Transcription of UV/visible spectroscopy - Home - Liskeard School ...
1 1UV/ visible spectroscopyFigure 210-1010-910-810-710-610-510-410-310-210 -11001011021033 x 10233 x 1043 x 1063 x 1083 x 1010X-rays -raysUltravioletVisibleInfraredAtomicele ctronictransitionsAtomic andmolecularelectronictransitionsMolecul ar vibrationsMicrowavesMolecularrotationsRa diowavesNuclearmagneticenergylevelsEnerg y levelsof appropriatetransitionsFrequency (MHz)Wavelength (m)Type of radiationDecreasing energythe visible range. Consequently, if you have everbeen to a nightclub and have seen a white shirtappear purple/blue under ultraviolet light this is is also the reason why people with false teethshould not smile!
2 An increasingly important use of the absorptionof ultraviolet / visible light is the coding of householditems with ultraviolet sensitive ink and usinginvisible but ultraviolet fluorescent inks forsignatures in building society savings books. Figure 2shows the electromagnetic spectrum indicating theultraviolet and visible UV/visible spectroscopy worksWhen light either visible or ultraviolet isabsorbed by valence (outer) electrons these electronsare promoted from their normal (ground) states tohigher energy (excited) states (Fig. 3). The energiesof the orbitals involved in electronic transitions havefixed values.
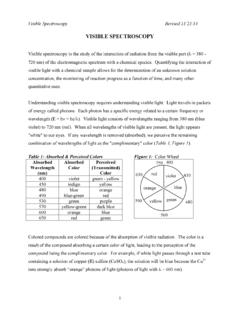
3 Because energy is quantised, it seemssafe to assume that absorption peaks in a UV/visibleThe absorption of light is familiar to everyone. Theabsorption of visible light is what makes thingscoloured. For example, a blue dye used in a pair ofjeans appears blue because the light at the red end ofthe spectrum is absorbed. This leaves the blue light tobe reflected to the observer s eye (Fig. 1). ultraviolet / visible spectroscopy is useful as ananalytical technique for two reasons. First it can beused to identify some functional groups in moleculesand secondly, it can be used for assaying. This secondrole determining the content and strength of asubstance is extremely useful.
4 ultraviolet /visiblespectroscopy is used extensively in chemical andbiochemical laboratories, for a variety of tasks. It canbe used to determine small quantities such as thetrace metal content in alloys or the amount of acertain drug reaching various parts of the optical whiteners used in washing anddetergent powders and toothpaste absorb ultraviolet / visible light to good effect. The whitener absorbsradiation in the near ultraviolet and then emits it inFigure (nm)Absorbance (log10 Io/I) visible spectrumYellow dyeRed dyeBlue dyeVioletIndigoBlueGreenYellowOrangeRed2 Figure 5spectrum will be sharp peaks.
5 However, this is rarely,if ever, observed. Instead the spectrum has broadpeaks (eg Fig. 5). This is because there are alsovibrational and rotational energy levels available toabsorbing materials (Fig. 3).Figure (nm)Absorbance (log10 Io/I)CH3CH3CH3CH3CH3CH3CH3CH3CH3CH3 Because light absorption can occur over a widerange, light from 190 nm to 900 nm is usually how is the absorption of light explained? Valenceelectrons are found in three types of electron , or , bonding orbitals; double or triple( bonding orbitals); and non-bonding orbitals (lonepair electrons). Sigma ( ) bonding orbitals tend to belower in energy than bonding orbitals, which inturn are lower in energy than non-bonding electromagnetic radiation of the correctfrequency is absorbed a transition occurs from one ofthese orbitals to an empty orbital, usually anantibonding orbital * or * (Fig.)
6 4). Most of thetransitions from bonding orbitals are too high afrequency (too short a wavelength to measure easily),so most of the absorptions involve only *, n *and n * exact energy differences between orbitalsvaries. In organic molecules double bonds which arenext to each other can conjugate join together anddelocalise the electrons over all of the atoms. Thislowers the energy needed to promote the outerelectrons. As a consequence molecules with manyconjugated double bonds can be coloured becausethey absorb energy in the visible as well as theultraviolet part of the spectrum eg -carotene(Fig.
7 5).The spectrometerSamples are used in solution and are placed in a smallsilica cell. Two lamps are used. A hydrogen ordeuterium lamp for the ultraviolet region and atungsten/halogen lamp for the visible region. In thisElectronicground stateElectronicexcited stateVibrationalenergy levelsRota-tionalenergylevelsEnergy levelsn * *AntibondingBondingTransitionsEnergy *n * *n *Figure 43 Figure 7 White sourceDiffractiongratingNarrow slitSample cellReference cellMirrorRotating segmented mirrorto allow radiationthrough to the sample andreflect it through the reference cell alternatelyDetectorChartrecorderRotating mirror inphase with firstrotating mirrorMirrorAll mirrors are surfacereflecting to avoidtransmission/absorptionthrough glassFigure 6way radiation across the whole range is scanned bythe
8 Spectrometer (Fig. 6).A reference cell containing only solvent is is passed simultaneously through the sample celland reference cell. The spectrometer compares thelight passing through the sample with that passingthrough the reference cell. The transmitted radiationis detected and the spectrometer records theabsorption spectrum by scanning the wavelength ofthe light passing through the cells. A schematicdiagram is shown in Fig. 7. Single beam instrumentsare now available as well as double beam across the whole range is monitoredsimultaneously. The principles are the same as fordouble beam instruments, but data on the referenceare taken first, followed by the sample.
9 In this waysingle beam instruments can record the spectrum little bit of theoryFor most spectra the solution obeys Beer s Law. Thisstates that the light absorbed is proportional to thenumber of absorbing molecules ie to theconcentration of absorbing molecules. This is onlytrue for dilute second law Lambert s law tells us that thefraction of radiation absorbed is independent of theintensity of the radiation. Combining these two lawsgives the Beer Lambert law:log10I0/I = lcIO= the intensity of the incident radiation I= the intensity of the transmitted radiation = the molar absorption coefficientl= the path length of the absorbing solution (cm)c= the concentration of the absorbing speciesin mol dm-3So what is the Beer Lambert law used tocalculate?
10 Two useful pieces of information are themolar absorption coefficient, and max which is thewavelength at which maximum absorption two pieces of information are sometimesenough to identify a substance. However, if and maxare known for a compound the concentration of thesolution can be calculated. This is the most hydrolysis of an ester(4-nitrophenylethanoate)4-Nitrophen ylethanoate hydrolyses in alkalinesolution to give 4-nitrophenoxide ions and ethanoateions (Fig. 8 overleaf).During the experiment the hydroxide ionconcentration is kept constant by buffer solution andthe progress of the reaction is followed by theabsorption of light of wavelength 400 nm.