Transcription of THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK …
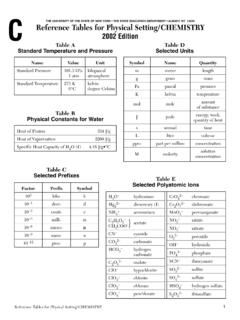
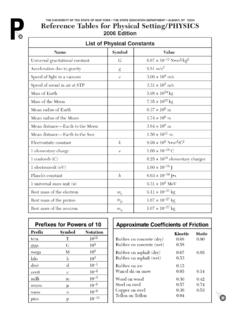
1 Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition1 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK THE STATE EDUCATION DEPARTMENT ALBANY, NY 12234 Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ CHEMISTRY2011 EditionTable AStandard Temperature and PressureTable BPhysical Constants for WaterTable CSelected PrefixesTable DSelected UnitsNameValueUnitStandard kPa kilopascal1 atm atmosphereStandard Temperature273 K kelvin0 Cdegree CelsiusHeat of Fusion334 J/gHeat of Vaporization2260 J/gSpecific Heat Capacity of H2O( ) J/g KFactorPrefixSymbol103kilo-k10 1deci-d10 2centi-c10 3milli-m10 6micro- 10 9nano-n10 12pico-pSymbolNameQuantitymmeterlengthgg rammassPapascalpressureKkelvintemperatur emolmoleamount ofsubstanceJjouleenergy, work,quantity of heatssecondtimeminminutetimehhourtimedda ytimeyyeartimeLlitervolumeppmparts per millionconcentrationMmolaritysolutioncon centrationuatomic mass unitatomic massCIons That FormSolubleCompoundsExceptionsGroup 1 ions (Li+, Na+, etc.)
2 Ammonium (NH4+)nitrate (NO3 )acetate (C2H3O2 or CH3 COO ) hydrogen carbonate(HCO3 )chlorate (ClO3 )halides (Cl , Br , I )when combined with Ag+, Pb2+, or Hg22+sulfates (SO42 )when combined with Ag+, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, or Pb2+Ions That FormInsolubleCompounds*Exceptionscarbona te (CO32 )when combined with Group 1ions or ammonium (NH4+)chromate (Cr O42 )when combined with Group 1ions, Ca2+, Mg2+, or ammonium (NH4+)phosphate (PO43 )when combined with Group 1ions or ammonium (NH4+)sulfide (S2 )when combined with Group 1ions or ammonium (NH4+)hydroxide (OH )when combined with Group 1ions, Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+, orammonium (NH4+)*compounds having very low solubility in H2 OFormulaNameFormulaNameReference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition2 Table FSolubility Guidelines for Aqueous SolutionsTable ESelected Polyatomic IonsH3O+hydroniumHg22+mercury(I)NH4+ammo niumC2H3O2 acetateCH3 COO }CN cyanideCO32 carbonateHCO3 hydrogen carbonateC2O42 oxalateClO hypochloriteClO2 chloriteClO3 chlorateClO4 perchlorateCr O42 chromateCr2O72 dichromateMnO4 permanganateNO2 nitriteNO3 nitrateO22 peroxideOH hydroxidePO43 phosphateSCN thiocyanateSO32 sulfiteSO42 sulfateHSO4 hydrogen sulfateS2O32 thiosulfateReference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition3010.
