Transcription of The Why, When, and How of Leak Checking a …
1 9/25/03 9:50 AM Page 2. The Why, When, and How of Leak Checking a Vacuum Furnace tate or reciprocate are other prime Tofferhecoming use of vacuum furnaces is be- more popular since they a number of processing advan- leak sites. tages, especially in critical applications, What is leak testing? provided they are properly main- In general, leak testing involves tained and kept in good operating measuring the amount of leakage condition. (vacuum degradation) over time in A common problem experienced the vacuum environment. The leak- by almost every user is that, over time, up rate of a vacuum system is a func- leaks develop that are both damaging tion of actual (real), internal (through), to product quality and to furnace in- and virtual (outgassing-related) leaks ternal components.
2 In extreme cases, in the chamber or vacuum system (see About the columnist .. table). the problem is obvious: the furnace Daniel H. Herring is president of The will not pump down and/or the hot Real vs. virtual: Outgassing is the Herring Group Inc., Elmhurst, Ill., a business specializing in practical solutions to problems zone shows signs of oxidation. Small release of low-vapor-pressure conta- facing the heat treating and sintering leaks, which are more common, often minants present in the vacuum industries (Web: www. go undetected because the pumping system. Sources of these contaminants ). system can more than offset any air include volatile liquids, dirt, grease, Dan Herring has spent infiltration. However, even small leaks oxides, water vapor, and gases ad- more than 25 years can cause continuous and sometimes sorbed on or in surfaces and pores.
3 Working for furnace equip- catastrophic damage. Thus, leak These contaminants outgas at dif- ment manufacturers in a Checking should become a routine ferent rates at different vacuum levels variety of roles, including and temperatures. To minimize out- part of any good vacuum furnace senior management and maintenance program. gassing, cleanliness is essential, espe- new business development. Now an independent entrepreneur, Dan cially of workpieces, part baskets, and lectures, writes, teaches, and consults. A fre- What is a vacuum leak? fixtures introduced into the furnace. quent speaker at local, national, and interna- A leak is an opening such as a It's also a good idea to limit the time tional conferences, he is dedicated to advancing crack or hole that allows a substance that an open furnace is exposed to the the state of the art in thermal processing.
4 To be admitted to or to escape from a factory environment. He has published more than 100 technical confined space. A vacuum system Outgassing is often made obvious papers, written three books, and contributes leak allows air to be admitted into during the process cycle by a large to Heat Treating Progress and other in- the vacuum vessel. Suspect areas on spike or rise in pressure during dustry publications. vacuum furnaces include threaded heating. It also can be detected by Dan's credentials include his appointment and brazed joints, fittings that have comparing successive leak-rate values as a research associate professor at the Ther- mal Processing Technology Center, Illinois In- been improperly sealed or installed, after long pump-down cycles.
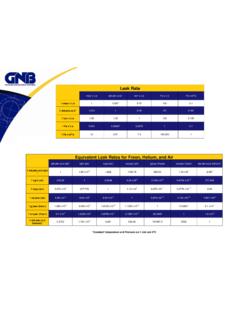
5 If the stitute of Technology, Chicago. He also is active and damaged (cut, worn, melted, or leak rate improves (decreases) with on several HTS Committees. dirty) O-ring seals, especially each successive pump down, then around doors. Components that ro- outgassing is suspected. If the rate re- Potential sources of vacuum system leaks Type Potential Source Actual (real) leaks Compression seals Welds and brazed joints Shaft seals and bellows on valves Flexible connectors in piping Threaded joints on vacuum gauge and plugs, for example. Static gasket seals on sight ports, feedthroughs, manifolds, and air-operated cylinder glands. Generic and practical information presented Internal (through) leaks Process gas delivery system here is not intended to replace or supplement Vent gas exit system federal, state, and local codes, government Seals between adjacent internal volumes standards, insurance requirements, company Improper gas ballast, gas purge, partial pressure control policies and procedures, or common sense.
6 In systems, and backfill valves. addition, all equipment manufacturers' in- Virtual (outgassing) leaks Residual solvents structions and operating and maintenance Residual liquids (water, cooling fluids) in blind holes and manuals should always be thoroughly read restricted passageways. and followed. Further, personnel training Pockets of trapped gases or liquids should be provided unequivocally to everyone High-vapor-pressure materials who will be associated with operating such Porous materials and condensed by-products from equipment. processes already run. 24 HEAT TREATING PROGRESS SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2003. 9/25/03 9:50 AM Page 4. THE HEAT TREAT DOCTOR Continued mains essentially the same, then an ac- the manufacturing process, be intro- for 2 to 4 hours, and then vacuum tual (real) leak may be considered the duced during maintenance or repair, cooling, usually overnight.
7 Fixtures, primary cause. or occur over time due to wear, fa- baskets, parts, and work thermocou- In most cases, both leaks and out- tigue, and stress. The possible source ples are removed from the furnace. The gassing are present simultaneously. of a leak may be revealed by the an- first 2 hours of the cycle should be run Bear in mind that real leaks are linear swer to the question, What was the in a partial pressure of 1000 microns and outgassing is not. Thus, for ex- last area worked on or modified? ( mbar) of nitrogen. (1 micron = 1. ample, a 4 hour leak-rate test, with However, the question that really micrometer of mercury.) This is to en- measurements taken at 30 minute in- matters is this: Can the system tol- sure that heat transfer takes place to the tervals, will generate a linear rate.
8 The erate the leak? In other words, can normally colder areas of the hot zone outgassing curve will deviate from lin- the process and equipment survive and furnace interior, since vacuum earity, yielding the true leak-up rate. and be unaffected by the leak? The an- alone is an excellent heat-loss insulator. There are many methods used to swer is almost always, No. The balance of the cycle is run in the measure leak rate and various types of lowest obtainable vacuum, which will leak-tracing agents. (The choice of How do I run a leak test? facilitate vaporization of unwanted tracing agent usually depends on the A furnace leak-up rate test does not process by-products. measurement method used.) Selection locate the leak, it only quantifies it.
9 The If it is not possible to perform a con- of the best method for a specific furnace must be clean, cold, empty, and ditioning, the alternative is to pump application requires consideration of outgassed to obtain a true leak-up rate down to 1 micron ( mbar), or to economics, accuracy, tolerance to en- value. If it isn't, which is often the case, the lowest attainable value of the vironmental conditions, leak-rate re- a conditioning cycle should be run. pumping system (if it is above 1 mi- quirements, and equipment limitations. How to condition: A conditioning cron), followed by an inert gas back- cycle bake out, burnout, cleanup fill to approximately 10 in. Hg (255 torr Why do I need to leak test? involves heating the equipment to or 340 mbar).
10 This is followed by an- Everything leaks. And although a 50 100 F (30 55 C) higher than the fur- other 1 micron pump down and, fi- leak may be extremely small, it still nace's normal operating temperature nally, by at least 1 hour of additional may pose a problem. Leaks can be in- (but lower than its maximum operating pumping. herent in the material, created during temperature), soaking at temperature Leak testing: To perform a leak-up 26 Circle 17 or visit 9/25/03 9:50 AM Page 6. THE HEAT TREAT DOCTOR Continued rate check, pump the furnace down to (differential, increase), vacuum decay containment. Remember that these ultimate pressure with the heat turned Amount-of-leak types: mass flow solvents will remove paint.