Transcription of Welding filler metals for power plant engineering
1 Welding filler metals for power plant engineeringContentsPageWelding filler metals for Creep Resistant Tube Steels Used in power plant ManufacturingIntroduction416 Mo 3 and 13 CrMo 4-5 (EN 10028 T2)615 NiCuMoNb 5 (WB 36) and 20 MnMoNi 5-5615 CrMoV 5-10 / GS-17 CrMoV 5-11710 CrMo 9-10 ; ASTM A 387, Gr. 22, Cl. 27 New kind of boiler tube steels HCM2S (T/P23) and 7 CrMoVTiB 10-10 (T/P24)8 Martensitic steels X 20 XCrMoV 12-1; P91; E911 and P9210A new 12 % martensitic chromium steel VM 1215 Quality assurance, competence16 Standardisation of the Welding filler metals for creep resistant steels 16 Submerged-arc Welding fluxes for creep resistant steels16 References17 Further publications18 Table 2.
2 T-PUT Welding consumables recommendationsWelding filler metals for Creep Resistant Tube and Pipe Steels Used in power plant Manufacturing4 IntroductionThe development and production of Welding consumables for creep resistant steels for power plant manufacturing have been a focus point atT-Phoenix Union Thermanit (T-PUT) for decades. Consequently, there are numerous experiences available in processing the wide range of creepresistant 1provides an overview of the most important ferritic / bainitic and martensitic steels for fossil-fired power 1.
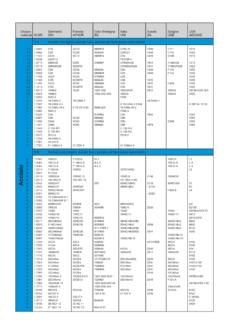
3 Chemical composition of proven and newly developed creep resistant steels for steam boiler in % by weight C1)16 Mo ,12-0,20< 0,350,40-0,90< 0,30< 0,300,25-0,35 < 46013 CrMo ,08-0,18< 0,350,40-1,00,7-1,15 0,40-0,60 < 54515 CrMoV 0,10-0,160,15-0,350,40-0,901,10-1,40 0,90-1,100,20-0,35 < 54515 NiCuMoNb 5 (WB 36) < 0,120,25-0,500,80-1,20 1,0-1,300,25-0,50 0,015-0,045Cu 0,50-0,80< 54520 MnMoNi 10 CrMo ,08-0,14< 0,500,40-0,802,0-2,5 0,90-1,10 < 545 HCM2S (T23)T/P230,04-0,10< 0,500,30-0,601,90-2,60 < 0,300,20-0,301,45-1,750,02-0,08N < 0,010 < 550B < 0,0067 CrMoVTiB 10-10 (T24) (T/P24)0,05-0,0950,15-0,450,30-0,702,20- 2,60 0,90-1,100,20-0,30 N < 0,010< 550B 0,0015-0,0070 Ti 0,05-0,10X 20 CrMoV 12-1 (X20) 0,17-0,23< 0,50< 1,0010,0-12,50,30-0,800,80-1,200,25-0,35 < 585X 10 CrMoVNb 9-1 (P91) ,08-0,120,20-0,500,30-0,608,0-9,5< 0,400,85-1,050,18-0,25 0,06-0,10N 0,030-0,070< 585X11 CrMoWVNb 9-1-1 (E911)
4 ,09-0,130,10-0,500,30-0,608,50-9,500,10- 0,400,90-1,100,18-0,250,90-1,100,06-0,10 N 0,05-0,09< 625X10 CrWMoVNb 9-2 (P92)T/P920,07-0,13< 0,50,30-0,608,5-9,5< 0,400,30-0,600,15-0,251,5-2,00,04-0,09N 0,03-0,07< 625B 0,001-0,006X12 CrCoWVNb 12-2-2 (VM 12) * 0,110,450,211,50,280,230,241,400,065Co 1,3N 0,055< 650B 0,003ferritic / bainitic steelsmartensitic steels (9-12 % Cr-steels)1)meaningful operation temperature limit in power plants from design standpoint*ongoing development in COST 536*currently under developmentBase Mo S 2 MoSH Schwarz 3 KE7015-GUnion I MoER80S-GUV 420 TTEA213 CrMo S 2 CrMoChromo 1E8018-B2 Union I CrMoER80S-GUV 420 TTEB2R15 CrMoV PhoenixSH Kupfer 3 KE9015-G 15 NiCuMoNb 5 (WB36) PhoenixUnion S 3 NiMo 1SH Schwarz 3 K NiE9015-GUnion I MoER80S-GUV 420 TT(R)EG (E F3 mod.
5 20 MnMoNi PhoenixUnion S 3 NiMo 1SH Schwarz 3 K NiE9018-GUnion I MoER80S-GUV 420 TT(R)EG (E F3 mod.)10 CrMo S 1 CrMo 2SH Chromo 2 KSE9015-B3 Union I CrMo 9-10ER90S-GUV 420 TTREB3 RHCM2ST/P23 Thermanit P23 Union I P23ER90S-GUnion S P23UV 430 TTR-W (UV 305)EG7 CrMoVTiB (Draft)Thermanit P24 Union I P24ER90S-GUnion S P24UV 430 TTR-W (UV 305)EGX20 CrMoV 12-1 (X20) Thermanit MTS 4 Thermanit MTS 4 SiER505(mod.)Thermanit MTS 4 Marathon 543 EGX10 CrMoVNb 9-1 (P91) Chromo 9 VThermanit MTS 3 Thermanit Chromo T91E9015-B9 Thermanit MTS 3ER90S-B9 Marathon 543EB9X11 CrMoWVNb 9-1-1 (E911) MTS 911E9015-GThermanit MTS 911(E9015-B9 mod.)