3 20. 30. 40. 50. 60. 70. 80. ( C) Solubility (g solute/100. g H2O) KClO3NH3 SO2 Table GSolubility Curves at Standard PressureReference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition4 Table HVapor Pressure of Four Pressure (kPa) kPapropanoneethanolwaterethanoicacidLiRb KCsBaSrCaNaMgAlTiMnZnCrFeCoNiSnPbH2 CuAgAuF2Cl2Br2I2 Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition5 Table IHeats of Reaction at kPa and 298 KTable JActivity Series**Reaction H(kJ)*CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O( ) (g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O( ) ( ) + 25O2(g) 16CO2(g) + 18H2O( ) 109432CH3OH( ) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 4H2O( ) 1452C2H5OH( ) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O( ) 1367C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 6H2O( ) 28042CO(g) + O2(g)
4 2CO2(g) (s) + O2(g) CO2(g) (s) + 3O2(g) 2Al2O3(s) 3351N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g)+ (g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g)+ (g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) (g) + O2(g) 2H2O( ) (g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) (s) + 3H2(g) C2H6(g) (s) + 2H2(g) C2H4(g)+ (s) + H2(g) C2H2(g)+ (g) + I2(g) 2HI(g)+ (s) H2OK+(aq) + NO3 (aq)+ (s) H2 ONa+(aq) + OH (aq) (s) H2 ONH4+(aq) + Cl (aq)+ (s) H2 ONH4+(aq) + NO3 (aq)+ (s) H2 ONa+(aq) + Cl (aq)+ (s) H2 OLi+(aq) + Br (aq) +(aq) + OH (aq) H2O( ) *The Hvalues are based on molar quantities represented in the minus sign indicates an exothermic reaction.
5 MetalsNonmetalsMostActiveMostActiveLeast ActiveLeastActive**Activity Series is based on the hydrogen standard. H2is nota Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition6 Table KCommon AcidsTable LCommon BasesTable NSelected RadioisotopesTable MCommon Acid Base IndicatorsFormulaNameHCl(aq)hydrochloric acidHNO2(aq)nitrous acidHNO3(aq)nitric acidH2SO3(aq)sulfurous acidH2SO4(aq)sulfuric acidH3PO4(aq)phosphoric acidH2CO3(aq) orcarbonic acidCO2(aq)CH3 COOH(aq) ethanoic acid or HC2H3O2(aq)(acetic acid)FormulaNameNaOH(aq)sodium hydroxideKOH(aq)potassium hydroxideCa(OH)2(aq)calcium hydroxideNH3(aq)aqueous ammoniaApproximate IndicatorpH Range Colorfor ColorChangeChangemethyl to yellowbromthymol to bluephenolphthalein8 9colorless to to bluebromcresol to bluethymol to blueNuclideHalf-LifeDecay Nuclide d gold-19814C5715 y carbon-1437Ca182 ms + y y min + s y d s + h y s s + d 104y plutonium-239226Ra1599 y d y 105y 1010y 105y 108y 109y uranium-238 Source: CRC Handbook of chemistry and Physics,91sted.
6 , 2010 2011,CRC PressSource:The Merck Index, 14thed., 2006, Merck Publishing GroupNameGeneralExamplesFormulaNameStruc tural Formulaalkanes CnH2n+2ethanealkenesCnH2nethenealkynesCn H2n 2ethyneReference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition7 Table OSymbols Used in Nuclear ChemistryTable POrganic PrefixesTable QHomologous Series of HydrocarbonsNameNotationSymbolalpha particle42He or 42 beta particle0 1e or 0 1 gamma radiation00 neutron10nnproton11H or 11pppositron0+1e or 0+1 +PrefixNumber of Carbon Atomsmeth-1eth-2prop-3but-4pent-5hex-6he pt-7oct-8non-9dec-10 HHHHHHCCCCHHHCCHHHNote:n= number of carbon atomsReference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition8 ORC HORC O R OCH3 CCH2CH2CH32-pentanoneORC R OC HTable ROrganic Functional GroupsClass ofCompoundFunctionalGroupGeneralFormulaE xamplehalide(halocarbon)alcoholetheralde hydeF (fluoro-)Cl (chloro-)Br (bromo-)I (iodo-)OHRX(Xrepresentsany halogen)ROHRO R CH3 CHClCH32-chloropropaneCH3CH2CH2OH1-propa nolCH3 OCH2CH3methyl ethyl etheramideO OC OHOC O OC NH N OC OCH3CH2C HpropanalO R RC NHR RN R ORC OHketoneorganic acidesteramineOCH3CH2C OHpropanoic acidOCH3CH2 COCH3methyl propanoateCH3CH2CH2NH21-propanamineOCH3C H2C NH2propanamideNote.
