Transcription of The Importance of Root Cause Analysis During Incident ...
1 FactSheetThe Importance of root Cause Analysis During Incident InvestigationThe occupational safety and health administration (OSHA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) urge employers (owners and operators) to conduct a root Cause Analysis following an Incident or near miss at a A root Cause is a fundamental, underlying, system-related reason why an Incident occurred that identifies one or more correctable system By conducting a root Cause Analysis and addressing root causes , an employer may be able to substantially or completely prevent the same or a similar Incident from Process safety Management and EPA Risk Management Program RequirementsEmployers covered by OSHA s Process safety Management (PSM)
2 Standard are required to investigate incidents that resulted in, or could reasonably have resulted in, catastrophic releases of highly hazardous Similarly, owners or operators of facilities regulated under EPA s Risk Management Program (RMP) regulations must conduct Incident During an Incident investigation , an employer must determine which factors contributed to the Incident , and both OSHA and the EPA encourage employers to go beyond the minimum investigation required and conduct a root Cause Analysis . A root Cause Analysis allows an employer to discover the underlying or systemic, rather than the generalized or immediate, causes of an Incident .
3 Correcting only an immediate Cause may eliminate a symptom of a problem, but not the problem to Conduct a root Cause AnalysisA successful root Cause Analysis identifies all root causes there are often more than the following example: A worker slips on a puddle of oil on the plant floor and falls. A traditional investigation may find the Cause to be oil spilled on the floor with the remedy limited to cleaning up the spill and instructing the worker to be more A root Cause Analysis would reveal that the oil on the floor was merely a symptom of a more basic, or fundamental problem in the employer conducting a root Cause Analysis to determine whether there are systemic reasons for an Incident should ask: Why was the oil on the floor in the first place?
4 Were there changes in conditions, processes, or the environment? What is the source of the oil? What tasks were underway when the oil was spilled? Why did the oil remain on the floor? Why was it not cleaned up? How long had it been there? Was the spill reported?6 It is important to consider all possible what, why, and how questions to discover the root Cause (s) of an this case, a root Cause Analysis may have revealed that the root Cause of the spill was a failure to have an effective mechanical integrity program that includes inspection and repair that would prevent or detect oil leaks. In contrast, an Analysis that focused only on the immediate Cause (failure to clean up the spill) would not have prevented future incidents because there was no system to prevent, identify, and correct framing and conducting a root Cause investigation is important for a PSM or RMP-related Incident .
5 Take, for example, an Incident involving an overfill and subsequent leak of hydrocarbons from a relief valve system that ignites and kills multiple workers. Prior to this fatal Incident , there were multiple flammable releases from the relief valve system, but none ignited. The employer previously performed Incident investigations on the non-lethal inci-dents and determined that operator error was the Cause of the overfills and subsequent leaks. However, a proper root Cause investigation would have looked deeper into the Incident , and determined that funding cuts which resulted in a deficient mechanical integrity program and malfunctioning instrumentation led to a dangerous situation that operators could not have prevented.
6 Had these root causes been previously identified, the employer could have taken action to improve the mechanical integrity program and repair the instrumentation system, preventing the fatal of root Cause Analysis for Employers Conducting a thorough investigation that identifies root causes will help to prevent similar events from happening again. In this way, employers will reduce the risk of death and/or injury to workers or the community or environmental using root Cause Analysis to prevent similar events, employers can avoid unnecessary costs resulting from business interruption, emergency response and clean-up, increased regulation, audits, inspections, and OSHA or EPA fines.
7 Regulatory fines can become costly, but litigation costs can often substantially exceed OSHA and EPA fines. Employers may find that they are spending money to correct immediate causes of incidents that could have been prevented, or reduced in severity or frequency, by identifying and correcting the underlying system management , when an employer focuses on prevention by using root Cause Analysis , public trust can be earned. Employers with an Incident free record may be more likely to attract and retain high performing staff. A robust process safety program, which includes root Cause Analysis , can also result in more effective control of hazards, improved process reliability, increased revenues, decreased production costs, lower maintenance costs, and lower insurance premiums.
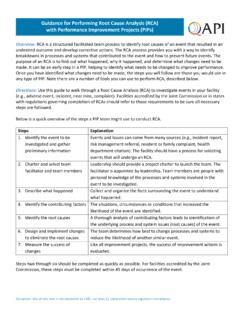
8 root Cause Analysis ToolsBelow is a list of tools that may be used by employers to conduct a root Cause Analysis . The tools are not meant to be used exclusively. Ideally, a combination of tools will be used. Brainstorming Checklists Logic/Event Trees Timelines Sequence Diagrams Causal Factor DeterminationFor simpler incidents, brainstorming and checklists may be sufficient to identify root causes . For more complicated incidents, logic/event trees should also be considered. Timelines, sequence diagrams, and causal factor identification are often used to support the logic/event tree of the combination of tools chosen, employers should use these tools to answer four important questions: What happened; How did it happen; Why it happened; and What needs to be and review of documents, such as maintenance logs, can be used to help answer these questions.
9 Involving employees in the root Cause investigative process, and sharing the results of those investigations, will also go a long way toward preventing future similar incidents. OSHA and EPA encourage employers to consult the resources below for more information about how to use these The Guidelines for Investigating Chemical Process Incidents, Center for Chemical Process safety , 2nd Edition, 2003. DOE Guideline- root Cause Analysis Guidance Document, Department of Energy, Washington, DC, February 1992. DOE Handbook-Accident and Operational safety Analysis , Volume I: Accident Analysis Techniques, July 2012, pp. 2-40 2-86. Quality Basics- root Cause Analysis for Beginners, James L.
10 Rooney and Lee N. Vanden Heuvel, Quality Progress, July 2004, pp. 45 53. Incident [Accident] Investigations, A Guide for Employers, A Systems Approach to Help Prevent Injuries and Illnesses, Department of Labor, occupational health and safety administration (OSHA), December 2015. OSHA s Incident investigation Topics Page. OSHA s On-site Consultation Program offers free and confidential occupational safety and health services to small and medium-sized businesses in all states and several territories, with priority given to high-hazard worksites. On-site consultation services are separate from enforcement and do not result in penalties or citations.