6 Thermanit MTS 911ER90S-GMarathon 543EG (B9 mod.)X10 CrWMoVNb 9-2 (P92)T/P92 Thermanit MTS 616E9015 GThermanit MTS 616(E9015-B9 mod.)Thermanit MTS 616ER90S-GMarathon 543EG (B9 mod.)X12 CrCoWVNb 12-2-2 (VM12) * Thermanit MTS 5 CoT *Thermanit MTS 5 CoT * Thermanit MTS 5 CoT *Marathon 54355 Apart from the proven creep resistant steels, the latest developments like T/P23,T/P24, E911, P92 and VM 12 have also been thesesteels, considerable increases in the efficiency of fossil-fired power plants can be realized. In addition to the higher cost efficiency the lowerconsumption of raw materials simultaneously results in a reduced is producing suitable tried and tested VdT V-approved Welding consumables for these creep and high temperature resistant selection of Welding filler metals for these steels listed in Table 1is partially aligned with the long-term properties.
7 Especially in the caseof tubes and pipes that are subjected to temperatures above 450 2shows an assignment of Welding filler metals to the different base materials depending on the Welding 3contains the chemical composition of similar Welding filler metals taking the example of SMAW electrodes specifying the recommend-ed heat treatment (PWHT) in order to achieve a sufficient impact 3: Chemical composition of matching Welding filler metals (SMAW) including recommended heat treatment (PWHT) filler metal acc. to EN 1599/1600 Mech. properties(all weld metal) at RTBase metal PWHTYSTSE longationCSiMnCrMoNiNbVWCoN C / h*(MPa)(MPa)(J)16 Mo 3E Mo B 420,080,301,20 0,45 (620 / 1)52059015013 CrMo 4-5E CrMo 1 B 420,080,300,901,000,50 700 / > 247058015015 CrMoV 5-10 GS-17 CrMoV 5-11E CrMoV 1 B 420,090,351,11,21,0 0,27 720 / > 252063016015 NiCuMoNb5 (WB36)E 50 4 1 NiMo B 42 H50,060,301,250,200,401,0 (Cu = 0,08)580 / 250059014010 CrMo 9-10E CrMo 2 B 420,070,250,702,200,90 690 / > 2510620180 HCM2S (T 23)
8 0,060,270,542,10,080,050,040,211,72 740/25096251367 CrMoVTiB 10-10 (T24)0,090,30,522,51,0 0,040,22 740/2577689150X20 CrMoWV 12-1E CrMoWV 12 B 420,180,250,511,51,00,6 0,30,5 760 / > 460075040X10 CrMoVNb 9-1 (P 91)E CrMo 9 B 420,090,220,659,01,10,800,050,20 0,04760 / > 260075050X12 CrWVNb 12-2-2 (E 911)EZ CrMoWV 9 11 B 420,090,200,578,850,920,830,0470,211,0 0,05760 / > 260075050X10 CrWMoVNb 9-2 (P 92)EZ CrMoWV 9 0,5 2 B 420,0980,230,669,230,530,660,0470,201,70 0,06760 / > 260075045X11 CrMoWVNb 9-1-1 (VM 12)EZ CrCoW 12 2 20,110,450,6511,150,300,700,060,251,501, 60,035770 / > 2600750> 27 Matching Welding deposit analysisDuration of annealing depends on the wall thicknessmartensiticferritic bainitic616 Mo 3 and 13 CrMo 4-5 (EN 10028 T2)From the group of classical creep resistant steels,the material 16 Mo 3 can be processed with the familiar arc Welding process without anyproblems.
9 The low alloyed creep resistant steel 13 CrMo 4-5 is generally welded in quenched and tempered condition with preheating (about250 C). To release the residual stresses and to improve the impact toughness of the weld deposit, the joints are subjected to a stress-reliefheat treatment after properties of the Welding filler metals must match those of the base materials. Apart from the optimised chemical composition, this is deci-sively influenced by the Welding , the special technical features of Welding application are briefly described 4: filler metal for creep resistant steels 20 MnMoNi 5-5 and 15 NiCuMoNb 5 (WB 36)15 NiCuMoNb 5 (WB 36) and 20 MnMoNi 5-5 For components in power plants (including nuclear plants) as well as in chemical reactors with operating temperatures above 350 C, high-strength fine-grained steels with the alloying concepts Ni-Mo and Ni-Cu-Mo have been used successfully for many years.
10 The material WB 36,in particular, has worldwide gained importance, especially in power plants, as a result of the standardisation in the ASME-Code. 20 MnMoNi 5-5 wasprimarily developed for pressure vessels (nuclear plants).There are high toughness requirements on these materials and hence also for the welded 4contains the well approved weldingfiller metals for both steels. It has to be observed that such welded joints require a heat treatment (PWHT), a stress-relief heat requirement has notbeen taken into consideration in the code EN 1shows the temperature cycle and the subsequent heat treatment after Welding of WB 36 Fig.