7 Rrepresents a bonded atom or group of +38939Rb2-8-8-119 CsNaLi(223)Fr87-18-32-18-8-1+1Ra88-18-32 -18-8-2+2(227)Ac-18-32-18-9-2+3(261) + *18-32-10-2+ + +2+3+ +2+3+ +2+3+ + + +2+3+4+ +2+ +2+ +2+ +1+ + + + + + 4+2+ 1 4+2+ +2+ 3+ 2+4+ 2+4+ 1+1+5+ +2+4+6(209)Po84-18-32-18-6+2+4(210) 1+1+ +2(222) + +2+ + + + + + + +2+ +2+3(145)Pm61+ + + +3+ + + +3+4+5+6(237)Np(244)Pu(243)Am(247)Cm+3(2 47)Bk+3+4(251)Cf+3(252)Es(257)Fm100(258) Md101(259)No102(262) 3+3+ 2+4+ 1+1+5+ +2+ 3 2 1+1+2+3+4+ + + +1+ +1+ +2+ + 3+ +2+ +2+ +1+ + +3+ +3+ +3(98)Tc432-8-18-13-2+4+6+ +4+6+ + (262)105(266)Sg106(272)Bh107(277)Hs108(2 76)Mt109(281)Ds(280)Rg111(285)Cn112(289) + + + + + + + + + + + + +1 1*denotes the presence of (2-8-) for elements 72 and above**The systematic names and symbols for elements of atomic numbers 113 and above will be used until the approval of trivial names by : CRC Handbook of chemistry and Physics, 91st ed.
8 , 2010 2011, CRC PressP eriod12112 GroupGroup987543 Group3457 Periodic Table of the 4+2+462-4 Atomic MassSymbolAtomic NumberElectron ConfigurationSelected Oxidation StatesRelative atomic masses are basedon 12C = 12 (exact)Note: Numbers in parenthesesare mass numbers of the moststable or common (226)66+5+5Db1029111213141516171849+5+5+ 5905991+592+3+4+5+69394+3+4+5+6+3+4+5+69 59697Tb98996918110(284)Uut113**(288)Uup1 15(292)Uuh116( ? )Uus117(294)Uuo118+4+3+2+3+2+3+3+3 Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition9 Reference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition10 Table SProperties of Selected ElementsFirstAtomic SymbolNameIonization Electro-MeltingBoiling*Density**Atomic NumberEnergynegativityPointPoint(g/cm3)R adius (kJ/mol)(K)(K)(pm).
9 (white) (monoclinic) (gray) (gray) Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition11 FirstAtomic SymbolNameIonization Electro-MeltingBoiling*Density**Atomic NumberEnergynegativityPointPoint(g/cm3)R adius (kJ/mol)(K)(K)(pm) (white) (gray) 58 71 have been 14886 Rnradon1037 90 and above have been omitted.*boiling point at standard pressure**density of solids and liquids at room temperature and density of gases at 298 K and kPa no data availableSource: CRC Handbook for chemistry and Physics, 91sted., 2010 2011, CRC PressReference Tables for Physical Setting/ chemistry 2011 Edition12 Table TImportant Formulas and EquationsDET 609 ADUd= densityDensityd= m= massV= volumeMole Calculationsnumber of moles = Percent Error% error = 100 Percent Composition% composition by mass = 100parts per million = 1 000 000 Concentrationmolarity =P= pressureCombined Gas Law=V= volumeT= temperatureMA= molarity of H+MB= molarity of OH TitrationMAVA= MBVBVA= volume of acidVB= volume of baseq= mC Tq= heatHf= heat of fusionHeatq= mHfm= massHv= heat of vaporizationq= mHvC=specific heat capacity T = change in temperatureTemperatureK = C + 273K = kelvin C = degree CelsiusP2V2T2P1V1T1moles of soluteliter of solutionmass of solutemass of solutionmass of
10 Partmass of wholemeasured value accepted valueaccepted valuegiven massgram-formula massmV