11 Nucleophilic Substitution And Elimination
Found 9 free book(s)Chapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination ...
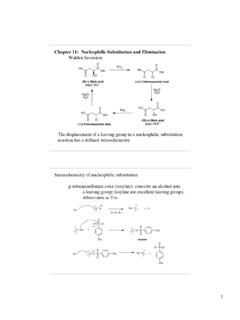
www.vanderbilt.eduChapter 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion OOH OH HO O (S)-(-) Malic acid [a]D= -2.3 ° PCl5 OCl OH HO O Ag2O, H2O OOH OH HO O (R)-(+) Malic acid [a]D= +2.3 ° PCl5 Ag2O, H2O OCl OH HO O (+)-2-Chlorosuccinic acid (-)-2-Chlorosuccinic acid The displacement of a leaving group in a nucleophilic substitution reaction has ...
The reaction of bromine with ethane is similar to ... - Weebly
drwainwright.weebly.com(Total 11 marks) € € ... B€€€€€€€nucleophilic substitution C€€€€€€€elimination D€€€€€€€nucleophilic addition-elimination (Total 1 mark) 14 Page 14 of 35 €€€€€€€€€ (a)€€€€ Crude oil is separated into fractions by fractional distillation. Outline how different fractions
Alkyl Halides - Rutgers University
crab.rutgers.eduCh06 Alkyl Halides (landscape).docx Page 8 Nucleophilic Substitution The nucleophile Nuc:¯ displaces the leaving group (producing X¯) from the carbon atom by using its lone pair to form a new bond to the carbon atom. Elimination A new bond is formed by the elimination of halide ion and another atom (usually H+
Professor J. Stephen Clark - chem.gla.ac.uk
www.chem.gla.ac.uk• Electrophilic substitution of pyridines • Nucleophilic substitution of pyridines • Metallation of pyridines ... 11 Functional Group Chemistry Enamines R1 O R2 N H R3 R3 H R1 N R2 R3 R3 E R1 N R3 R3 R2 E R1 N R3 R3 R2 H H H2O R1 O R2 E R1 N ... • Unsaturation is often introduced by elimination e.g. dehydration, dehydrohalogenation X [O ...
ACS Examination guide (Selected Questions) Organic ...
www.mdc.eduNucleophilic Substitution and Elimination 2) When 2-bromo -2-methybutane is treated with a base, a mixture of 2-methyl-2-butene and 2-methyl-1-butene is produced When potassium hydroxide is the base, 2 methyl-1-butene accounts for 45% of the mixture, but when potassium tert-butoxide is the base, 2 methyl-1-butene accounts for 70% of the mixture.
IONIC REACTIONS — NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION AND ...
www.austincc.eduRelative Rates of Nucleophilic Substitution 6.20 (a) 1-Bromopropane would react more rapidly because, being a primary halide, it is less hindered. (b) 1-Iodobutane, because iodide ion is a better leaving group than chloride ion. (c) 1-Chlorobutane, because the carbon bearing the leaving group is less hindered than in 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Preview For ACS-Sandardized Final Exam
web.mnstate.edusubstitution, which benefit from electron donors…) o The withdrawing groups must be ortho and/or para, not meta, otherwise the anionic gets no resonance benefit. o Meta withdrawers don’t help much. • Leaving groups: Cl, Br, I, even F (which halogen doesn’t matter much, because addition is rate determining step, not the elimination)
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
sites.tufts.edu6.1 General Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions A deprotonation step is required to complete the reaction when the nucelophile was a neutral atom that bore a proton Example showing deprotonation 4 :
Organic Chemistry (AS) - CIE Notes
www.cienotes.com11 | P a g e h t t p s : / / w w w . c i e n o t e s . c o m / Page 11 Nitration – Electrophilic substitution: Conc. HNO3 & conc. H2SO4 to create the electrophile – nitronium ion (NO2+ ion): Reflux with benzene at 55℃ to make nitrobenzene:
Similar queries
11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination, 11: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Walden Inversion, Nucleophilic Substitution, Elimination, Nucleophilic, Substitution, ACS Examination guide (Selected Questions) Organic, Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination, IONIC REACTIONS — NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION