Transcription of toolkit Guidelines for the and Post-Exposure …
1 toolkit (including needlestick and sharps injuries, sexual exposure and human bites) where there is a risk of transmission of bloodborne viruses and other infectious diseasesGuidelines for the Emergency Management of Injuries and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)toolkitReport of the Scientific Advisory Committee of the Health Protection Surveillance 2012 Revised and updated 2016 HiV PEP updated June 2018toolkit ContentsBackground to the Guidelines 4 Acknowledgements 8 Working group 10 The Guidelines 111.
2 Introduction 122. Initial assessment 12 Urgent first aid 12 initial wound care 12 Complete the patient management form 12 Decide if a significant exposure has occurred 133. Assessing the risk of transmission of infection 14 Risk assessment bloodborne viruses 14 Factors increasing the risk of transmission 14 investigation of source 14 Assessing the recipient 164. Treatment of recipient following a significant exposure 17 Actions to be taken 17 Hepatitis B Post-Exposure prophylaxis 18 Hepatitis C 18 HiV Post-Exposure prophylaxis 18 tetanus 19 Antibiotic treatment 195.
3 Specific injuries and settings 19 occupational exposure 19 Sexual exposure 19 Human bites 20 Community acquired needlestick injury 20 injury in dental practice 20 injury in primary care medical practice 216. Information and follow-up of recipient 21 information 21 Precautions 21 Follow-up 217. Records/documentation 22 Patient management form 22 Recording of medication 22 Notifiable diseases 22 occupational injuries 22 Risk management forms for hospital 22 References 23 Glossary of abbreviations and terms 24 2012 Health Protection Surveillance CentreISBN 978-0-9565622-2-7-2-eMI Guidelinestoolkittoolkit -3-eMI GuidelinesAppendicesAppendix 1 Patient management form 28 Appendix 2 Flow chart for management of injuries 31 Appendix 3
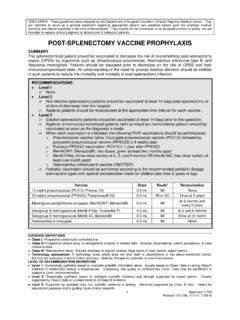
4 Algorithm for needlestick/sharps exposure 32 Appendix 4 Algorithm for mucous membrane exposure 33 Appendix 5 Algorithm for sexual exposure 34 Appendix 6 Algorithm for human bite exposure 35 Appendix 7 HiV Post-Exposure prophylaxis (PEP) 36 Appendix 8 Hepatitis B Post-Exposure prophylaxis 45 Appendix 9 testing of recipient 46 Appendix 10 interpretation of HBV results 48 Appendix 11 Hepatitis B vaccine 49 Appendix 12 Hepatitis B vaccination patient record card 51 Appendix 13 Hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBiG) 52 Appendix 14 Management of acute hepatitis C 53 Appendix 15 tetanus 54 Appendix 16 Prescribing information for emergency contraception 56 Appendix 17 occupational blood or body fluid exposure 60 Appendix 18 Human bite injuries, saliva and transmission of bloodborne viruses 61 Appendix 19 Community acquired needlestick injuries 66 Appendix 20 on-site assessment form (Dental/Primary care) 69 Appendix 21 Hepatitis B virus: epidemiology and transmission risks 70 Appendix 22 Maps of global distribution of hepatitis B infection 76 Appendix 23 Hepatitis C virus.
5 Epidemiology and transmission risks 77 Appendix 24 Maps of global distribution of hepatitis C infection 83 Appendix 25 Human immunodeficiency virus: epidemiology and transmission risks 84 Appendix 26 Maps of global distribution of HiV infection 91 Appendix 27 information leaflet no risk of exposure to bloodborne viruses 92 Appendix 28 information leaflet significant exposure to bloodborne viruses 94 Appendix 29 Checklist: testing of source person or recipient 96 Appendix 30 Source information leaflet testing for hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HiV 97 Appendix 31 information leaflet HiV Post-Exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
6 99 Appendix 32 information leaflet contraception & emergency contraception 101 Appendix 33 information leaflet sexual exposure 106 Appendix 34 Referral letter to infectious disease/HiV physician 108 Appendix 35 Referral letter to GP/ occupational health department 109 Appendix 36 Useful contact information 110toolkiteMI Guidelines -4- toolkit Introductioninjuries where there is a risk of transmission of infection frequently present in emergency departments, sexual assault units, occupational health departments and primary care settings. Bloodborne virus (BBV) infections such as hepatitis B (HBV), hepatitis C (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HiV) are of particular concern because of the potential long-term health effects for people who become infected, the anxiety experienced by the injured persons, and the increase in their prevalence in the population in recent decades.
7 The appropriate management of such injuries, in the emergency and follow-up periods, has important implications in terms of minimising the risk of transmission of BBVs and in allaying the psychological impact on the injured emergency departments and occupational health departments throughout ireland have developed Guidelines for the management of injuries where there is a risk of BBV transmission. However, these Guidelines differ in their scope ( all BBVs versus HiV; all exposures versus occupational or sexual), their level of detail, and recommended actions, such as testing schedules and the use of Post-Exposure prophylaxis (PEP).
8 The development of these Guidelines was prompted by the idea of having standardised Guidelines on the management of these injuries that could be used in all relevant settings throughout the country and that would be based on best available evidence and expert and scopethe purpose of these Guidelines is to provide comprehensive guidance on the appropriate management of injuries where there is a risk of transmission of BBVs and other infections. the Guidelines are intended for use as follows:Setting: Any medical setting where the patient first presents with the injury, for example, a hospital emergency department or occupational health department, a general practice, a dental practice, a Garda occupational health department, a clinic for sexually transmitted infections or a sexual assault treatment unit (SAtU).
9 Patient population: Members of the public in a healthcare or community setting; healthcare workers (HCW) or other workers ( members of the Garda or defence forces) in an occupational setting; adults and children; both recipients and sources of of injury: Needlestick or other sharps injury, sexual exposure , human bites, exposure of broken skin or of mucous membranes. these Guidelines do not cover injuries where the source is an : Emergency management on first presentation, and also arrangements for any necessary Guidelines cover the following aspects of management: first aid, risk assessment, testing, treatment (including PEP for HBV and HiV), counselling and follow-up, records and documentation.
10 Although the focus is mainly on BBVs, the management of other risks is also covered in to the Guidelines -4-eMI GuidelinestoolkiteMI Guidelines -5- toolkit The main questions covered by the Guidelines are: What first aid treatment should be administered? Is the exposure significant? What materials are significant for BBVs? What injuries are significant for BBVs? How to assess the risk of transmission of BBVs? What is the level of risk of HBV, HCV or HIV? What factors in the injury increase the risk of transmission? How should the source be investigated?