000 if married filing jointly).Social security number (SSN) required for child tax credit. Your child must have an SSN issued before the due date of your 2018 return (including extensions) to be claimed as a quali-fying child for the child tax credit or additional child tax credit. If your dependent child has an ITIN, but not an SSN, issued before the due date of your 2018 return (including extensions), you may be able to claim the new credit for other dependents for that income of children. For 2018, the tax rates and brackets for the unearned income of children have changed. The new tax rates applicable to unearned income in excess of $2,550 are 24%, 35%, and 37%.
7 Changes to itemized deductions. For 2018, the following changes have been made to item-ized deductions that can be claimed on Sched-ule itemized deductions are no longer limited if your adjusted gross income is over a certain can deduct the part of your medical and dental expenses that is more than of your adjusted gross deduction of state and local income , sales, and property taxes is limited to a combined, total deduction of $10,000 ($5,000 if married filing separately).You can no longer deduct job-related ex-penses or other miscellaneous itemized deductions that were subject to the 2% of AGI floor. You may still deduct certain other items on Schedule A, such as gam-bling indebtedness incurred after December 15, 2017, the deduction for home mort-gage interest is limited to interest on up to $750,000 of home acquisition indebted-ness.
8 This new limit doesn t apply if you had a binding contract to close on a home after December 15, 2017, and closed on or before April 1, 2018, and the prior limit would can no longer deduct interest on home equity indebtedness, which means indebt-edness not incurred for the purpose of buy-ing, building, or substantially improving the qualified residence secured by the limit on charitable contributions of cash has increased from 50% to 60% of your adjusted gross more information, see the Instructions for Schedule for qualified business income . For tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, taxpayers other than corporations are en-titled to a deduction of up to 20% of their quali-fied business income from a qualified trade or business. The deduction is subject to multiple limitations based on the type of trade or busi-ness, the taxpayer s taxable income , the amount of Form W-2 wages paid with respect to the qualified trade or business, and the unad-justed basis of qualified property held by the trade or business.
9 The deduction can be taken in addition to the standard or itemized deduc-tions. For more information, see Code section minimum tax (AMT) exemption amount increased. The AMT exemption amount is increased to $70,300 ($109,400 if married filing jointly or qualifying widow(er); $54,700 if married filing separately). The in-come level at which the AMT exemption begins to phase out has increased to $500,000 ($1,000,000 if married filing jointly).Standard deduction amount increased. For 2018, the standard deduction amount has been increased for all filers, and the amounts are as or Married Filing Sepa-rately $12, Filing Jointly or Qualifying Widow(er) $24, of Household $18, to the increase in the standard deduc-tion and reduced usage of itemized deductions, you may want to consider filing a new Form learning credit income limits.
10 In or-der to claim a lifetime learning credit, your modi-fied adjusted gross income (MAGI) must be less than $57,000 ($114,000 if married filing jointly).Retirement savings contribution credit in-come limits increased. In order to claim this credit for 2018, your MAGI must be less than $31,500 ($63,000 if married filing jointly; $47,250 if head of household).Adoption credit or exclusion. The maximum adoption credit or exclusion for employer-provi-ded adoption benefits has increased to $13,810. In order to claim either the credit or ex-clusion, your MAGI must be less than $247, income credit (EIC). You may be able to take the EIC in 2018 if:Three or more children lived with you and you earned less than $49,194 ($54,884 if married filing jointly),Two children lived with you and you earned less than $45,802 ($51,492 if mar-ried filing jointly),One child lived with you and you earned less than $40,320 ($46,010 if married filing jointly), orA child didn t live with you and you earned less than $15,270 ($20,950 if married filing jointly).